Abstract
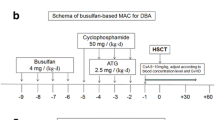
Shwachman-Diamond syndrome (SDS) is a rare congenital disorder featuring exocrine pancreatic insufficiency, growth retardation, and bone marrow dysfunction. Reports suggest that nearly 25% of all cases are complicated with leukemia. Although stem cell transplantation is the sole option for these patients, successful results are rarely obtained. Poor outcomes are often related to graft failure and cardiac and other organ toxicitics. We describe in this report successful unrelated donor bone marrow transplantation for a patient with SDS who progressed to acute myelogenous leukemia. The patient received attenuated intensified chemotherapy because of his intolerance to ordinary chemotherapy and went into remission. Sustained unrelated donor bone marrow engraftment was accomplished after treatment with a reduced amount of cyclophosphamide and antithymocyte globulin with 12 Gy of total body irradiation as a conditioning regimen. To the best of our knowledge, this report is the first to describe unrelated donor bone marrow transplantation with complete engraftment for an SDS patient with myelogenous leukemia.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shwachman H, Diamond LK, Oski FA, Khaw KT. The syndrome of pancreatic insufficiency and bone marrow dysfunction.J Pediatr.1964;65:645–663.
Boocock GRB, Morrison JA, Papovic M, et al. Mutations in SBDS are associated with Shwachman-Diamond syndrome.Nat Genet. 2003;33:97–10l.
Smith OP, Hann IM, Chessells JM, Reeves BR, Milla P. Haemato- logical abnormalities in Shwachman-Diamond syndrome.Br J Haemalol. 1996;94:279–284.
Mack DR, Forstner GG, Wilschanski M, Freedman MH, Durie PR. Shwachman syndrome: exocrine pancreatic dysfunction and variable phenotypic expression.Gastroenterology. 1996;111:1593–1602.
Woods WG, Roloff JS, Lukens JN, Krivit W. The occurrence of leukemia in patients with the Shwachman syndrome.J Pediatr. 1981;99:425–428.
Smith OP. Shwachman-Diamond syndrome.Semin Hematol. 2002; 39:95–102.
DrorY, Freedman MH. Shwachman-Diamond syndrome.Br J Haematol. 2002;118:701–713.
Smith OP, Chan M, Evans J, Veys P. Shwachman-Diamond syndrome and matched unrelated donor BMT.Bone Marrow Transplant. 1995;16:717–718.
Davies SM, Wagner JE, Defor T, et al. Unrelated donor bone marrow transplantation for children and adolescents with aplastic anemia or myelodysplasia.Br J Haematol. 1997;96:749–756.
Faber J, Lauener R,Wick F, et al. Shwachman-Diamond syndrome: early bone marrow transplantation in a high risk patient and new dues to pathogenesis.Eur J Pediatr. 1999;158:995–1000.
Cesaro S, Guariso G, Calore E, et al. Successful unrelated marrow transplantation for Shwachman-Diamond syndrome.Bone Marrow Transplant. 2001;27:97–99.
Crutzig U, Ritter J, Zimmermann M, Schellong G. Does cranial irradiation reduce the risk for bone marrow relapse in acute myel- ogenous leukemia? Unexpected results of the Childhood Acute Myelogenous Leukemia Study BFM-87.J Clin Oncol. 1993:11:279–286.
Seymour J, Escudier S. Acute leukemia complicating bone marrow hypoplasia in an adult with Shwachman’s syndrome.Leuk Lym- photna. 1993;12:131–135.
Cipolli M, D’Orazio C, Delmarco A, Marchesini C, Miano A, Mas-tella G. Shwachman’s syndrome: pathomorphosis and long-term outcome.J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1999;29:265–272.
Savilahti E, Rapola J. Frequent myocardial lesions in Shwachman’s syndrome.Acta Paediatr Scand. 1984;73:642–651.
Dokal I, Rule S, Chen F, Potter M, Goldman J. Adult onset of acute myeloid leukemia (M6) in patients with Shwachman-Diamond syndrome.Br J Haematol. 1997;99:171–173.
Dror Y, Freedman MH. Shwachman-Diamond syndrome is an inherited pre-leukemia bone marrow failure disorder with aberrant hematologic progenitors and faulty marrow microenviron- ment.Blood. 1999;94:3048–3054.
Dror Y, Freedman MH. Shwachman-Diamond syndrome marrow cells show abnormally increased apoptosis mediated through the Fas pathway.Blood. 2001;97:3011–3016.
Fleiz J, Rumelhart S, Goldman F, et al. Successful allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) for Shwachman- Diamond syndrome.Bone Marrow Transplant. 2002;29:75–79.
Nash RA, Pineiro LA, Storb R, et al. FK506 in combination with methotrexate for the prevention of graft-versus-host disease after marrow transplantation from matched unrelated donors.Blood. 1996;88:3634–3641.
Okcu F, Roberts W, Chan K. Bone marrow transplantation in Shwachman-Diamond syndrome: report of two cases and review of the literature.Bone Marrow Transplant. 1998;21:849–851.
Tsai PH. Sahdev I, Henry A, Lipton JM. Fatal cyclophosphamide- induced congestive heart failure in a 10-year-old boy with Shwachman-Diamond syndrome and severe bone marrow failure treated with allogeneic bone marrow transplantation.Am J Pediatr Hema- tol Oncol. 1990;12:472–476.
Barrios N, Kirkpatrick D, Regueira O.Wuttke B, McNeil J, Humbert J. Bone marrow transplantation in Shwachman Diamond syndrome.Br J Haematol. 1991;79:337–338.
Arseniev L, Diedrich H, Link H. Allogeneic bone marrow transplantation in a patient with Shwachman-Diamond syndrome.Ann Hematol. 1996;72:83–84.
Bunin N, Leahey A, Dunn S. Related donor liver transplant for veno-occlusive disease following T-depleted unrelated donor bone marrow transplantation.Transplantation. 1996;61:664–666.
Ritchie D, Angus P, Bhathal P, Grigg A. Liver failure complicating non-alcoholic steatohepatitis following allogeneic bone marrow transplantation for Shwachman-Diamond syndrome.Bone Marrow Transplant. 2000;29:931–933.
Hsu J, Vogelsang G, Jones R, Brodsky R. Bone marrow transplantation in Shwachman-Diamond syndrome.Bone Marrow Transplant. 2002;30:255–258.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Mitsui, T., Kawakami, T., Sendo, D. et al. Successful unrelated donor bone marrow transplantation for shwachman-diamond syndrome with leukemia. Int J Hematol 79, 189–192 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1532/IJH97.03103
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1532/IJH97.03103