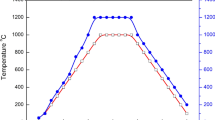
Abstract
Nanocrystalline Ag–Fe–Ni powders were produced by a reduction of the aqueous metal ion solutions with sodium borohydride and then converted to fine-grained silver–Invar alloys that offer attractive thermal, electrical, and mechanical properties. The samples were characterized by x-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, wavelength dispersive x-ray spectrometry, thermomechanical analysis, microhardness measurements, and electrical conductivity measurements; thermal conductivity was estimated using the Wiedemann–Franz law. Sintering of a specimen with a nominal composition of 60 wt% Ag–25.6 wt% Fe–14.4 wt.% Ni led to the formation of a two-phase silver–Invar alloy with a grain size of approximately 2 μm, a hardness of 133 HK200g, coefficient of thermal expansion of 12.44 × 10−6 / °C, and electrical conductivity of 2.13 × 105 (Ω cm) −1.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W.R. Johannes and W. Johnson, Int. J. Microcircuits Elec. Packaging, 17 (2), 135 (1994).
Texas Instruments, Metallurgical Materials Division, Microwave Journal, 38 (2), 124 (1995).
D.E. Jech and J.L. Sepulveda, Intl. Symp. on Microelectronics, Las Vegas, NV, SPIE Proceedings Series 3235, 90 (1997).
P. Yih and D.D.L. Chung, J. Mater. Sci. 32, 2873 (1997).
C. Zweben, JOM 50 (6), 47 (1998).
R. Kumar, J.J. Stiglich, T.S. Sudarshan, and C.C. Yu, Materials and Manufacturing Processes 11, (Marcel Dekker, New York, 1996), p. 1029.
S. Yamagata, M. Imamura, Y. Hirose, Y. Abe, Y. Takano, and A. Fukui, Int. Sym. on Microelectronics, San Diego, CA, SPIE Proc. Series 3582, 675 (1998).
R.D. Cottle, X. Chen, R.K. Jain, Z. Eliezer, L. Rabenberg, and M.E. Fine, JOM 50 (6), 67 (1998).
J. Stolk and A. Manthiram, Mater. Sci. Eng. 60, 112 (1999).
ASTM B 742-90 (Reapproved 1995) Standard Specification for Fine Silver Electrical Contact Fabricated Material, Standard 3.04, Annual Book of ASTM Standards (American Society for Testing and Materials, West Conshohocken, PA, 1998), p. 440.
ASTM F 1684-96 Standard Specification for Iron-Nickel and Iron-Nickel-Cobalt Alloys for Low Thermal Expansion Applications, Standard 10.04, Annual Book of ASTM Standards (American Society for Testing and Materials, West Conshohocken, PA, 1998), p. 392.
Metals Handbook, 9th ed., edited by D. Wenschhof (American Society for Metals, Metals Park, OH, 1980), Vol. 3, p. 792.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stolk, J., Gross, M., Stolk, D. et al. Synthesis and processing of nanocrystalline Ag–Fe–Ni for low thermal expansion–high conductivity thermal management applications. Journal of Materials Research 16, 340–343 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.2001.0053
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.2001.0053