Abstract
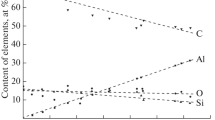
Results of a study of compositional, optical, electrical, and structural properties of hydrogen amorphous silicon carbide (a-SiC:H) prepared, respectively, by glow-discharge (GD) and reactive sputtering (SP) techniques at power densities varying between 1.25 · 10−2 and 1.25 · 10−1 W · cm−2 for GD samples are presented. Measurements are reported on the composition, optical and IR spectroscopy, and on the temperature dependence of electrical conductivity. All experimental observations suggest that the power density only slightly affects the physical properties of GD silicon-rich samples, whereas those of the carbon-rich SP samples depend more strongly on this deposition parameter. Finally, it is shown that the GD technique can provide films with better characteristics, whereas samples of similar composition prepared by sputtering have higher compositional disorder and are more inhomogeneous.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Kuwano, M. Ohnishi, H. Nishiwaski, S. Tsuda, T. Fukatsu, K. Enomoto, Y. Nakashima, and H. Tazni, 16th IEEE PV Spec Conference, San Diego, CA (IEEE, New York, 1982), p. 1331.
H. Munekata and H. Kukimoto, Appl. Phys. Lett. 42, 432 (1983).
J. Pezzin, I. Solomon, B. Bourdon, J. Fontenille, and E. Ligeon, Thin Solid Films 62, 327 (1979).
M.P. Schmidt, J. Bullot, M. Gauthier, P. Cordier, I. Solomon, and H. Tran-Quoc, Philos. Mag. B 51, 581 (1985).
D. A. Anderson and W. E. Spear, Philos. Mag. B 35, 1 (1977).
J. Bullot and M. P. Schmidt, Phys. Status Solidi (B) 143, 345 (1987).
M.P. Schmidt, I. Solomon, H. Tran-Quoc, and J. Bullot, J. Non-Cryst. Solids 77–78, 849 (1985).
F. Demichelis, G. Kaniadakis, A. Tagliaferro, and E. Tresso, Appl. Opt. 26, 1717 (1987).
A. H. Mahan, B. von Roedern, D. L. Williamson, and A. Madan, J. Appl. Phys. 57, 8 (1985).
W. Paul and D. Anderson, Solar Energy Materials 5, 229 (1981).
J. Robertson, Adv. Phys. 35, 4, 317 (1986).
M. H. Brodsky, M. Cardona, and J. J. Cuomo, Phys. Rev. B 16, 3556 (1977).
E. C. Freeman and W. Paul, Phys. Rev. B 18, 4288 (1978).
B. Dishler, Proc. 7th Int. Symp. on Plasma Chemistry (Eindhoven, July 1985), Vol. I, p. 45.
F. Demichelis, G. Kaniadakis, E. Mezzetti, P. Mpawenayo, A. Tagliaferro, E. Tresso, P. Rava, and G. Delia Mea, Nuovo Ci-mento 9D, 393 (1987).
T. D. Moustakas, Semiconductors and Semimetals, edited by J. I. Pankove (Academic Press, New York, 1984), Vol. 21, p. 55.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carbone, A., Demichelis, F., Kaniadakis, G. et al. Physical properties of amorphous silicon-carbon alloys produced by different techniques. Journal of Materials Research 5, 2877–2881 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.1990.2877
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.1990.2877