Abstract
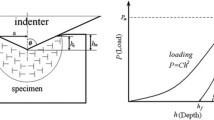
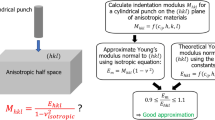
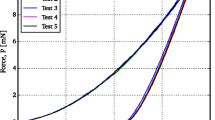
Both analysis and numerical calculations have been carried out to investigate the relationship between Young’s modulus and nonideally sharp indentation parameters. The results confirm that there exists an approximate one-to-one correspondence between the ratio of nominal hardness/reduced Young’s modulus (Hn/Er) and the ratio of elastic work/total work (We/W) for any definite bluntness ratio (Δh/hm) of a nonideally sharp indenter. Based on this relationship, the Young’s modulus of the indented material can be determined just from the values of Hn, We, and W, which are directly measurable quantities in an indentation test.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.B. Pethica, R. Hutchings, and W.C. Oliver: Hardness measurement at penetration depth as small as 20nm. Philos. Mag. A 48, 593 (1983).
J.L. Loubet, J.M. Georges, O. Marchesini, and G. Meille: Vickers indentation curves of magnesium oxide (MgO). J. Tribology 106, 43 (1984).
D. Newey, M.A. Wilkens, and H.M. Pollock: An ultra-low-load penetration hardness tester. J. Phys. E. Sci. Instrum. 15, 119 (1982).
W.C. Oliver and G.M. Pharr: An improved technique for determining hardness and elastic modulus using load and displacement sensing indentation experiments. J. Mater. Res. 7, 1564 (1992).
G.M. Pharr, W.C. Oliver, and F.R. Brotzen: On the generality of the relationship among contact stiffness, contact area, and elastic modulus during indentation. J. Mater. Res. 7, 613 (1992).
Y-T. Cheng, Z. Li, and C-M. Cheng: Scaling approach to modeling indentation measurements, in Fundamentals of Nanoindentation and Nanotribology II, edited by S.P. Baker, R.F. Cook, S.G. Corcoran, and N.R. Moody (Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 649, Warrendale, PA, 2001), p. Q1.1.
Y-T. Cheng and C-M. Cheng: Relationships between hardness, elastic modulus, and the work of indentation. Appl. Phys. Lett. 73, 614 (1998).
A.E. Giannakopoulos and S. Suresh: Determination of elastoplastic properties by instrumented sharp indentation. Scripta Mater. 40, 1191 (1999).
T.A. Venkatesh, K.J. Van Vliet, A.E. Giannakopoulos, and S. Suresh: Determination of elasto-plastic properties by instrumented sharp indentation: guidelines for property extraction. Scripta Mater. 42, 833 (2000).
M. Dao, N. Chollacoop, K.J. Van Vliet, T.A. Venkatesh, and S. Suresh: Computational modeling of the forward and reverse problems in instrumented sharp indentation. Acta Mater. 49, 3899 (2001).
W.Y. Ni, Y.T. Cheng, C.M. Cheng, and D.S. Grummon: An energy-based method for analyzing instrumented spherical indentation experiments. J. Mater. Res. 19, 149 (2004).
Y-T. Cheng and C-M. Cheng: Further analysis of indentation loading curves: effect of tip rounding on mechanical property measurements. J. Mater. Res. 13, 1059 (1998).
W. Yu and J.P. Blanchard: An elastic-plastic indentation model and its solutions. J. Mater. Res. 11, 2358 (1996).
S. Timoshenko and J.N. Goodier: Theory of Elasticity (McGraw Hill, New York, 1951).
J.L. Loubet, M. Bauer, A. Tonck, S. Bec, and B. Gauthier-Manuel: Nanoindentation with a surface force apparatus, in Mechanical Properties and Deformation Behaviour of Materials Having Ultra-Fine Microstructures, edited by M.A. Nastasi, D.M. Parkin, and H. Gleiter (Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1993).
D. Tabor, The Hardness of Metals (Claredon Press, Oxford, U.K., 1951).
J. Alcala, A.E. Giannakopoulos, and S. Suresh: Continuous measurements of load-penetration curves with spherical microindenters and the estimation of mechanical properties. J. Mater. Res. 13, 1390 (1998).
ABAQUS: Version 6.2 (Hibbitt, Karlsson & Sorensen, Inc., Pawtucket, RI, 2001).
J.L. Bucaille, S. Stauss, E. Felder, and J. Michler: Determination of plastic properties of metals by instrumented indentation using different sharp indenters. Acta Mater. 51, 1663 (2003).
S.Dj. Mesarovic and N.A. Fleck: Spherical indentation of elasticplastic solids. Proc. R. Soc. London. 455, 2707 (1999).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, D., Ong, C.W. & Wong, S.F. New relationship between Young’s modulus and nonideally sharp indentation parameters. Journal of Materials Research 19, 2144–2151 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.2004.0274
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.2004.0274