Abstract
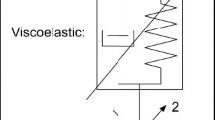
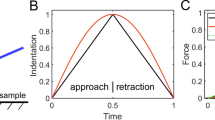
A model is developed that describes the sharp indentation behavior of time-dependent materials. The model constitutive equation is constructed from a series of quadratic mechanical elements, with independent viscous (dashpot), elastic (spring), and plastic (slider) responses. Solutions to this equation describe features observed under load-controlled indentation of polymers, including creep, negative unloading tangents, and loading-rate dependence. The model describes a full range of viscous–elastic–plastic responses and includes as bounding behaviors time-independent elastic–plastic indentation (appropriate to metals and ceramics) and time-dependent viscous–elastic indentation (appropriate to elastomers). Experimental indentation traces for a range of olymers with different material properties (elastic modulus, hardness, viscosity) are econvoluted and ranked by calculated time constant. Material properties for these polymers, deconvoluted from single load–unload cycles, are used to predict the indentation load–displacement behavior at loading rates three times slower and faster, as well as the steady-state creep rate under fixed load.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.F. Doerner and W.D. Nix, J. Mater. Res. 1, 601 (1986).
W.C. Oliver and G.M. Pharr, J. Mater. Res. 7, 1564 (1992).
B. Wolf, Cryst. Res. Technol. 25, 377 (2000).
J.S. Field and M.V. Swain, J. Mater. Res. 10, 101 (1995).
Y-T. Cheng and C-M. Cheng, J. App. Phys. 84, 1284 (1998).
Fundamentals of Nanoindentation and Nanotribology, edited by N.R. Moody, W.W. Gerberich, S.P. Baker, and N. Burnham (Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 522, Warrendale, PA, 1998).
Fundamentals of Nanoindentation and Nanotribology II, edited by S.P. Baker, R.F. Cook, S.G. Corcoran, and N.R. Moody (Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 649, Warrendale, PA, 2001).
J-Y. Rho, M.E. Roy, T.Y. Tsui, and G.M. Pharr, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 45, 48 (1999).
P.K. Zysset, X.E. Guo, C.E. Hoffler, K.E. Moore, and S.A. Goldstein, J. Biomech. 32, 1005 (1999).
E. Mahoney, A. Holt, M. Swain, and N. Kilpatrick, J. Dent. 28, 589 (2000).
B.J. Briscoe, K.S. Sebastian, and S.K. Sinha, Philos. Mag. A 74, 1159 (1996).
B.J. Briscoe, L. Fiori, and E. Pelillo, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 31, 2395 (1998).
L. Cheng, X. Xia, W. Yu, L.E. Scriven, and W.W. Gerberich, J. Polym. Sci. B: Polym. Phys. 38, 10 (2000).
M. Sakai and S. Shimizu, J. Non-Cryst. Solids 282, 236 (2001).
K.B. Yoder, S. Ahuja, K.T. Dihn, D.A. Crowson, S.G. Corcoran, L. Cheng, W.W. Gerberich, in Fundamentals of Nanoindentation and Nanotribology, edited by N.R. Moody, W.W. Gerberich, S.P. Baker, and N. Burnham (Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 522, Warrendale, PA, 1998), p. 205.
S. Shimizu, T. Yanagimoto, and M. Sakai, J. Mater. Res. 14, 4075 (1999).
G. Feng and A.H.W. Ngan, J. Mater. Res. 17, 660 (2002).
B.N. Lucas, W.C. Oliver, G.M. Pharr, L-L. Loubet, in Thin Films: Stresses and Mechanical Properties VI, edited by W.W. Gerberich, H. Gao, J-E. Sundgren, and S.P. Baker . (Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 436, Warrendale, PA, 1997), p. 233.
M.J. Adams, D.M. Gorman, and S.A. Johnson, in Fundamentals of Nanoindentation and Nanotribology II, edited by S.P. Baker, R.F. Cook, S.G. Corcoran, and N.R. Moody (Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 649, Warrendale, PA, 2001), p. Q7.10.1.
M. Oyen-Tiesma, Y.A. Toivola, and R.F. Cook, in Fundamentals of Nanoindentation and Nanotribology II, edited by S.P. Baker, R.F. Cook, S.G. Corcoran, and N.R. Moody (Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 649, Warrendale, PA, 2001), p. Q1.5.1.
W.N. Findley, J.S. Lai, and K. Onaran, Creep and Relaxation of Nonlinear Viscoelastic Materials (Dover Publications, New York, 1989).
I.N. Sneddon, Int. J. Eng. Sci. 3, 47 (1965).
R.F. Cook and G.M. Pharr, J. Hard Mater. 5, 179 (1994).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oyen, M.L., Cook, R.F. Load–displacement behavior during sharp indentation of viscous–elastic–plastic materials. Journal of Materials Research 18, 139–150 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.2003.0020
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.2003.0020