Abstract
Background and Objectives
Diabetes and especially insulin resistance are associated with an increased risk of developing cognitive dysfunction, making anti-diabetic drugs an interesting therapeutic option for the treatment of neurodegenerative disorders. Dual amylin and calcitonin receptor agonists (DACRAs) elicit beneficial effects on glycemic control and insulin sensitivity. However, whether DACRAs affect cognition is unknown.
Design and Intervention
Zucker Diabetic Fatty rats were treated with either the DACRA KBP-336 (4.5 nmol/kg Q3D), the amylin analog AM1213 (25 nmol/kg QD), or vehicle for 18 weeks. Further, the efficacy of a late KBP-336 intervention was evaluated by including a group starting treatment on day 30. Glucose control and tolerance were evaluated throughout the study and spatial learning and memory were evaluated by Morris Water Maze after 17 weeks of treatment.
Results
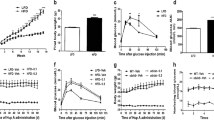
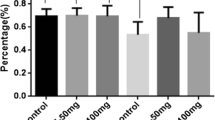
When evaluating spatial learning, rats receiving KBP-336 throughout the study performed significantly better than AM1213, vehicle, and late intervention KBP-336. Both KBP-336 and AM1213 treatments improved spatial memory compared to the vehicle. The overall performance in the cognitive tests was reflected in the treatment efficacy on glycemic control, where KBP-336 was superior to AM1213.
Conclusion
In summary, the DACRA KBP-336 ameliorates diabetes-induced spatial learning and memory impairment in diabetic rats. Further, KBP-336 improves long-term glycemic control superior to the amylin analog AM1213. Taken together, KBP-336 is, due to its anti-diabetic and insulin-sensitizing properties, a promising candidate for the treatment of cognitive impairments.

Graphical abstract. created with BioRender.com




Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data: The data supporting the findings of this manuscript are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- DACRA:
-
Dual amylin and calcitonin receptor agonist
- GLP-1:
-
Glucagon-like peptide 1
- KBP:
-
KeyBioscience Peptide
- OGTT:
-
Oral glucose tolerance test
- PPARγ:
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma
- SGLT2:
-
Sodium-glucose co-transporter 2
- ZDF:
-
Zucker diabetic Fatty
References
Kosiborod M, Gomes MB, Nicolucci A, Pocock S, Rathmann W, Shestakova M V., et al. Vascular complications in patients with type 2 diabetes: Prevalence and associated factors in 38 countries (the DISCOVER study program). Cardiovasc Diabetol [Internet]. 2018;17(1):1–13. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12933-018-0787-8
Katon W, Pedersen HS, Ribe AR, Fenger-Grøn M, Davydow D, Waldorff FB, et al. Impact of Depression and Diabetes on Risk of Dementia In a National Population-Based Cohort. JAMA Psychiatry [Internet]. 2015;72(6):612–9. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4666533/pdf/nihms739510.pdf
Santiago JA, Karthikeyan M, Lackey M, Villavicencio D, Potashkin JA. Diabetes: a tipping point in neurodegenerative diseases. Trends Mol Med [Internet]. 2023;1–16. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmed.2023.09.005
Razay G, Vreugdenhil A, Wilcock G. The metabolic syndrome and Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol. 2007;64(1):93–6.
Hishikawa N, Fukui Y, Sato K, Kono S, Yamashita T, Ohta Y, et al. Cognitive and affective functions in Alzheimer’s disease patients with metabolic syndrome. Eur J Neurol. 2016;23(2):339–45.
Valussi M, Antonelli M, Donelli D, Firenzuoli F. The link between Alzheimer disease and metabolic syndrome: A mutual relationship and long rigorous investigation. Perspect Med [Internet]. 2023;100451. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hermed.2021.100451
Neergaard JS, Dragsbæk K, Christiansen C, Nielsen HB, Brix S, Karsdal MA, et al. Metabolic syndrome, insulin resistance, and cognitive dysfunction: Does your metabolic profile affect your brain? Diabetes. 2017;66(7):1957–63.
Kullmann S, Heni M, Hallschmid M, Fritsche A, Preissl H, Häring HU. Brain insulin resistance at the crossroads of metabolic and cognitive disorders in humans. Physiol Rev. 2016;96(4):1169–209.
Kellar D, Craft S. Brain insulin resistance in Alzheimer’s disease and related disorders: mechanisms and therapeutic approaches. Lancet Neurol. 2020;19(9):758–66.
Koshatwar M, Acharya S, Prasad R, Lohakare T, Wanjari M, Taksande AB. Exploring the Potential of Antidiabetic Agents as Therapeutic Approaches for Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Diseases: A Comprehensive Review. Cureus. 2023;15(9):1–12.
Nowell J, Blunt E, Gupta D. Antidiabetic agents as a novel treatment for Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease. Ageing Res Rev [Internet]. 2023;101979. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2023.101979
Defo AK, Bakula V, Pisaturo A, Labos C, Wing SS, Daskalopoulou SS. Diabetes, antidiabetic medications and risk of dementia: A systematic umbrella review and meta-analysis. Diabetes, Obes Metab. 2023;(May):1–22.
Koenig AM, Mechanic-Hamilton D, Xie SX, Combs MF, Cappola AR, Xie L, et al. Effects of the Insulin Sensitizer Metformin in Alzheimer’s Disease: Pilot Data from a Randomized Placebo-Controlled Crossover Study. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord. 2017;31(2):107–13.
Shi Q, Liu S, Fonseca VA, Thethi TK, Shi L. Effect of metformin on neurodegenerative disease among elderly adult US veterans with type 2 diabetes mellitus. BMJ Open. 2019;9(7).
Siao WZ, Lin TK, Huang JY, Tsai CF, Jong GP. The association between sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors and incident dementia: A nationwide population-based longitudinal cohort study. Diabetes Vasc Dis Res. 2022;19(2):1–8.
Wu CY, Iskander C, Wang C, Xiong LY, Shah BR, Edwards JD, et al. Association of Sodium–Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors With Time to Dementia: A Population-Based Cohort Study. Diabetes Care. 2023;46(2):297–304.
Chou PS, Ho BL, Yang YH. Effects of pioglitazone on the incidence of dementia in patients with diabetes. J Diabetes Complications [Internet]. 2017;31(6):1053–7. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2017.01.006
Edison P, Femminella GD, Ritchie CW, Holmes C, Walker Z, Ridha BH, et al. Evaluation of liraglutide in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2021;17(S9):26–8.
Corrigan RR, Piontkivska H, Casadesus G. Amylin Pharmacology in Alzheimer’s Disease Pathogenesis and Treatment. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2021;20(10):1894–907.
Mietlicki-Baase EG. Amylin in Alzheimer’s disease: Pathological peptide or potential treatment? Neuropharmacology. 2018;176(1):139–48.
Fu W, Patel A, Kimura R, Soudy R, Jhamandas JH. Amylin Receptor: A Potential Therapeutic Target for Alzheimer’s Disease. Trends Mol Med [Internet]. 2017;23(8):709–20. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmed.2017.06.003
Sonne N, Karsdal MA, Henriksen K. Mono and dual agonists of the amylin, calcitonin, and CGRP receptors and their potential in metabolic diseases. Mol Metab [Internet]. 2020;preprint(November). Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmet.2020.101109
Larsen AT, Melander SA, Sonne N, Bredtoft E-M, Mays A-R, Karsdal MA, et al. Dual amylin and calcitonin receptor agonist treatment improves insulin sensitivity and increases muscle-specific glucose uptake independent of weight loss. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023;164(May):1–10.
Larsen AT, Mohamed KE, Sonne N, Bredtoft E, Andersen F, Karsdal MA, et al. Does receptor balance matter ?–Comparing the efficacies of the dual amylin and calcitonin receptor agonists cagrilintide and KBP-336 on metabolic parameters in preclinical models. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;156(113842):1–13.
Andreassen KV, Larsen AT, Sonne N, Mohamed KE, Karsdal MA, Henriksen K. KBP-066A, a long-acting dual amylin and calcitonin receptor agonist, induces weight loss and improves glycemic control in obese and diabetic rats. Mol Metab [Internet]. 2021;53(June):101282. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmet.2021.101282
Melander SA, Katri A, Karsdal MA, Henriksen K. Improved metabolic efficacy of a dual amylin and calcitonin receptor agonist when combined with semaglutide or empagliflozin. Eur J Pharmacol [Internet]. 2023;938(175397):1–11. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2022.175397
Larsen AT, Karsdal MA, Henriksen K. Treatment sequencing using the dual amylin and calcitonin receptor agonist KBP-336 and semaglutide results in durable weight loss. Eur J Pharmacol. 2023;954(March):175837.
Larsen AT, Melander SA, Sonne N, Bredtoft E, Al-Rubai M, Karsdal MA, et al. Dual amylin and calcitonin receptor agonist treatment improves insulin sensitivity and increases muscle-specific glucose uptake independent of weight loss. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023;164.
Adler BL, Yarchoan M, Hwang HM, Louneva N, Blair JA, Palm R, et al. Neuroprotective effects of the amylin analogue pramlintide on Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis and cognition. Neurobiol Aging [Internet]. 2014;35(4):793–801. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2013.10.076
Zhu H, Wang X, Wallack M, Li H, Carreras I, Dedeoglu A, et al. Intraperitoneal injection of the pancreatic peptide amylin potently reduces behavioral impairment and brain amyloid pathology in murine models of Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Psychiatry. 2015;20(2):232–9.
Patrick S, Corrigan R, Grizzanti J, Mey M, Blair J, Pallas M, et al. Neuroprotective effects of the amylin analog, pramlintide, on Alzheimer’s disease are associated with oxidative stress regulation mechanisms. J Alzheimer’s Dis. 2019;69(1):157–68.
Soudy R, Patel A, Fu W, Kaur K, MacTavish D, Westaway D, et al. Cyclic AC253, a novel amylin receptor antagonist, improves cognitive deficits in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement Transl Res Clin Interv [Internet]. 2017;3(1):44–56. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trci.2016.11.005
Jhamandas JH, Li Z, Westaway D, Yang J, Jassar S, MacTavish D. Actions of β-amyloid protein on human neurons are expressed through the amylin receptor. Am J Pathol. 2011;178(1):140–9.
Fu W, Ruangkittisakul A, MacTavish D, Shi JY, Ballanyi K, Jhamandas JH. Amyloid β (Aβ) peptide directly activates amylin-3 receptor subtype by triggering multiple intracellular signaling pathways. J Biol Chem [Internet]. 2012;287(22):18820–30. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.331181
Jhamandas JH, MacTavish D. β-Amyloid protein (Aβ) and human amylin regulation of apoptotic genes occurs through the amylin receptor. Apoptosis. 2012;17(1):37–47.
Chiu WC, Ho WC, Liao DL, Lin MH, Chiu CC, Su YP, et al. Progress of diabetic severity and risk of dementia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015;100(8):2899–908.
Reinke C, Buchmann N, Fink A, Tegeler C, Demuth I, Doblhammer G. Diabetes duration and the risk of dementia: A cohort study based on German health claims data. Age Ageing. 2022;51(1):1–9.
Larsen AT, Sonne N, Andreassen KV, Gehring K, Karsdal MA, Henriksen K. The dual amylin and calcitonin receptor agonist KBP-088 induces weight loss and improves insulin sensitivity superior to chronic amylin therapy. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2019;370:35–43.
Gydesen S, Andreassen KV, Hjuler ST, Christensen JM, Karsdal MA, Henriksen K. KBP-088, a novel DACRA with prolonged receptor activation, is superior to davalintide in terms of efficacy on body weight. Am J Physiol Metab. 2016;310(10):E821–7.
Larsen AT, Sonne N, Andreassen KV, Karsdal MA, Henriksen K. The Calcitonin Receptor Plays a Major Role in Glucose Regulation as a Function of Dual Amylin and Calcitonin Receptor Agonist Therapy. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2020;374(1):74–83.
Khan A, Petropoulos IN, Ponirakis G, Malik RA. Visual complications in diabetes mellitus: beyond retinopathy. Diabet Med. 2016;478–84.
Vilsbøll T, Brock B, Perrild H, Levin K, Lervang HH, Kølendorf K, et al. Liraglutide, a once-daily human GLP-1 analogue, improves pancreatic B-cell function and arginine-stimulated insulin secretion during hyperglycaemia in patients with Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabet Med. 2008;25(2):152–6.
Holst JJ. The physiology of glucagon-like peptide 1. Physiol Rev. 2007;87(4):1409–39.
Frias JP, Hsia S, Eyde S, Liu R, Ma X, Konig M, et al. Efficacy and safety of oral orforglipron in patients with type 2 diabetes: a multicentre, randomised, dose-response, phase 2 study. Lancet (London, England) [Internet]. 2023;6736(23):1–12. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/37369232
Becerril S, Frühbeck G. Cagrilintide plus semaglutide for obesity management. Lancet. 2021;397(10286):1687–9.
Monney M, Jornayvaz FR, Gariani K. GLP-1 receptor agonists effect on cognitive function in patients with and without type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Metab [Internet]. 2023;49(5):101470. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabet.2023.101470
Chen X, Chen S, Li Z, Zhu R, Jia Z, Ban J, et al. Effect of semaglutide and empagliflozin on cognitive function and hippocampal phosphoproteomic in obese mice. Front Pharmacol. 2023;14(March):1–18.
Chen X, Ma L, Gan K, Pan X, Chen S. Phosphorylated proteomics-based analysis of the effects of semaglutide on hippocampi of high-fat diet-induced-obese mice. Diabetol Metab Syndr [Internet]. 2023;15(1):1–15. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13098-023-01023-y
Guo X, Lei M, Zhao J, Wu M, Ren Z, Yang X, et al. Tirzepatide ameliorates spatial learning and memory impairment through modulation of aberrant insulin resistance and inflammation response in diabetic rats. Front Pharmacol. 2023;14(August):1–14.
Gabery S, Salinas CG, Paulsen SJ, Ahnfelt-Rønne J, Alanentalo T, Baquero AF, et al. Semaglutide lowers body weight in rodents via distributed neural pathways. JCI Insight. 2020;5(6):1–18.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Christina Hansen and Majbrith Sprankel for their technical assistance.
Funding
Funding: We acknowledge the Innovation Fund Denmark for the funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Authors’ contributions: ATL designed the study, performed the experiments, analyzed and interpreted the data, and wrote the manuscript. KEM performed some experiments, assisted with data analysis and interpretation, and manuscript preparation. EAP assisted with some experiments and data analysis. KH and MAK assisted with data analysis and manuscript preparation. All authors have read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval: All animal procedures were performed in accordance with guidelines from the Animal Welfare Division of the Danish Ministry of Justice under the institutional licenses issued to Nordic Bioscience (2021–15–0201–00886) and were carried out in accordance with the ARRIVE guidelines.
Conflicts of interests: MAK and KH own stock in Nordic Bioscience A/S. All authors are employed by Nordic Bioscience A/S.
Additional material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Larsen, A.T., Mohamed, K.E., Petersen, E.A. et al. The Insulin Sensitizer KBP-336 Prevents Diabetes-Induced Cognitive decline in ZDF Rats. J Prev Alzheimers Dis (2024). https://doi.org/10.14283/jpad.2024.74
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.14283/jpad.2024.74