Abstract
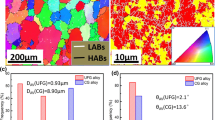
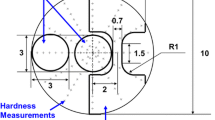
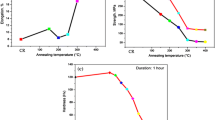
Highest strength for 7075 Al alloy was obtained by combining the equal-channel-angular pressing (ECAP) and natural aging processes. The tensile yield strength and ultimate strength of the ECAP processed and naturally aged sample were 103% and 35% higher, respectively, than those of the coarse-grained 7075 Al alloy counterpart. The enhanced strength resulted from high densities of Guinier–Preston (G-P) zones and dislocations. This study shows that severe plastic deformation has the potential to significantly enhance the mechanical properties of precipitate hardening 7000 series Al alloys.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W.F. Smith and N.J. Grant: The effect of multi-step aging on the strength properties and precipitate-free zone widths in Al-Zn-Mg alloys, Metall. Trans. 1, 979 (1970).
A. Kelly and R.B. Nicholson: Precipitate hardening, Prog. Mater. Sci. 10, 216 (1963).
G. Thomas and J. Nutting: The aging characteristics of aluminum alloys, J. Inst. Met. 88, 81 (1959).
J.D. Embury and R.B. Nicholson: The nucleation of precipitates: The system Al-Zn-Mg, Acta Metall. 13, 403 (1965).
W.F. Smith: Structure and Properties of Engineering Alloys (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1993), Chap. 5–9, pp. 209–215.
R.Z. Valiev, R.K. Islamgaliev, and I.V. Alexandrov: Bulk nanostructured materials from severe plastic deformation, Prog. Mater. Sci. 45, 103 (2000).
Y.T. Zhu, and T.C. Lowe: Observations and issues on mechanisms of grain refinement during ECAP process, Mater. Sci. Eng. A291, 46 (2000).
Y. Iwahashi, J. Wang, Z. Horita, M. Memoto, and T.G. Langdon: Principle of equal-channel angular pressing for the processing of ultra-fine grained materials, Scripta Mater. 35, 143 (1996).
D.G. Morris and M.A. Munoz-Morris: Microstructure of severely deformed Al-3Mg and its evolution during annealing, Acta Mater. 50, 4047 (2002).
J. Wang, Y. Iwahashi, Z. Horita, M. Furukawa, M. Nemoto, R.Z. Valiev, and T.G. Langdon: An investigation of microstructural stability in an Al-Mg alloy with submicrometer grain size, Acta Mater. 44, 2973 (1996).
Y.H. Zhao, K. Zhang, and K. Lu: Structure characteristics of nanocrystalline element selenium with different grain sizes, Phys. Rev. B. 56, 14322 (1997).
T. Ungar: The meaning of size obtained from broadened x-ray diffraction peaks, Adv. Eng. Mater. 5, 323 (2003).
J. Gubicza, I.C. Dragomir, G. Ribarik, Y.T. Zhu, R.Z. Valiev, and T. Ungar: Characterization of the microstructures of severely deformed titanium by x-ray diffraction profile analysis, Mater. Sci. Forum. 229, 414 (2003).
Y.H. Zhao, H.W. Sheng, and K. Lu: Microstructure evolution and thermal properties in nanocrystalline Fe during mechanical attrition, Acta Mater. 49, 365 (2001).
Y.H. Zhao, K. Zhang, and K. Lu: Microstructure evolution and thermal properties in nanocrystalline Cu during mechanical attrition, Phys. Rev. B. 66, 085404 (2002).
Y.H. Zhao, X.Z. Liao, J. Jin, R.Z. Valiev, and Y.T. Zhu: In Ultrafine-Grained Materials III, edited by Y.T. Zhu, T.G. Langdon, R.Z. Valiev, S.L. Semiatin, D.H. Sin, and T.C. Lowe (TMS, Warrendale, PA, 2004), p. 511.
Di E. Risso, M. Conserva, F. Gatto, and H. Markus: Thermomechanical treatments on high strength Al-Zn-Mg(-Cu) alloys, Metall. Trans. 4, 1133 (1973).
M. Consera, M. Nuratti, Di E. Risso, and F. Gatto: Age hardening behavior of TMT processed Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. 11, 103 (1973).
Y.H. Zhao, X.Z. Liao, R.Z. Valiev, and Y.T. Zhu: Structures and mechanical properties of ECAP processed 7075 Al alloy upon natural aging and T651 treatment, in Nanoscale Materials and Modeling—Relations Among Processing Microstructure and Mechanical Properties, edited by P.M. Anderson, T. Foecke, A. Misra, and R.E. Rudd (Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 821, Warrendale, PA, 2004), p. 59.
Y.H. Zhao, X.Z. Liao, Z. Jin, R.Z. Valiev, and Y.T. Zhu: Microstructures and mechanical properties of ultrafine grained 7075 Al alloy processed by ECAP and their evolutions during annealing, Acta Mater. 52, 4589 (2004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Y.H., Liao, X.Z., Zhu, Y.T. et al. Enhanced mechanical properties in ultrafine grained 7075 Al alloy. Journal of Materials Research 20, 288–291 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.2005.0057
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.2005.0057