Abstract
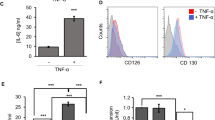
We explored the possibility that interferon γ (IFN-γ) has bidirectional functions in the survival and growth of hematopoietic progenitors, especially with regard to interactions with stromal cell-derived factor 1 (SDF-1). IFN-γ partially rescued normal bone marrow CD34+ cells and colony-forming cells from apoptosis induced by serum and hematopoietic growth factor (HGF) deprivation, and SDF-1 further enhanced cell survival. Short-term IFN-γ treatment of CD34+ cells in the absence of serum and HGFs enhanced the clonal growth of the cells in synergy with SDF-1. In contrast, IFN-γ inhibited the clonal growth of hematopoietic progenitor cells in a standard methylcellulose clonogenic assay and inhibited the HGF-mediated survival of normal CD34+ cells. The addition of SDF-1 did not alter these outcomes. IFN-γ did not enhance SDF-1-induced activation of PI3K/Akt or up-regulate the expression of CXCR4 or its function in bone marrow CD34+ cells. IFN-γ up-regulated Socs1 messenger RNA expression in normal CD34+ cells, which was further enhanced with the addition of HGFs. These results indicate that IFN-γ, partly in concert with SDF-1, exerts dual effects on the survival and growth of hematopoietic progenitor cells; the effects of IFN-γ on hematopoietic progenitor cells can differ, depending on the particular in vitro experimental conditions, especially the presence of HGFs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zoumbos NC, Gascon P, Djeu JY, Young NS. Interferon is a mediator of hematopoietic suppression in aplastic anemia in vitro and possibly in vivo. Proc Nat Acad Sci U S A. 1985;82:188–192.
Mamus SW, Beck-Schroeder S, Zanjani ED. Suppression of normal human erythropoiesis by gamma interferon in vitro: role of monocytes and T lymphocytes. J Clin Invest. 1985;75:1496–1503.
Nistico A, Young NS. Gamma-interferon gene expression in the bone marrow of patients with aplastic anemia. Ann Intern Med. 1994;120:463–469.
Dufour C, Corcione A, Svahn J, Haupt R, Battilana N, Pistoia V. Interferon γ and tumour necrosis factor α are overexpressed in bone marrow T lymphocytes from paediatric patients with aplastic anemia. Br J Haematol. 2001;115:1023–1031.
Yu J-M, Emmons RV, Hanazono Y, Sellers S, Young NS, Dunbar CE. Expression of interferon-γ by stromal cells inhibits murine long-term repopulating hematopoietic stem cell activity. Exp Hematol. 1999;27:895–903.
Selleri C, Sato T, Anderson S, Young NS, Maciejewski JP. Inter-feron-gamma and tumour necrosis factor-alpha suppress both early and late stages of hematopoiesis and induce programmed cell death. J Cell Physiol. 1995;165:538–546.
Shimozato O, Ortaldo JR, Komschlies KL, Young HA. Impaired NK cell development in an IFN-γ transgenic mouse: aberrantly expressed IFN-γ enhances hematopoietic stem cell apoptosis and affects NK cell differentiation. J Immunol. 2002;168:1746–1752.
Murray PJ, Young RA, Daley GQ. Hematopoietic remodelling in interferon-γ-deficient mice infected with mycobacteria. Blood. 1998;91:2914–2924.
Gabriele L, Phung J, Fukumoto J, et al. Regulation of apoptosis in myeloid cells by interferon consensus sequence-binding protein. J Exp Med. 1999;190:411–422.
Maciejewski J, Selleri C, Anderson S, Young NS. Fas antigen expression on CD34+ human marrow cells is induced by interferon gamma and tumour necrosis factor alpha and potentiates cytokinemediated hematopoietic suppression in vitro. Blood. 1995;85:3183–3190.
Dai C, Krantz SB. Interferon-γ induces upregulation and activation of caspases 1, 3, and 8 to produce apoptosis in human erythroid progenitor cells. Blood. 1999;93:3309–3316.
Richman CM, Slapak CA, Toh B. Interferon protects normal human granulocyte/macrophage colony-forming cells from Ara-C cytotoxicity. J Biol Response Mod. 1990;9:570–575.
Caux C, Moreau I, Saeland S, Bancherau J. Interferon-gamma enhances factor-dependent myeloid proliferation of human CD34+ hematopoietic progenitor cells. Blood. 1992;79:2628–2635.
Shiohara M, Koike K, Nakahata T. Synergism of interferon-gamma and stem cell factor on the development of murine hematopoietic progenitors in serum-free culture. Blood. 1993;81:1435–1441.
Kawano Y, Takaue Y, Hirao A, et al. Synergy among erythropoietin, interleukin 3, stem cell factor (c-kit ligand) and interferongamma on early human hematopoiesis. Stem Cells. 1994;12:514–520.
Snoeck HW, Lenjou M, Nys G, et al. Interleukin 4 and interferon gamma costimulate the expansion of early human myeloid colonyforming cells: proposal of a model for the regulation of myelopoiesis by interleukin 4 and interferon gamma and its integration with the regulation of the immune response. Leukemia. 1996;10:117–122.
Choi I, Muta K, Wickrema A, Krantz SB, Nawata H. Interferon gamma delays apoptosis of mature erythroid progenitor cells in the absence of erythropoietin. Blood. 2000;95:3742–3749.
Tsuji-Takayama K, Tahata H, Harachima A, et al. Interferon-gamma enhances megakaryocyte colony-stimulating activity in murine bone marrow cells. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 1996;16:701–708.
Peled A, Petit I, Kollet O, et al. Dependence of human stem cell engraftment and repopulation of NDO/SCID mice on CXCR4. Science. 1999;283:845–848.
Lataillade JJ, Clay D, Dupuy C, et al. Chemokine SDF-1 enhances circulating CD34+ cell proliferation in synergy with cytokines: possible role in progenitor survival. Blood. 2000;95:756–768.
Lee Y-H, Gotoh A, Kwon H-J, et al. Enhancement of intracellular signalling associated with hematopoietic progenitor cell survival in response to SDF-1/CXCL12 in synergy with other cytokines. Blood. 2002;99:4307–4317.
Aiuti A,Webb IJ, Springer T, Gutierrez-Ramos JC. The chemokine SDF-1 is a chemoattractant for human CD34+ hematopoietic progenitor cells and provides a new mechanism to explain the mobilization of CD34+ progenitors to peripheral Blood. J Exp Med. 1997;185:111–120.
Grafte-Faure S, Leveque C, Ketata E, et al. Recruitment of primitive peripheral blood cells: synergism of interleukin 12 with inter-leukin 6 and stromal cell-derived factor-1. Cytokine. 2000;12:1–7.
Broxmyeler HE, Cooper S, Kohli L, et al. Transgenic expression of stromal cell-derived factor-1/CXC chemokine ligand 12 enhances myeloid progenitor cell survival/antiapoptosis in vitro in response to growth factor withdrawal and enhances myelopoiesis in vivo. J Immunol. 2003;170:421–429.
Rosu-Myles M, Bhatia M. SDF-1 enhances the expansion and maintenance of highly purified human hematopoietic progenitors. Hematol J. 2003;4:137–145.
Lataillade J-J, Clay D, Bourin P, et al. Stromal cell-derived factor-1 regulates primitive hematopoiesis by suppressing apoptosis and by promoting G0/G1 transition in CD34+ cells: evidence for an autocrine/paracrine mechanism. Blood. 2002;99:1117–1129.
Cashman J, Clark-Lewis I, Eaves A, Eaves C. Stromal-derived factor-1 inhibits the cycling of very primitive human hematopoietic cells in vitro and in NOD/SCID mice. Blood. 2002;99:792–799.
Nguyen H, Ramana CV, Bayes J, Stark GR. Roles of phos-phatidylinositol 3-kinase in interferon-γ-dependent phosphorylation of STAT1 on serine 727 and activation of gene expression. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:33361–33368.
Krebs DL, Hilton DJ. SOCS protein: negative regulators of cytokine signalling. Stem Cells. 2001;19:378–387.
Turnley AM, Starr R, Bartlett PF. SOCS1 regulates interferon-γ mediated sensory neuron survival. Neuroreport. 2001;12:3443–3445.
De Sepulveda P, Okkenhaug K, Rose JL, Hawley RG, Dubreuil P, Rottapel R. Socs1 binds to multiple signaling proteins and suppresses Steel factor-dependent proliferation. EMBO J. 1999;18:904–915.
Ratajczak J, Kucia M, Reca R, Zhang J, Machalinski B, Ratajczak MZ. Quiescent CD34+ early erythroid progenitors are resistant to several erythropoietic ‘inhibitory’ cytokines: role of FLIP. Br J Haematol. 2003;123:160–169.
Jonsson M, Engstrom M, Jonsson JI. FLT3 ligand regulates apoptosis through AKT-dependent inactivation of transcription factor FoxO3. Biochem Biophy Res Commun. 2004;318:899–903.
Myklebust JH, Blomhoff HK, Rusten LS, Stokke T, Smeland EB. Activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase is important for ery-thropoietin-induced erythropoiesis from CD34+ hematopoietic progenitor cells. Exp Hematol. 2002;30:990–1000.
Sporn MB, Robert AB. Peptide growth factors are multifunctional. Nature. 1998;332:217–219.
Nakajima K, Yamanaka Y, Nakae K, et al. A central role for Stat3 in IL-6-induced regulation of growth and differentiation in M1 leukemic cells. EMBO J. 1996;15:3651–3658.
Asao H, Fu X-Y. Interferon-γ has dual potential in inhibiting or promoting cell proliferation. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:867–874.
Budd RC. Death receptors couple to both cell proliferation and apoptosis. J Clin Invest. 2002;109:437–441.
Muhl H, Pfeilschifter J. Anti-inflammatory properties of proinflammatory interferon γ. Int Immunopharmacol. 2003;3:1247–1255.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Hwang, JH., Kim, SW., Lee, HJ. et al. Interferon γ Has Dual Potential in Inhibiting or Promoting Survival and Growth of Hematopoietic Progenitors: Interactions with Stromal Cell-Derived Factor 1. Int J Hematol 84, 143–150 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1532/IJH97.A30606
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1532/IJH97.A30606