Abstract
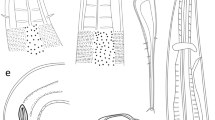
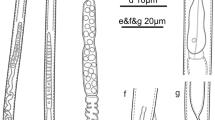
Three species belonging to the family Tylenchidae, Malenchus nanellus, M. undulatus and Tylenchus naranensis, are reported for the first time for Iran. These species are characterized based on morphological and morphometric data. The Iranian population of M. nanellus is characterized by its body length ranging from 410–485 μm, cuticle annuli 1.1–1.5 μm wide at mid-body and lateral field with two crenate lines, starting at the mid-region of procorpus and ending near 1/3 of tail length. The population of M. undulatus is characterized by its 458–526 μm body length, cuticle coarsely annulated, annuli 1.8–2.4 μm wide at mid-body, lateral field with crenate incisures, beginning at about half of the stylet length, ending at middle of tail, head narrower than adjacent body, median bulb well developed with prominent valve plates and functional males in population. Iranian population of T. naranensis, is characterized by having a 631–774 μm body length, lateral field with four lines, outer lines crenate, a stylet length ranging from 10–11 μm and a tail of 102–131 μm long. Molecular phylogenetic analyses based on partial 28S rDNA sequences of T. naranensis revealed its close affinity with the genus Filenchus. Other Tylenchidae genera, such as Aglenchus (including the newly sequenced isolate from Iran) and Coslenchus were sister taxa and formed a well-supported clade. Malenchus exiguus, a previously reported species from Iran and sequenced in the present study, formed a monophyletic clade with other species of Malenchus and Lelenchus leptosoma.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrássy I. 1954. Revision der Gattung Tylenchus Bastian, 1865 (Tylenchidae, Nematoda). Acta Zool. Hung. 1: 5–42.
Andrássy I. 1963. Freilebende Nematoden aus Angola.I. Einige moosbewohnende Nematoden. Publicações Culturais da Companhia de Diamantes de Angola (Lisboa) 66: 57–79.
Andrássy, I. 1968. Fauna Paraguayensis. 2. Nematoden aus den Galeriewäldern des Acaray-Flusses. Opusc. Zool. Budapest 8 (2): 167–315.
Andrássy I. 1981. The genera and species of the family Tylenchidae Orley, 1880 (Nematoda). The genus Malenchus Andrassy, 1968. Acta Zool. Acad. Sci. Hung. 27: 1–47.
Andrássy I. 2007. Free-living Nematodes of Hungary (Nematoda errantia), II. In: Csuzdi Cs. & Mahunka S. (eds), Pedozoologica Hungarica, No. 4. Hungarian Natural History Museum Budapest, 496 pp. ISBN: 9637093982
Ashrafi S., Mugniéry D., van Heesel E.Y.J., van Aelst A.C., Helder J. & Karssen G. 2012. Description of Meloidoderita salina sp. in. (Nematoda, Sphaeronematidae) from a microtidal salt marsh at Mont-Saint-Michel Bay in France. ZooKeys 249: 1–26. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3897/zookeys.249.4138
Atighi M.R., Pourjam E., Pereira T.J., Okhovaat S.M., Alizadah B.A., Ocampo M.M. & Baldawin J.G. 2012. Redescription of Filenchus annulatus (Siddiqui & Khan, 1983) Siddiqi, 1986 based on specimens from Iran with contributions to the molecular phylogeny of the Tylenchidae. Nematology 15 (2): 129–141. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1163/156854112X649819
Bastian H.C. 1865. Monograph on the Anguillulidae or free nematoides, marine, land, and freshwater; with descriptions of 100 new species. Trans. Linn. Soc. London 25: 73–184.
Carta L., Skantar A. & Handoo Z. 2010. Molecular rDNA phylogeny of Telotylenchidae Siddiqi, 1960 and evaluation of tail termini. J. Nematol. 42 (4): 359–369. PMID: 22736870
Ciobanul M., Geraertz E. & Popovici I. 2003. The Genus Tylenchus Bastian, 1865 in Romania (Nematoda: Tylenchidae). Nematol. Medit. 31 (1): 47–54.
Cobb N.A. 1913. New nematode genera found inhabiting fresh water and non-brackish soils. J. Wash. Acad. Sci. 3 (16): 432–444.
de Grisse A.T. 1969. Redescription et modification de quelques techniques utilisées dans l’étude des nematodes phytoparasitaires. Meded. Fac. Landbouwwet. Rijksuniv. Gent 34: 351–369.
de Man J.G. 1884. Die, frei in der reinen Erde und im süssen Wasser lebenden Nematoden der Niederländischen Fauna: eine systematisch-faunistische Monographie. Brill, Leiden, 206 pp.
De Man J.G. 1921. Nouvelles recherches sur les nematodes libres terrico de la Hollande. Capita Zoologica 1: 3–62.
Geraert E. 2008. The Tylenchidae of the World. Identification of the family Tylenchidae (Nematoda). Academia Press Belgium, 540 pp. ISBN: 9789038213552
Geraert E. & Raski D. 1986. Unusual Malenchus species (Nematoda: Tylenchidae). Nematologica 32 (1): 27–55. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1163/187529286X00020
Ghaderi R., Kashi L. & Karegar A. 2012. The nematodes of Iran, based on the published reports until 2011. Education and Agricultural Promotion Publisher, Tehran, Iran, 379 pp. ISBN: 9786006362229
Ghaemi R., Pourjam E., Atighi M.R., Pedram M. & Karssen G. 2012. First record of the genus Discotylenchus Siddiqi, 1980 (Nematoda: Tylenchidae) from Iran, with description of one new and data on two known species. Zootaxa 3493: 72–82.
Goodey J.B. 1962. Tylenchus (Cephalenchus) megacephalus n.sbg. n.sp. Nematologica 7 (4): 331–333. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1163/187529262X00639
Holterman M.H.M. 2008. Phylogenetic relationships within the phylum Nematoda as revealed by ribosomal DNA, and their biological implications. Ph.D Thesis Wageningen University, Wageningen, The Netherlands. Dissertation No. 4402, 208 pp. ISBN: 9789085048800
Huson D.H. & Scornavacca C. 2012. Dendroscope 3: An interactive tool for rooted phylogenetic trees and networks. Syst. Biol. 61(6): 1061–1067. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/sysbio/sys062
Khan E. 1964. Boleodorus mirus n.sp. (Tylenchidae: Boleodorinae N. Sub-family) from Kufri, Simla (H.P.), India, with a key to the species of the genus Boleodorus Thome, 1941. Zool. Anz. 173: 336–341.
Larget B. & Simon D.L. 1999. Markov chain Monte Carlo algorithms for the Bayesian analysis of phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 16 (6): 750–759.
Maqbool M., Zarina B. & Ghazala P. 1987. Description of Tylenchus naranensis n. sp. (Nematoda: Tylenchinae) [collected around the roots of Silene conoidea L.]. Pak. J. Nematol. 5 (1): 1–4.
Massey C.L. 1969. New species of Tylenchs associated with bark beetles in New Mexico and Colorado. Proc. Helminthol. Soc. Wash. 36 (1): 43–52.
Merny G. 1970. Les nématodes phytoparasites des rizières Inondées en Cote d’Ivoire I. — Les espèces observées. Cahiers ORSTOM, sér. Biol. 11: 3–43.
Meyl A.H. 1961. Die freilebenden Erd- und Süsswassernematoden (Fadenwtirmer). In: Die Tierwelt Mitteleuropas, Quelle & Meyer, 164 pp.
Mirbabaei Karani H., Kashi L., Ghaderi R. & Karegar A. 2015. Five species of Tylenchidae and Dolichodoridae (Nematoda: Tylenchoidea) from Iran. J. Agr. Sci. Techn. 17 (1): 227–240.
Nunn G.B. 1992. Nematode molecular evolution. Ph.D. dissertation, University of Nottingham, UK, 192 pp.
Nylander J.A.A. 2004. MrModeltest v2. Program distributed by the author, Evolutionary Biology Centre, Uppsala University.
Örley L. 1880. Monographie der Anguilluliden. Természettudományi. Füzetek, Budapest 4, 165 pp.
Palomares-Rius J.E., Subbotin S.A., Liebanas G., Landa B.B. & Castillo P. 2009. Eutylenchus excretorius Ebsary & Eveleigh, 1981 (Nematoda: Tylodorinae) from Spain with approaches to molecular phylogeny of related genera. Nematology 11 (3): 343–354. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1163/156854109X446944
Panahandeh Y., Pourjam E., Aliramaji F., Atighi M.R. & Pedram M. 2015. First record of three known species of the family Tylenchidae Örley, 1880 (Nematoda, Tylenchina) from Iran with new morphological and molecular data. J. Agr. Sci. Tech. 18 (3).
Panahandeh Y., Pourjam E. & Pedram M. 2014. Four new tylenchids (Tylenchina: Nematoda) for nematode fauna of Iran. J. Agr. Sci. Tech. 16 (2): 461–477.
Paramonov A.A. 1968. Principi ekologo-morfologicheskogo analiza organizacii Tylenchida Thorne, 1949 [Principles of ecological and morphological analysis of the classification of Tylenchida Thorne, 1949]. Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR, Ser. Biol. 6: 793–801.
Rahaman P.F., Ahmad I. & Jairajpuri M. 1994. One new and two known species of the family Tylenchidae. Ind. J. Nematol. 24 (1): 62–68.
Ronquist F. & Huelsenbeck J.P. 2003. MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics 19 (12): 1572–1574. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btg180
Siddiqi M.R. 1978. The unusual position of the phasmids in Coslenchus costatus (de Man, 1921) gen. in., comb. n., and other Tylenchidae (Nematoda: Tylenchida). Nematologica 24 (4): 449–455. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1163/187529278X00597
Siddiqi M.R. 1979. Seven new species in a new nematode subfamily Duosulciinae (Tylenchidae), with proposals for Duosulcius gen. in., Zanenchus gen. n. and Neomalenchus gen. n. Nematologica 25 (2): 215–236. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1163/187529279X00244
Siddiqi M.R. 2000. Tylenchida Parasites of Plants and Insects. 2nd ed. Wallingford, UK, CABI Publishing, 864 pp. ISBN: 0851992021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1079/9780851992020.0000
Silvestro D. & Michalak I. 2012. raxmlGUI: a graphical frontend for RAxML. Methods and Applications. Organisms Diversity & Evolution 12 (4): 335–337. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13127011-0056-0
Skarbilovich T.S. 1959. On the structure of systematics of nematodes order Tylenchida Thorne, 1949. Acta Parasitol. Polon. 7: 117–132.
Subbotin S.A., Sturhan D., Chizhov V.N., Vovlas N. & Baldwin J.G. 2006. Phylogenetic analysis of Tylenchida Thorne, 1949 as inferred from D2 and D3 expansion fragments of the 28S rRNA gene sequences. Nematology 8 (3): 455–474. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1163/156854106778493420
Tamura K., Stecher G., Peterson D., Filipski A. & Kumar S. 2013. MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 30 (12): 2725–2729. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/mstl97
Thorne G. 1949. On the classification of the Tylenchida, new order (Nematoda: Phasmida). Proc. Helminthol. Soc. Wash. 16 (2): 37–73.
Whitehead A.G. & Hemming J.R. 1965. A comparison of some quantitative methods for extracting small vermiform nematodes from soil. Ann. Appl. Biol. 55 (1): 25–38. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-7348.1965.tb07864.x
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Panahandeh, Y., Pourjam, E., Aliramaji, F. et al. Data on some members of the family Tylenchidae (Nematoda: Tylenchina) from Iran. Biologia 70, 1376–1387 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1515/biolog-2015-0160
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1515/biolog-2015-0160