Abstract
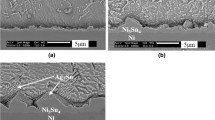
The reaction mechanism between electroless Ni–P and Sn was investigated to understand the effects of Sn on solder reaction-assisted crystallization at low temperatures as well as self-crystallization of Ni–P at high temperatures. Ni3Sn4 starts to form in a solid-state reaction well before Sn melts. Heat of reaction for Ni3Sn4 was measured during the Ni–P and Sn reaction (241.2 J/g). It was found that the solder reaction not only promotes crystallization at low temperatures by forming Ni3P in the P-rich layer but also facilitates self-crystallization of Ni–P by reducing the transformation temperature and heat of crystallization. The presence of Sn reduces the self-crystallization temperature of Ni–P by about 10 °C. The heat of crystallization also decreases with an increased Sn thickness.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Brenner and G. Riddell, J. Res. Nat. Bur. Stand. 37, 1 (1946).
H. Kreye, F. Müller, K. Lang, D. Isheim, T. Hentschel, Z. Metallkd. 86, 184 (1995).
H. Kreye, H-H. Müller, and T. Petzel, Galvanotechnik 77, 561 (1986).
G. Dietz and H.D. Schneider, J. Phys, Condens. Matter 2, 2169 (1990).
K.H. Hur, J.H. Jeong, and D.N. Lee, J. Mater. Sci. 25, 2573 (1990).
Th. Hentschel, D. Isheim, R. Kirchheim, F. Müller, and H. Kreye, Acta Mater. 48, 933 (2000).
S. Wiegele, P. Thompson, R. Lee, and E. Ramsland, in Proceedings of IEEE Electronic Component and Technology Conference, (1998), p. 861.
J.W. Jang, P.G. Kim, K.N. Tu, D.R. Frear, and P. Thompson, J. Appl. Phys. 85, 8456 (1999).
F. Stepniak, Adv. Electron. Packaging 1, 353 (1997).
K.C. Hung, Y.C. Chan, C.W. Tang, and H.C. Ong, J. Mater. Res. 15, 2534 (2000).
P.L. Liu, Z. Xu, and J.K. Shang, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 31A, 2857 (2000).
J.W. Jang, D.R. Frear, T.Y. Lee, and K.N. Tu, J. Appl. Phys. 88, 6359 (2000).
K. Zeng and K.N. Tu, Mater. Sci. Eng. R 38, 55 (2002).
S.K. Kang and V. Ramachandran, Scipta Metall. 14, 421 (1980).
C.Y. Lee and K.L. Lin, Thin Solid Films 249, 201 (1994).
I. Barin, O. Knacke, and O. Kubaschewski, Thermochemical Properties of Inorganic Substances (Springer, New York, 1977).
S.H. Park and D.N. Lee, J. Mater. Sci. 23, 1643 (1988).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sohn, Y.C., Yu, J., Kang, S.K. et al. Study of the reaction mechanism between electroless Ni–P and Sn and its effect on the crystallization of Ni–P. Journal of Materials Research 18, 4–7 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.2003.0002
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.2003.0002