Abstract
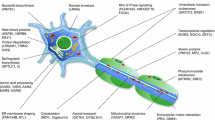
Hereditary sensory neuropathies (HSN), also known as hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathies (HSAN), are a clinically and genetically heterogeneous group of disorders. They are caused by neuronal atrophy and degeneration, predominantly affecting peripheral sensory and autonomic neurons. Both congenital and juvenile to adulthood onset is possible. Currently, the classification of the HSN depends on the mode of inheritance, age at onset, and clinical presentation. Hallmark features are progressive sensory loss, chronic skin ulcers, and other skin abnormalities. Spontaneous fractures and neuropathic arthropathy are frequent complications and often necessitate amputations. Autonomic features vary between different subgroups. Distal muscle weakness and wasting may be present and is sometimes so prominent that it becomes difficult to distinguish HSN from Charcot-Marie-Tooth syndrome. Recent major advances in molecular genetics have led to the identification of seven gene loci and six-disease causing genes for autosomal-dominant and autosomal-recessive HSN. These genes have been shown to play roles in lipid metabolism and the regulation of intracellular vesicular transport, but also a presumptive transcriptional regulator, a nerve growth factor receptor, and a nerve growth factor have been described among the causative genes in HSN. Nevertheless, it remains unclear how mutations in the known genes lead to the phenotype of HSN. In this review, we summarize the recent progress of the molecular genetics of the HSN and the implicated genes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anand P. (2004) Neurotrophic factors and their receptors in human sensory neuropathies. Prog. Brain Res. 146, 477–492.
Anderson S. L., Coli, R., Daly I. W., et al. (2001) Familial dysautonomia is caused by mutations of the IKAP gene. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 68, 753–758.
Anderson S. L., Qiu J., and Rubin, B. Y. (2003a) EGCG corrects aberrant splicing of IKAP mRNA in cells from patients with familial dysautonomia. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 310, 627–633.
Anderson S. L., Qiu J., and Rubin B. Y. (2003b) Tocotrienols induce IKBKAP expression: a possible therapy for familial dysautonomia. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 306, 303–309.
Auer-Grumbach M., De Jonghe P., Verhoeven K., et al. (2003) Autosomal dominant inherited neuropathies with prominent sensory loss and mutilations: a review. Arch. Neurol. 60, 329–334.
Auer-Grumbach M., De Jonghe P., Wagner K., Verhoeven K., Hartung H. P., and Timmerman V. (2000) Phenotype-genotype correlations in a CMT2B family with refined 3q13-q22 locus. Neurology 55, 1552–1557.
Axelrod F. B. (2004) Familial dysautonomia. Muscle Nerve 29, 352–363.
Axelrod F. B. and Hilz M. J. (2003) Inherited autonomic neuropathies. Semin. Neurol. 23, 381–390.
Axelrod F. B., Goldberg J. D., Ye X. Y., and Maayan C. (2002) Survival in familial dysautonomia: Impact of early intervention. J. Pediatr. 141, 518–523.
Bejaoui K., Uchida Y., Yasuda S., et al. (2002) Hereditary senory neuropathy type 1 mutations confer dominant negative effects on serine palmitoyltransferase, critical for sphingolipid synthesis. J. Clin. Invest. 110, 1301–1308.
Bejaoui K., Wu C., Scheffler M. D., et al. (2001) SPTLC1 is mutated in hereditary sensory neuropathy, type 1. Nat. Genet. 27, 261, 262.
Blumenfeld A., Slaugenhaupt S. A., Axelrod F. B., et al. (1993) Localization of the gene for familial dysautonomia on chromosome 9 and definition of DNA markers for genetic diagnosis. Nat. Genet. 4, 160–164.
Bonkowsky J. L., Johnson J., Carey J. C., Smith A. G., and Swoboda K. J. (2003) An infant with primary tooth loss and palmar hyperkeratosis: a novel mutation in the NTRK1 gene causing congenital insensitivity to pain with anhidrosis. Pediatrics 112, e237-e241.
Bureau Y. (1955) Acropathies pseudosyringomyeliques des membres inferieures. Sem. Hôp. (Paris), 3, 1419–1429.
Coen K., Pareyson D., Auer-Grumbach M., et al. (2006) Novel mutations in the HSN2 gene causing hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy type II. Neurology, in press.
Dawkins J. L., Brahmbhatt S., Auer-Grumbach M., et al. (2002) Exclusion of serine palmitoyltransferase long chain base subunit 2 (SPTLC2) as a common cause for hereditary sensory neuropathy. Neuromuscul. Disord. 12, 656–658.
Dawkins J. L., Hulme D. J., Brahmbhatt S. B., Auer-Grumbach M., and Nicholson G. A. (2001) Mutations in SPTLC1, encoding serine palmitoyltransferase, long chain base subunit-1, cause hereditary sensory neuropathy type 1. Nat. Genet. 27, 309–312.
Dedov V. N., Dedova I. V., Merrill A. H., Jr., and Nicholson G. A. (2004) Activity of partially inhibited serine palmitoyltransferase is sufficient for normal spingoliped metabolism and viability of HSN1 patient cells. Biochem. Biophys. Acta 1688, 168–175.
De Jonghe P., Timmerman V., FitzPatrick D., Spoelders P., Martin J. J., and Van Broeckhoven C. (1997) Mutilating neuropathic ulcerations in a chromosome 3q13-q22 linked Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 2B family. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 62, 570–573.
Dong J., Edelmann L., Bajwa A. M., Kornreich R., and Desnick R. J. (2002) Familial dysautonomia: detection of the IKBKAP IVS20(+6T→C) and R696P mutations and frequencies among Ashkenazi Jews. Am. J. Med. Genet. 110, 253–257.
Dubourg O., Barhoumi C., Azzedine H., et al. (2000) Phenotypic and genetic study of a family with hereditary sensory neuropathy and prominent weakness. Muscle Nerve 23, 1508–1514.
Dyck P. J. (1993) Neuronal atrophy and degeneration predominatly affecting peripheral sensory and autonomic neurons, in Peripheral Neuropathy, 3rd ed., Dyck P. J., Thomas, P. K., Griffin J. W., Low P. A., and Poduslo J. F., ed., W.B. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp. 1065–1093.
Echard A., Jollivet F., Martinez O., et al. (1998) Interaction of a Golgi-associated kinesin-like protein with Rab6. Science 279, 580–585.
Einarsdottir E., Carlsson A., Minde J., et al. (2004) A mutation in the nerve growth factor beta gene (NGFB) causes loss of pain perception. Hum. Mol. Genet. 13, 799–805.
Elliott J. L., Kwon J. M., Goodfellow P. J., and Yee W. C. (1997) Hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy IIB: clinical and electrodiagnostic characteristics. Neurology 48, 23–28.
Gable K., Han G., Monaghan E., et al. (2002) Mutations in the yeast LCB1 and LCB2 genes, including those corresponding to the hereditary sensory neuropathy type I mutations, dominantly inactivate serine palmitoyltransferase. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 10,194–10,200.
Geraldes R., de Carvalho M., Santos-Bento M., and Nicholson G. (2004) Hereditary sensory neuropathy type 1 in a Portuguese family-electrodiagnostic and autonomic nervous system studies. J. Neurol. Sci. 227, 35–38.
Greco A., Villa R., and Pierotti M. A. (1996) Genomic organization of the human NTRK1 gene. Oncogene 13, 2463–2466.
Hanada K. (2003) Serine palmitoyltransferase, a key enzyme of sphingolipid metabolism. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1632, 16–30.
Hawkes N. A., Otero G., Winkler G. S. et al. (2002) Purification and characterization of the human elongator complex. J. Biol. Chem 277, 3047–3052.
Holmberg C., Katz S., Lerdrup M., et al. (2002) A novel specific role for I kappa B kinase complex-associated protein in cytosolic stress signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 31,918–31,928.
Houlden H., Blake J., and Reilly M. M. (2004a Hereditary sensory neuropathies. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 17, 569–577.
Houlden H., King R. H., Hashemi-Nejad A., et al. (2001) A novel TRKA (NTRK1) mutation associated with hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy type V. Ann. Neurol. 49, 521–525.
Houlden H., King R. H., Muddle J. R., et al. (2004b) A novel RAB7 mutation associated with ulceromutilating neuropathy. Ann. Neurol. 56, 586–590.
Indo Y., Tsuruta M., Hayashida Y., et al. (1996) Mutations in the TRKA/NGF receptor gene in patients with congenital insensitivity to pain with anhidrosis. Nat. Genet. 13, 485–488.
Klein C. J., Wu Y., Kruckeberg K. E., et al. (2005) SPTLC1 and RAB7 mutation analysis in dominantly inherited and idiopathic sensory neuropathies. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 76, 1022–1024.
Kok C., Kennerson M. L., Spring P. J., Ing A. J., Pollard J. D., and Nicholson G. A. (2003) Alocus for hereditary sensory neuropathy with cough and gastroesophageal reflux on chromosome 3p22-p24. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 73, 632–637.
Kwon J. M., Elliott J. L., Yee W. C., et al. (1995) Assignment of a second Charcot-Marie-Tooth type II locus to chromosome 3q. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 57, 853–858.
Lafreniere R. G., MacDonald M. L., Dube M. P., et al. (2004) Identification of a novel gene (HSN2) causing hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy type II through the Study of Canadian Genetic Isolates. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 74, 1064–1073.
Lee M. J., Stephenson D. A., Groves M. J., et al. (2003) Hereditary sensory neuropathy is caused by a mutation in the delta subunit of the cytosolic chaperonin-containing t-complex peptide-1 (Cct4) gene. Hum. Mol. Genet. 12, 1917–1925.
Levi-Montalcini R. (1987) The nerve growth factor: thirty-five years later. Biosci. Rep. 7, 681–699.
Leyne M. (2003) Identification of the first non-Jewish mutation in familial dysautonomia. Am. J. Med. Genet. 118A, 305–308.
Matsuo M., Kurokawa T., Goya N., and Ohta M. (1981) Congenital insensitivity to pain with anhidrosis in a 2-month-old boy. Neurology 31, 1190–1192.
McCampbell A., Truong D., Broom D. C., et al. (2005) Mutant SPTLC1 dominantly inhibits serine palmitoyltransferase activity in vivo and confers an agedependent neuropathy. Hum. Mol. Genet. 14(22), 3507–3521.
Minde J., Toolanen G., Andersson T., et al. (2004) Familial insensitivity to pain (HSAN V) and a mutation in the NGFB gene. A neurophysiological and pathological study. Muscle Nerve 30, 752–760.
Nicholson G. A., Dawkins J. L., Blair I. P., Auer-Grumbach M., Brahmbhatt S. B., and Hulme D. J. (2001) Hereditary sensory neuropathy type I: haplotype analysis shows founders in southern England and Europe. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 69, 655–659.
Nielsen E., Severin F., Backer J. M., Hyman A. A., and Zerial M. (1999) Rab5 regulates motility of early endosomes on microtubules. Nat. Cell Biol. 1, 376–382.
Otero G., Fellows J., Li Y., et al. (1999) Elongator, a multisubunit component of a novel RNA polymerase II holoenzy me for transcriptional elongation. Mol. Cell 3, 109–118.
Pinsky L. and DiGeorge A. M. (1966) Congenital familial sensory neuropathy with anhidrosis. J. Pediatr. 68, 1–13.
Rafel E., Alberca R., Bautista J., Navarrete M., and Lazo J. (1980) Congenital insensitivity to pain with anhidrosis. Muscle Nerve 3, 216–220.
Riley C. D., Day R. L., Greeley D. M., Langford W. S. (1949) Central autonomic dysfunction with defective lacrimation. I. Report of five cases. Pediatrics 3, 468–478.
Riviere J. B., Verlaan D. J., Shekarabi M., et al. (2004) A mutation in the HSN2 gene causes sensory neuropathy type II in a Lebanese family. Ann. Neurol. 56, 572–575.
Roddier K., Thomas T., Marleau G., et al. (2005) Two mutations in the HSN2 gene explain the high prevalence of HSAN2 in French Canadians. Neurology 64, 1762–1767.
Seeman P., Mazanec R., Boehm J., et al. (2005) Inherited ulcero-mutilating neuropathies CMT2B and HSN1 in Czech families. In PNS-Meeting, p. 235.
Shatzky S., Moses S., Levy J., et al. (2000) Congenital insensitivity to pain with anhidrosis (CIPA) in Israeli-Bedouins: genetic heterogeneity, novel mutations in the TRKA/NGF receptor gene, clinical findings, and results of nerve conduction studies. Am. J. Med. Genet. 92, 353–360.
Slaugenhaupt S. A., Blumenfeld A., Gill S. P., et al. (2001) Tissue-specific expression of a splicing mutation in the IKBKAP gene causes familial dysautonomia. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 68, 598–605.
Smeyne R. J., Klein R., Schnapp A., et al. (1994) Severe sensory and sympathetic neuropathies in mice carying a disrupted Trk/NGF receptor gene. Nature 368, 246–249.
Spring P. J. (2002) Autosomal Dominant Hereditary Sensory Neuropathy with Gastro-Oesophageal Reflux and Cough: Clinical Features of a Family. S64.
Sugarman E. (2002) Familial dysautonomia mutation frequency: clinical testing of greater than 2700 specimens confirms high frequency in Ashkenazi Jews. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 71(Suppl. 1), 387.
Thevenard A. (1942) L'Acropathie ulcero-mutilante familiale. Rev. Neurol. (Paris) 74, 193–212.
Vance J. M., Speer M. C., Stajich J. M., et al. (1996) Misclassification and linkage of hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy type 1 as Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, type 2B. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 59, 258–262.
Verhoeven K., Coen K., De Vriendt E., et al. (2004) SPTLC1 mutation in twin sisters with hereditary sensory neuropathy type I. Neurology 62, 1001–1002.
Verhoeven K., De Jonghe P., Coen K., et al. (2003) Mutations in the small GTP-ase late endosomal protein RAB7 cause Charcot-Marie-Tooth type 2B neuropathy. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 72, 722–727.
Weier H. U., Rhein A. P., Shadravan F., Collins C., and Polikoff D. (1995) Rapid physical mapping of the human trk protooncogene (NTRK1) to human chromosome 1q21-q22 by P1 clone selection, fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH), and computer-assisted microscopy. Genomics 26, 390–393.
Whitaker J. N., Falchuck Z. M., Engel W. K., Blaese R. M. and Strober W. (1974) Hereditary sensory neuropathy. Association with increased synthesis of immunoglobulin A. Arch. Neurol. 30, 359–371.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Auer-Grumbach, M., Mauko, B., Auer-Grumbach, P. et al. Molecular genetics of hereditary sensory neuropathies. Neuromol Med 8, 147–158 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1385/NMM:8:1-2:147
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/NMM:8:1-2:147