Abstract
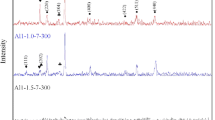
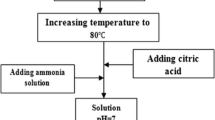
Ultrafine BaFe12O19 powder with crystallite sizes less than 200 nm was prepared via a citric acid precursor method. Citric acid was added into an aqueous solution, containing nitrates of Ba2+ and Fe3+ in a stoichiometric ratio to form barium ferrite, to chelate metallic ions in the solution. The pH of aqueous solutions was adjusted with NH4OH. After ethylene glycol was added into the solution and the system temperature was raised, esterification and dehydratation led to the formation of solid ester precursor. The distribution and contents of metallic ions in the ester are affected by the [citric acid]/[metallic ions] molar ratio used and the pH of starting solutions. When the ester-precursor obtained at pH = 9 with [citric acid]/[metallic ions] = 1.5 was used, crystalline BaFe12O19 appeared at temperatures as low as 923 K, and pure barium ferrite was obtained at 1073 K. According to the experimental results obtained, the reaction mechanism involved in the pyrolysis of esters is proposed and discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Imamura, Y. Ito, M. Fujiki, T. Hasegawa, H. Kubota, and T. Fujiwara, IEEE Trans. Magn. 22, 1185 (1986).
K. Yamamori, T. Suzuki, and T. Fujiwara, IEEE Trans. Magn. 22, 1188 (1986).
J. Smit and H.P.J. Wijn, Ferrites (Wiley, New York, 1959), p. 369.
R.C. Tenzer, J. Appl. Phys. 34, 1267 (1963).
S.E. Jacobo, M.A. Blesa, C. Domingo-Pascual, and R. Rodpiguez-Clemente, J. Mater. Sci. 32, 1025 (1997).
Z. Zheng, B. Guo, and X. Mei, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 78, 73 (1989).
W. Roos, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 63, 601 (1980).
B.T. Shirk and W.R. Buessem, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 53, 192 (1970).
E. Lucchini, S. Meriani, and G. Slokar, J. Mater. Sci. 18, 1331 (1983).
O. Kubo, T. Ido, and H. Yokoyama, IEEE Trans. Magn. 18, 1122 (1982).
D. Barb, L. Diamandescu, and A. Rusi, J. Mater. Sci. 21, 1118 (1986).
D. Bahadur, W. Fischer, and M.V. Rane, Mater. Sci. Eng. A252, 109 (1998).
L. Tai and P.A. Lessing, J. Mater. Res. 7, 502 (1992).
F. Lucchini, S. Meriani, F. Dolben, and S. Paoletti, J. Mater. Sci. 19, 121 (1984).
H.P. Steier, J. Requena, and J.S. Moya, J. Mater. Sci. 14, 3647 (1999).
G. Benito, M.P. Morales, J. Requena, V. Raposo, M. Vazquez, and J.S. Moya, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 234, 65 (2001).
K. Eisenbeiser, J.M. Finder, Z. Yu, J. Ramdani, J.A. Curless, J.A. Hallmark, R.W. Droopad, J. Ooms, L. Salem, S. Bradshaw, and C.D. Overgaard, Appl. Phys. Lett. 76, 1324 (2000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, HF., Huang, KC. Preparation and Characterization of Ester-derived BaFe12O19 Powder. Journal of Materials Research 17, 199–203 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.2002.0029
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.2002.0029