Abstract
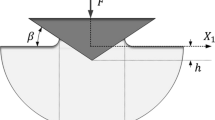
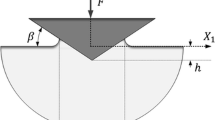
Finite-element analyses for elastoplastic cone indentations were conducted in which the effect of linear strain hardening on indentation behavior was intensively examined in relation to the influences of the frictional coefficient (μ) at the indenter/material contact interface and of the inclined face angle (β) of the cone indenter. A novel procedure of “graphical superposition” was proposed to determine the representative yield stress YR. It was confirmed that the concept of YR applied to elastic-perfectlyplastic solids is sufficient enough for describing the indentation behavior of strainhardening elastoplastic solids. The representative plastic strain of εR (plastic) ≈ 0.22 tan β, at which YR is prescribed, is applicable to the strain-hardening elastoplastic solids, affording a quantitative relationship of YR = Y + ε;R (plastic) × EP in terms of the strain-hardening modulus EP. The true hardness H as a measure for plasticity is estimated from the Meyer hardness HM and then successfully related to the yield stress Y as H = C(β,μ) × Y for elastic-perfectly-plastic solids and as H = C(β,μ) × YR for strain-hardening solids, by the use of a β- and μ-dependent constraint factor C(β,μ) ranging from 2.6 to 3.2.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Tabor, Hardness of Metals (Clarendon Press, Oxford, U.K., 1951), Chap. 4–7.
B.R. Lawn and V.R. Howes, J. Mater. Sci. 16, 2745 (1981).
M. Sakai, Acta Metall. Mater. 41, 1751 (1993).
M. Sakai, S. Shimizu, and T. Ishikawa, J. Mater. Res. 14, 1471 (1999).
M. Sakai, J. Mater. Res. 14, 3630 (1999).
M. Sakai and Y. Nakano, J. Mater. Res. 17, 2161 (2002).
N.A. Stilwell and D. Tabor, Proc. Phys. Soc. London 78, 169 (1961).
J.L. Loubet, J.M. Georges, and G. Meille, in Microindentation Techniques in Materials Science and Engineering, edited by P.J. Blay and B.R. Lawn (ASTM STP889, Philadelphia, PA, 1986), p. 72.
M.F. Doerner and W.D. Nix, J. Mater. Res. 1, 601 (1986).
W.C. Oliver and G.M. Pharr, J. Mater. Res. 7, 1564 (1992).
G.M. Pharr, W.C. Oliver, and F.R. Brotzen, J. Mater. Res. 7, 613 (1992).
J.S. Field and M.V. Swain, J. Mater. Res. 8, 297 (1993).
E. Söderlund and D.J. Rowcliffe, J. Hard Mater. 5, 149 (1994).
R.F. Cook and G.M. Pharr, J. Hard Mater. 5, 179 (1994).
P.S. Follansbee and G.B. Sinclair, Int. J. Solids Struct. 20, 81 (1984).
P.S. Follansbee, G.B. Sinclair, and K.L. Johnson, Int. J. Solids Struct. 21, 865 (1985).
A.K. Bhattacharya and W.D. Nix, Int. J. Solids Struct. 27, 1047 (1991).
T.A. Laursen and J.C. Simo, J. Mater. Res. 7, 618 (1992).
Y. Murakami and K. Matsuda, J. App. Mech. 61, 822 (1994).
A.E. Giannakopoulos, P.E. Larsson, and R. Vestergaard, Int. J. Solids Struct. 31, 2679 (1994).
K. Matsuda and M. Kaneta, Philos. Mag. A 74, 1171 (1996).
P.E. Larsson, A.E. Giannakopoulos, E. Söderlund, D.J. Rowcliffe, and R. Vestergaard, Int. J. Solids Struct. 33, 221 (1996).
K. Zeng, E. Söderlund, A.E. Giannakopoulos, and D.J. Rowcliffe, Acta Mater. 44, 1127 (1996).
Y. Murakami and M. Itokazu, Int. J. Solids Struct. 34, 4005 (1997).
V. Marx and H. Balke, Acta Mater. 45, 3791 (1997).
A.E. Giannakopoulos and S. Suresh, Int. J. Solids Struct. 34, 2357 (1997).
Y.T. Cheng and C.M. Cheng, J. App. Phys. 84, 1284 (1998).
X. Chen and J.J. Vlassak, J. Mater. Res. 16, 2974 (2001).
K. Matsuda, Philos. Mag. A 82, 1941 (2002).
K.L. Johnson, Contact Mechanics (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, U.K., 1985), Chap. 3–6.
R. Hill, Mathematical Theory of Plasticity (Clarendon Press, Oxford, U.K., 1951), Chap. 8.
R.T. Shield, Proc. Roy. Soc. A 233, 267 (1955).
F.J. Lockett, J. Mech. Phys. Solids 11, 345 (1963).
I.N. Sneddon, Int. J. Eng. Sci. 3, 47 (1965).
M. Mata, M. Anglada, and A. Alcala´, Philos. Mag. A 82, 1831 (2002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sakai, M., Akatsu, T., Numata, S. et al. Linear strain hardening in elastoplastic indentation contact. Journal of Materials Research 18, 2087–2096 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.2003.0293
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.2003.0293