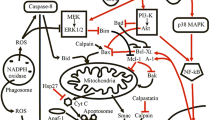
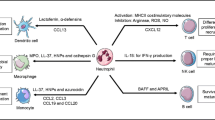
Abstract
Various functions of mature human neutrophils are activated or potentiated by hematopoietic growth factors or proinflammatory cytokines such as granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, tumor necrosis factor α, and interleukin 1β. The major signaling pathways activated in human neutrophils stimulated by proinflammatory cytokines include mitogen-activated protein kinases, Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, and nuclear factor κB. These signaling pathways are involved in cytokine-mediated regulation of neutrophil functions in a cytokine-specific manner.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kitagawa S, Yuo A, Souza LM, Saito M, Miura Y, Takaku F. Recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor enhances superoxide release in human granulocytes stimulated by the chemotactic peptide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987;144: 1143–1146.
Yuo A, Kitagawa S, Ohsaka A, et al. Recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor as an activator of human granulocytes: potentiation of responses triggered by receptor-mediated agonists and stimulation of C3bi receptor expression and adherence. Blood. 1989;74:2144–2149.
Yuo A, Kitagawa S, Suzuki I, et al. Tumor necrosis factor as an activator of human granulocytes: potentiation of the metabolisms triggered by the Ca2+-mobilizing agonists. J Immunol. 1989;142: 1678–1684.
Suzuki K, Hino M, Hato F, Tatsumi N, Kitagawa S. Cytokine-specific activation of distinct mitogen-activated protein kinase subtype cascades in human neutrophils stimulated by granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, and tumor necrosis factor-α. Blood. 1999;93:341–349.
Suzuki K, Hasegawa T, Sakamoto C, et al. Cleavage of mitogen-activated protein kinases in human neutrophils undergoing apoptosis: role in decreased responsiveness to inflammatory cytokines. J Immunol. 2001;166:1185–1192.
Lambeth JD. NOX enzymes and the biology of reactive oxygen. Nat Rev Immunol. 2004;4:181–189.
Hoyal CR, Gutierrez A, Young BM, et al. Modulation of p47PHOX activity by site-specific phosphorylation: Akt-dependent activation of the NADPH oxidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100:5130–5135.
Suzuki K, Hino M, Kutsuna H, et al. Selective activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade in human neutrophils stimulated by IL-1β. J Immunol. 2001;167:5940–5947.
Dang PM, Stensballe A, Boussetta T, et al. A specific p47phox-serine phosphorylated by convergent MAPKs mediates neutrophil NADPH oxidase priming at inflammatory sites. J Clin Invest. 2006;116:2033–2043.
Zhu QS, Xia L, Mills GB, Lowell CA, Touw IP, Corey SJ. G-CSF induced reactive oxygen species involves Lyn-PI3-kinase-Akt and contributes to myeloid cell growth. Blood. 2006;107:1847–1856.
Hermans MH, Antonissen C, Ward AC, Mayen AE, Ploemacher RE, Touw IP. Sustained receptor activation and hyperproliferation in response to granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) in mice with a severe congenital neutropenia/acute myeloid leukemia-derived mutation in the G-CSF receptor gene. J Exp Med. 1999;189: 683–692.
Kamata N, Kutsuna H, Hato F, et al. Activation of human neutrophils by granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and tumor necrosis factor-a: the role of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Int J Hematol. 2004;80: 421–427.
Chen Q, Powell DW, Rane MJ, et al. Akt phosphorylates p47phox and mediates respiratory burst activity in human neutrophils. J Immunol. 2003;170:5302–5308.
Han H, Fuortes M, Nathan C. Critical role of the carboxyl terminus of proline-rich tyrosine kinase (Pyk2) in the activation of human neutrophils by tumor necrosis factor: separation of signals for the respiratory burst and degranulation. J Exp Med. 2003;197:63–75.
Fuortes M, Melchior M, Han H, Lyon GJ, Nathan C. Role of the tyrosine kinase pyk2 in the integrin-dependent activation of human neutrophils by TNF. J Clin Invest. 1999;104:327–335.
Sims JE, Gayle MA, Slack JL, et al. Interleukin 1 signaling occurs exclusively via the type I receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993;90:6155–6159.
Takahashi T, Hato F, Yamane T, et al. Activation of human neutrophil by cytokine-activated endothelial cells. Circ Res. 2001;88: 422–429.
Bourke E, Cassetti A, Villa A, Fadlon E, Colotta F, Mantovani A. IL-1β scavenging by the type II IL-1 decoy receptor in human neutrophils. J Immunol. 2003;170:5999–6005.
Kutsuna H, Suzuki K, Kamata N, et al. Actin reorganization and morphological changes in human neutrophils stimulated by TNF, GM-CSF and G-CSF: role of mitogen-activated protein kinases. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2004;286:C55-C64.
Vollmer KL, Alberts JS, Carper HT, Mandell GL. Tumor necrosis factor-a decreases neutrophil chemotaxis toN-formyl-l-methionyl-l-leucyl-l-phenylalanine:analysis of single cell movement. J LeukocBiol. 1992;52:630–636.
Peppelenbosch M, Boone E, Jones GE, et al. Multiple signal transduction pathways regulate TNF-induced actin reorganization in macrophages: inhibition of Cdc-42-mediated filopodium formation by TNF. J Immunol. 1999;162:837–845.
Nakamae-Akahori M, Kato T, Masuda S, et al. Enhanced neutrophil motility by granulocyte colony-stimulating factor: the role of extracellular signal-regulated kinase and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Immunology. In press.
Vial E, Pouyssegur J. Regulation of tumor cell motility by ERK mitogen-activated protein kinases. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2004;1030:208–218.
Alblas J, Ulfman L, Hordijk P, Koenderman L. Activation of RhoA and ROCK are essential for detachment of migrating leukocytes. Mol Biol Cell. 2001;12:2137–2145.
Sakamoto C, Suzuki K, Hato F, et al. Anti-apoptotic effect of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and cyclic AMP on human neutrophils: protein synthesis-dependent and protein synthesis-independent mechanisms and role of Janus kinase-STAT pathway. Int J Hematol. 2003;77:60–70.
Epling-Burnette PK, Zhong B, Bai F, et al. Cooperative regulation of Mcl-1 by Janus kinase/STAT and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase contribute to granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor-delayed apoptosis in human neutrophils. J Immunol. 2001;166:7486–7495.
Derouet M, Thomas L, Cross A, Moots RJ, Edwards SW. Granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor signaling and protea-some inhibition delay neutrophil apoptosis by increasing the stability of Mcl-1. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:26915–26921.
Cowburn AS, Cadwallader KA, Reed BJ, Farahi N, Chilvers ER. Role of PI3-kinase-dependent Bad phosphorylation and altered transcription in cytokine-mediated neutrophil survival. Blood. 2002;100:2607–2616.
Hasegawa T, Suzuki K, Sakamoto C, et al. Expression of the inhibitor of apoptosis (IAP) family members in human neutrophils: up-regulation of cIAP2 by granulocyte colony-stimulating factor and overexpression of cIAP2 in chronic neutrophilic leukemia. Blood. 2003;101:1164–1171.
Maianski NA, Roos D, Kuijpers TW. Bid truncation, Bid/Bax targeting to the mitochondria, and caspase activation associated with neutrophil apoptosis are inhibited by granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. J Immunol. 2004;172:7024–7030.
Altznauer F, Martinelli S, Yousefi S, et al. Inflammation-associated cell cycle-independent block of apoptosis by survivin in terminally differentiated neutrophils. J Exp Med. 2004;199:1343–1354.
Sakamoto E, Hato F, Kato T, et al. Type I and type II interferons delay human neutrophil apoptosis via activation of STAT3 and up-regulation of cellular inhibitor of apoptosis 2. J Leukoc Biol. 2005;78:301–309.
Kato T, Sakamoto E, Kutsuna H, Kimura-Eto A, Hato F, Kitagawa S. Proteolytic conversion of STAT3α to STAT3γ in human neutrophils:role of granule-derived serine proteases. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:31076–31080.
Wang K, Scheel-Toellner D, Wong SH, et al. Inhibition of neutrophil apoptosis by type 1 IFN depends on cross-talk between phosphoinositol 3-kinase, protein kinase C-δ, and NF-κB signaling pathways. J Immunol. 2003;171:1035–1041.
Kilpatrick LE, Sun S, Korchak HM. Selective regulation by δ-PKC and PI 3-kinase in the assembly of the antiapoptotic TNFR-1 signaling complex in neutrophils. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2004;287:C633-C642.
Kobayashi S, Yamashita K, Takeoka T, et al. Calpain-mediated X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis degradation in neutrophil apoptosis and its impairment in chronic neutrophilic leukemia. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:33968–33977.
Nishiki S, Hato F, Kamata N, et al. Selective activation of STAT3 in human monocytes stimulated by G-CSF: implication in inhibition of LPS-induced TNF-α production. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2004;286:C1302-C1311.
Görgen I, Hartung T, Leist M, et al. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor treatment protects rodents against lipopolysaccharide-induced toxicity via suppression of systemic tumor necrosis factor-α. J Immunol. 1992;149:918–924.
Hartung T, Döcke WD, Gantner F, et al. Effect of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor treatment on ex vivo blood cytokine response in human volunteers. Blood. 1995;85:2482–2489.
Joshi SS, Lynch JC, Pavletic SZ, et al. Decreased immune functions of blood cells following mobilization with granulocyte colony-stimulating factor: association with donor characteristics. Blood. 2001;98:1963–1970.
Volpi I, Perruccio K, Tosti A, et al. Postgrafting administration of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor impairs functional immune recovery in recipients of human leukocyte antigen haplotype-mis-matched hematopoietic transplants. Blood. 2001;97:2514–2521.
Ringdén O, Remberger M, Runde V, et al. Peripheral blood stem cell transplantation from unrelated donors: a comparison with marrow transplantation. Blood. 1999;94:455–464.
Barton GM, Medzhitov R. Toll-like receptor signaling pathways. Science. 2003;300:1524–1525.
Yamamoto M, Sato S, Hemmi H, et al. Role of adaptor TRIF in the MyD88-independent Toll-like receptor signaling pathway. Science. 2003;301:640–643.
Demetri GD, Griffin JD. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor and its receptor. Blood. 1991;78:2791–2808.
Ohsaka A, Kitagawa S, Sakamoto S, et al. In vivo activation of human neutrophil functions by administration of recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in patients with malignant lymphoma. Blood. 1989;74:2743–2748.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Kato, T., Kitagawa, S. Regulation of Neutrophil Functions by Proinflammatory Cytokines. Int J Hematol 84, 205–209 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1532/IJH97.06141
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1532/IJH97.06141