Abstract
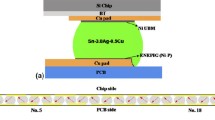
An electromigration failure mechanism in flip chip solder joints is reported in this communication. The solder joints failed by a very rapid, asymmetrical, and localized dissolution of the Cu metallization on the cathode side. The average dissolution rate was about 1 μm/min. The dissolved Cu included not only the Cu under bump metallurgy but also the on-chip Cu conducting trace. From the location and geometry of the dissolved Cu, it can be concluded that current crowding plays a critical role in the rapid dissolution. The dissolved Cu atoms were driven to the anode side by electromigration, and a large amount of Cu6Sn5 was formed there.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Brandenberg and S. Yeh, in Proceedings of the 1998 Surface Mount International Conference and Exhibition (SMTA, Edina, MN, 1998), p. 337.
K. Zeng and K.N. Tu, Mater. Sci. & Eng. R 38, 55 (2002).
J.D. Wu, P.J. Zheng, K. Lee, C.T. Chiu, and J.J. Lee, in Proceedings of the 2002 Electronic Components and Technology Conference (IEEE, New York, 2002), p. 452.
C.Y. Liu, C. Chen, C.N. Liao, and K.N. Tu, Appl. Phys. Lett. 75, 58 (1999).
C.Y. Liu, C. Chen, and K.N. Tu, J. Appl. Phys. 88, 5703 (2000).
Q.T. Huynh, C.Y. Liu, C. Chen, and K.N. Tu, J. Appl. Phys. 89, 4332 (2001).
N.A. Gjostein, in Diffusion, edited by H.I. Aaronson (American Society for Metals, Metals Park, OH, 1973), Chapter 9, p. 241; see Fig. 15.
P. Wynblatt and N.A. Gjostein, Surf. Sci., 12, 109 (1968).
E.C.C. Yeh, W.J. Choi, K.N. Tu, P. Elenius, and H. Balkan, Appl. Phys. Lett. 80, 580 (2002).
B.F. Dyson, T.R. Anthony, and D. Turnbull, J. Appl. Phys. 37, 2370 (1966).
W.K. Warburton and D. Turnbull, in Diffusion in Solids: Recent Developments, edited by A.S. Nowick and J.J. Burton (Academic Press, New York, 1975) p. 171.
C.K. Hu and H. Huntington, Phys. Rev. B 26, 2782 (1982).
C.K. Hu and H. Huntington, Phys. Rev. B 28, 579 (1983).
H. Ye, C. Basaran, and D. Hopkins, Appl. Phys. Lett. 82, 1045 (2003).
W.G. Beder, Welding Research Supplement, 551-s (1969).
A. Rahn, The Basics of Soldering (John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1993), p. 28.
D. Gupta, K. Vieregge, and W. Gust, Acta Mater. 47, 5 (1999).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This author was an editor of this journal during the review and decision stage. For the JMR policy on review and publication of manuscripts authored by editors, please refer to http://www.mrs.org/publications/jmr/policy.html
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, Y.C., Lin, Y.H., Kao, C.R. et al. Electromigration failure in flip chip solder joints due to rapid dissolution of copper. Journal of Materials Research 18, 2544–2548 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.2003.0355
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.2003.0355