Abstract
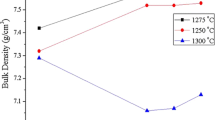
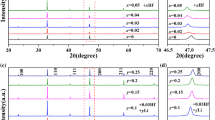
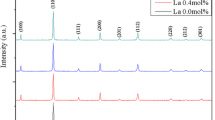
The effect of lanthanum (La) addition on the piezoelectric properties of lead zirconate titanate–lead zinc niobate (PZT–PZN) was investigated. When small amounts of La were added to the 0.82PZT–0.18PZN, the phase of the specimen changed from rhombohedral to tetragonal and the grain size was steadily reduced. To retain the morphotropic phase boundary (MPB) condition of the specimens with La contents of up to 4 mol%, the Zr/Ti ratio in the PZT was increased to 54/46. When more than 5 mol% La was added, pyrochlore phases were formed, and the piezoelectric properties were reduced. Therefore, the optimum piezoelectric properties (d33 = 545 pC/N, kp = 0.64, and s33 = 0.39% at 2 kV/mm) were observed in the specimen having MPB composition and with an La content of 4 mol%.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G.H. Haertling, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 82, 797 (1999).
S. Takahashi, Ferroelectrics 41, 143 (1982).
B. Jaffe, W.R. Cook, Jr., and H. Jaffe, Piezoelectric Ceramics (Academic Press, London, U.K., 1971).
G.H. Haertling and C.E. Land, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 54, 1 (1971).
A. Garg and D.C. Agrawal, Mater. Sci. Eng. B 86, 134 (2001).
Y. Ito, K. Nagatsuma, H. Takeuchi, and S. Jyomura, J. Appl. Phys. 52, 4479 (1981).
S.M. Gupta, J.F. Li, and D. Viehland, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 81, 557 (1998).
H. Yamaguchi, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 82, 1459 (1999).
H.Q. Fan and H.E. Kim, J. Appl. Phys. 91, 317 (2002).
J.C. Shaw, K.S. Liu, and I.N. Lin, J. Mater. Sci. 28, 4255 (1993).
J.C. Shaw, K.S. Liu, and I.N. Lin, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 78, 178 (1995).
K.H. Yoon and H.R. Lee, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 83, 2693 (2000).
S.J. Yoon, S.Y. Yoo, J.H. Moon, H.J. Jung, and H.J. Kim, J. Mater. Res. 11, 348 (1996).
S.J. Yoon, A. Joshi, and K. Uchino, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 80, 1035 (1997).
S.B. Seo, M.S. Thesis, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea (2002).
IEEE Standard on Piezoelectricity, IEEE Standard 176-1978 (Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers, New York, 1978).
S.M. Gupta and D. Viehland, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 80, 477 (1997).
W.Z. Zhu, A. Kholkin, P.Q. Mantas, and J.L. Baptista, Mater. Chem. Phys. 73, 62 (2002).
H. Liu, J.F. Wang, J.Y. Wang, H.D. Jiang, X.B. Hu, and H.M. Dong, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 20, 2337 (2000).
M. Hammer and M.J. Hoffmann, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 81, 3277 (1998).
Y. Yamashita, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 33, 5328 (1994).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, SH., Yoon, CB., Seo, SB. et al. Effect of lanthanum on the piezoelectric properties of lead zirconate titanate–lead zinc niobate ceramics. Journal of Materials Research 18, 1765–1770 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.2003.0245
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.2003.0245