Abstract
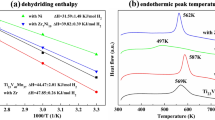
Effect of nano ZnO on the hydrogen absorption performance of Ti-30V-15Mn-15Cr alloy was investigated. It was found that a small amount addition of nano ZnO (3 wt%) drastically improves the hydrogen absorption property of this alloy powder. The modification enables the aur-exposed powder to absorb hydrogen quickly without activation. It could be attributed to the synergetic action of nano ZnO, which might expedite the dissociation of hydrogen on the oxidized alloy surface and play as entrance for hydrogen into the bulk alloy. The fact that nano ZnO addition improves the hydrogen absorption performance of Ti-30V-15Mn-15Cr alloy pioneers a new way for developing highly active Ti-V-based body-centered-cubic phase alloys.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Z. Dehouche, T. Klassen, W. Oelerich, J. Goyette, T.K. Bose, and R. Schulz: Cycling and thermal stability of nanostructured MgH2–Cr2O3 composite for hydrogen storage. J. Alloys Compd. 347, 319 (2002).
G. Liang, J. Huot, S. Boily, A.V. Neste, and R. Schulz: Catalytic effect of transition metals on hydrogen sorption in nanocrystalline ball milled MgH2–Tm (Tm = Ti, V, Mn, Fe and Ni) systems. J. Alloys Compd. 292, 247 (1999).
G. Barkhordarian, T. Klassen, and R. Bormann: Fast hydrogen sorption kinetics of nanocrystalline Mg using Nb2O5 as catalyst. Scripta Mater. 49, 213 (2003).
W. Oelerich, T. Klassen, and R. Bormann: Metal oxides as catalysts for improved hydrogen sorption in nanocrystalline Mg-based materials. J. Alloys Compd. 315, 237 (2001).
J.L. Bobet, E. Grigorova, M. Khrussanova, M. Khristov, P. Stefanov, P. Peshev, and D. Radev: Hydrogen sorption properties of graphite-modified magnesium nanocomposites prepared by ball-milling. J. Alloys Compd. 366, 298 (2004).
J.L. Bobet, S. Desmoulins-Krawiec, E. Grigorova, F. Cansell, and B. Chevalier: Addition of nanosized Cr2O3 to magnesium for improvement of the hydrogen sorption properties. J. Alloys Compd. 351, 217 (2003).
G. Liang, J. Hout, S. Boily, and R. Schulz: Hydrogen desorption kinetics of a mechanically milled MgH2 + 5 at.%V nanocomposite. J. Alloys Compd. 305, 239 (2000).
J. Huot, J.F. Pelletier, L.B. Lurio, M. Sutton, and R. Schulz: Investigation of dehydrogenation mechanism of MgH2–Nb nanocomposites. J. Alloys Compd. 348, 319 (2003).
E. Akiba and H. Iba: Hydrogen absorption by Laves phase related BCC solid solution. Intermetallics 6, 461 (1998).
H. Iba and E. Akiba: Hydrogen absorption and modulated structure in Ti–V–Mn alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 253, 21 (1997).
H. Iba and E. Akiba: The relation between microstructure and hydrogen absorbing property in Laves phase-solid solution multiphase alloys. J. Alloys Comp. 231, 508 (1995).
X.B. Yu, Z. Wu, T.Z. Huang, J.Z. Chen, B.J. Xia, and N.X. Xu: Hydrogen storage in Ti–V-based body-centered-cubic phase alloys. J. Mater. Res. 18, 2533 (2003).
X.B. Yu, Z. Wu, B.J. Xia, and N.X. Xu: Enhancement of hydrogen storage capacity of Ti-V-Cr-Mn BCC phase alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 372, 272 (2004).
Q. Wan, C.L. Lin, X.B. Yu, and T.H. Wang: Room-temperature hydrogen storage characteristics of ZnO nanowires. Appl. Phys. Lett. 84, 124 (2004).
X.B. Yu, J.Z. Chen, Z. Wu, B.J. Xia, and N.X. Xu: Effect of Cr content on hydrogen storage properties for Ti-V-based BCC phase alloys. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 29, 1377 (2004).
X.B. Yu, Z. Wu, T.Z. Huang, J.Z. Chen, B.J. Xia, and N.X. Xu: Effect of surface oxide layer on activation performance of hydrogen storage alloy TiMn1.25Cr0.25. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 29, 81 (2004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, X.B., Wan, Q., Wu, Z. et al. Synergism of nano ZnO for improvement of hydrogen absorption performance of Ti–V-based alloys. Journal of Materials Research 19, 2799–2802 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.2004.0390
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.2004.0390