Abstract
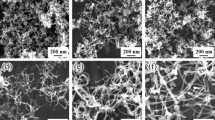
The size distributions of Si and ZnTe nanoparticles produced by low energy density ArF (193 nm) pulsed laser ablation into ambient gases were measured as a function of the gas pressure, P, and target-substrate separation, Dts. For both Si and ZnTe, the largest nanoparticles were found closest to the ablation target, and the mean nanoparticle size decreased with increasing Dts. For Si ablation into He, the mean nanoparticle diameter did not increase monotonically with gas pressure but reached a maximum near P = 6 Torr. High resolution Z-contrast transmission electron microscopy and energy loss spectroscopy revealed that ZnTe nanoparticles consist of a crystalline core surrounded by an amorphous ZnO shell; growth defects and surface steps are clearly visible in the crystalline core. A pronounced narrowing of the ZnTe nanocrystal size distribution with increasing Dts also was found. The results demonstrate that the size of laser-ablated nanoparticles can be controlled by varying the molecular weight and pressure of an ambient gas and that nanometer-scale particles can be synthesized. Larger aggregates of both ZnTe and Si having a “flakelike” or “weblike” structure were formed at the higher ambient gas pressures; for ZnTe these appear to be open agglomerates of much smaller (∼10 nm) particles.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. H. Lowndes, D. B. Geohegan, A. A. Puretzky, D. P. Norton, and C. M. Rouleau, Science 273, 898 (1996).
D. E. Powers, S. G. Hansen, M. E. Geusic, A. C. Pulu, J. B. Hopkins, T. G. Dietz, M.A. Duncan, P. R. R. Langridge-Smith, and R. E. Smalley, J. Phys. Chem. 86, 2556 (1982).
C.M. Rouleau, D.H. Lowndes, J.W. McCamy, J.D. Budai, D.B. Poker, D. B. Geohegan, A. A. Puretzky, and S. Zhu, Appl. Phys. Lett. 67, 2545 (1995).
D. H. Lowndes, C. M. Rouleau, D. B. Geohegan, A. A. Puretzky, M. A. Strauss, A. J. Pedraza, J. W. Park, J. D. Budai, and D. B. Poker, in Advanced Laser Processing of Materials—Fundamentals and Applications, edited by R. Singh, D. Norton, L. Laude, J. Narayan, and J. Cheung (Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 397, Pittsburgh, PA, 1996), p. 107.
C. M. Rouleau, D. H. Lowndes, M. A. Strauss, S. Cao, A. J. Pedraza, D. B. Geohegan, A. A. Puretzky, and L. F. Allard, in Advanced Laser Processing of Materials—Fundamentals and Applications, edited by R. Singh, D. Norton, L. Laude, J. Narayan, and J. Cheung (Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 397, Pittsburgh, PA, 1996), p. 119.
W. M. K. P. Wijekoon, M. Y. M. Lyktey, P. N. Prasad, and J. F. Garvey, Appl. Phys. Lett. 67, 1698 (1995).
T. Yoshida, S. Takeyama, Y. Yamada, and K. Mutoh, Appl. Phys. Lett. 68, 1772 (1996).
Y. Yamada, T. Orii, I. Umezu, S. Takeyama, and T. Yoshida, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 35, 1361 (1996).
T. Yoshida, Y. Yamada, and T. Orii, in Technical Digest of the Inter. Electron Devices Mtg., San Francisco, CA, Dec. 8–11, 1996, IEEE, p. 417.
T. Makimura, Y. Kunii, and K. Murakami, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 35, 4780 (1996).
T. Makimura, T. Sakuramoto, and K. Murakami, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 35, L735 (1996).
T. Makimura, Y. Kunii, N. Ono, and K. Murakami, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 35, L1703 (1996).
T. Yoshida, personal communication. In the deposition experiments the laser pulse energy was 60 mJ, measured before the quartz entrance window. Assuming a transmission factor of 0.91 and the 1 × 3 mm area of Refs. 7 and 8, this corresponds to Ed ~ 1.8 J/cm2.
A. Matsunawa, S. Katayama, A. Susuki, and T. Ariyasu, Trans. Jpn. Welding Res. Institute 15, 233 (1986).
0.003-inch × 3-inch #3 edge 1095 steel ribbon, tempered, polished, and blued; Amstek Metal, Joliet, IL.
D.B. Geohegan, Appl. Phys. Lett. 60, 2732 (1992).
G. Duscher, D. B. Geohegan, A. A. Puretzky, and S.J. Pennycook, personal communication.
Al. L. Efros and A. L. Efros, Sov. Phys. Semicond. 16, 772 (1982).
L.E. Brus, J. Chem. Phys. 79, 5566 (1983).
L. Brus, J. Phys. Chem. 90, 2555 (1986).
R.P. Camata, H. A. Atwater, K. J. Vahala, and R. C. Flagan, Appl. Phys. Lett. 68, 3162 (1996).
T. Ifuku, M. Otobe, A. Itoh, and S. Oda, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 36, 4031 (1997).
R.F. Wood, J. N. Leboeuf, K. R. Chen, D.B. Geohegan, and A.A. Puretzky, Fourth Int. Conf. on Laser Ablation (COLA’97), Monterey, CA, July 21–25, 1997; Surf. Sci. in press.
Yu. P. Raizer, Sov. Phys. JETP 37, 1229 (1960).
D.B. Geohegan, personal communication and unpublished data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lowndes, D.H., Rouleau, C.M., Thundat, T.G. et al. Silicon and zinc telluride nanoparticles synthesized by low energy density pulsed laser ablation into ambient gases. Journal of Materials Research 14, 359–370 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.1999.0053
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.1999.0053