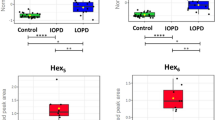
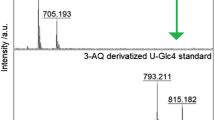
Abstract
Pompe disease, glycosomal storage disorder type II, is caused by a deficiency of lysosomal exo-α-1,4-glucosidase, which participates in glycogen degradation. Due to the wide variety of its clinical symptoms, this lysosomal storage disorder is difficult to diagnose. The “gold standard” diagnosis of Pompe disease is based on an enzyme activity analysis in leucocytes, dried blood spots or tissues, followed by confirmation through mutational analysis. Screening of many inborn metabolic diseases normally requires also the detection of a specific metabolite. In Pompe disease, high levels of a specific glucose tetrasaccharide, αGlc(1→6)αGlc(1→4)αGlc(1→4)Glc, accumulate in patients’ urine. Some medical laboratories continue to favour traditional 1-dimensional TLC for the analysis of urine oligosaccharides, however, this method has some limitations in its analytical specificity and sensitivity. More modern and robust spectral techniques, including mass spectrometry and NMR spectroscopy, possess many advantages and are increasingly used. Here, the different analytical methods applied in Pompe disease diagnosis are experimentally compared.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fu, L., Qiu, W., Yu, Y., Guo, Y., Zhao, P., Zhang, X., Liu, C., Li, F., Huang, H., Huang, M., & Chen, S. (2014). Clinical and molecular genetic study of infantile-onset Pompe disease in Chinese patients: Identification of 6 novel mutations. Gene, 535, 53–59. DOI: 10.1016/j.gene.2013.10.066.
Hallgren, P., Hansson, G., Henriksson, K. G., Häger, A., Lundblad, A., & Svensson, S. (1974). Increased excretion of a glucose-containing tetrasaccharide in the urine of a patient with glycogen storage disease type II (Pompe’s disease). European Journal of Clinical Investigation, 4, 429–433. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1974.tb02358.x.
Harvey, K., Manwearing, V., Lukovic, B., Prunty, H., Burke, D., & Heales, S. (2013). Glucose tetrasaccharide as a biomarker in Pompe disease and other glycogen storage diseases. Molecular Genetics and Metabolism, 108, S47–S47. DOI: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2012.11.107.
Chien, Y. H., Lee, N. C., Chen, C. A., Tsai, F. J., Tsai, W. H., Shieh, J. Y., Huang, H. J., Hsu, W. C., Tsai, T. H., & Hwu, W. L. (2015a). Long-term prognosis of patients with infantile-onset Pompe disease diagnosed by newborn screening and treated since birth. The Journal of Pediatrics, 166, 985–991.e2. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2014.10.068.
Chien, Y. H., van der Ploeg, A., Jones, S., Byrne, B., Vellodi, A., Leslie, N., Mengel, E., Shankar, S. P., Tanpaiboon, P., Stockton, D. W., Hennermann, J. B., Devecseri, Z., Kempf, J., Keutzer, J., & Kishnani, P. (2015b). Survival and developmental milestones among Pompe registry patients with classic infantile-onset Pompe disease with different timing of initiation of treatment with enzyme replacement therapy. Journal of Neuromuscular Diseases, 2, S61–S62. DOI: 10.3233/jnd-159053.
Kishnani, P. S., Steiner, R. D., Bali, D., Berger, K., Byrne, B. J., Case, L. E., Crowley, J. F., Downs, S., Howell, R. R., Kravitz, R. M., Mackey, J., Marsden, D., Martins, A. M., Millington, D. S., Nicolino, M., O’Grady, G., Patterson, M. C., Rapoport, D.M., Slonim, A., Spencer, C. T., Tifft, C. J., & Watson, M. S. (2006). Pompe disease diagnosis and management guideline. Genetics in Medicine, 8, 267–288. DOI: 10.1097/01.gim.0000218152.87434.f3.
Klein, A., Lebreton, A., Lemoine, J., Périni, J. M., Roussel, P., & Michalski, J. C. (1998). Identification of urinary oligosaccharides by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization timeof-flight mass spectrometry. Clinical Chemistry, 44, 2422–2428.
Kumlien, J., Gr¨onberg, G., Nilsson, B., M˚ansson, O., Zopf, D., & Lundblad, A. (1989). Structural and immunochemical analysis of three α-limit dextrin oligosaccharides. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 269, 678–689. DOI: 10.1016/ 0003-9861(89)90152-5.
Mechtler, T., Stary, S., Metz, T. F., De Jesús, V. R., Greber-Platzer, S., Pollak, A., Herkner, K. R., Streubel, B., & Kasper, D. C. (2012). Neonatal screening for lysosomal storage disorders: feasibility and incidence from a nationwide study in Austria. The Lancet, 379, 335–341. DOI: 10.1016/s0140-6736(11)61266-x.
Palmio, J., Auranen, M., Kiuru-Enari, S., L¨ofberg, M., Bodamer, O., & Udd, B. (2014). Screening for late-onset Pompe disease in Finland. Neuromuscular Disorders, 24, 982–985. DOI: 10.1016/j.nmd.2014.06.438.
Rozaklis, T., Ramsay, S. L., Whitfield, P. D., Ranieri, E., Hopwood, J. J., & Meikle, P. J. (2002). Determination of oligosaccharides in Pompe disease by electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Clinical Chemistry, 48, 131–139.
Van den Hout, J. M. P., Kamphoven, J. H. J., Winkel, L. P. F., Arts, W. F. M., De Klerk, J. B. C., Loonen, M. C. B., Vulto, A. G., Cromme-Dijkhuis, A., Weisglas-Kuperus, N., Hop, W., Van Hirtum, H., Van Diggelen, O. P., Boer, M., Kroos, M. A., Van Doorn, P. A., Van der Voort, E., Sibbles, B., Van Corven, E. J. J. M., Brakenhoff, J. P. J., Van Hove, J., Smeitink, J. A. M., de Jong, G., Reuser, A. J. J., & Van der Ploeg, A. T. (2004). Long-term intravenous treatment of Pompe disease with recombinant human α-glucosidase from milk. Pediatrics, 113, e448–e457. DOI: 10.1542/peds.113.5.e448.
Van der Ploeg, A. T., & Reuser, A. J. J. (2008). Pompe’s disease. The Lancet, 372, 1342–1353. DOI: 10.1016/s0140-6736(08)61555-x.
Young, S. P., Piraud, M., Goldstein, J. L., Zhang, H., Rehder, C., Laforet, P., Kishnani, P. S., Millington, D. S., Bashir, M. R., & Bali, D. S. (2012). Assessing disease severity in Pompe disease: The roles of a urinary glucose tetrasaccharide biomarker and imaging techniques. American Journal of Medical Genetics Part C: Seminars in Medical Genetics, 160C, 50–58. DOI: 10.1002/ajmg.c.31320.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pakanová, Z., Matulová, M., Behúlová, D. et al. Molecular diagnosis of Pompe disease using MALDI TOF/TOF and 1H NMR. Chem. Pap. 70, 265–271 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1515/chempap-2015-0218
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1515/chempap-2015-0218