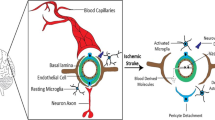
Abstract
Chemokines constitute a large family of structurally related small cytokines originally identified as the factors regulating the migration of leukocytes in inflammatory and immune responses. Enhanced production and release of chemokines are observed also in the central nervous system under diverse neuronal stresses including ischemia, axonal injury, and neurotoxic substances such as an Aβ-peptide. There is growing evidence that brain chemokines play crucial roles in the neuro-glio-vascular interaction underlying the pathology of various brain disorders. Here the evidence of the involvement of chemokines in ischemic brain injury is reviewed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andjelkovic A. V., Spencer D. D., and Pachter J. S. (1999) Visualization of chemokine binding sites on human brain microvessels. J. Cell Biol. 145, 403–412.
Arai H., Tsou C. -L., and Charo I. F. (1997) Chemotaxis in a lymphocyte cell line transfected with C-C chemokine receptor 2B: evidence that directed migration is mediated by βγ dimmers released by activation of Gαi-coupled receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94, 14,495–14,499.
Asensio V. C. and Campbell I. L. (1999) Chemokines in the CNS: plurifunctional mediators in diverse states. Trends Neurosci. 22, 504–512.
Ashida N., Arai H., Yamasaki M., and Kita T. (2001) Distinct signaling pathways for MCP-1-dependent integrin activation and chemotaxis. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 16,555–16,560.
Ayata C. and Ropper A. H. (2002) Ischaemic brain oedema. J. Clin. Neurosci. 9, 113–124.
Bazan J. F., Bacon K. B., Hardiman G., et al. (1997) A new class of membrane-bound chemokine with a CX3C motif. Nature 385, 640–644.
Beech J. S., Reckless J., Mosedale D. E., Grainger D. J., Williams S. C. R., and Menon D. K. (2001) Neuroprotection in ischemia-reperfusion injury: an anti-inflammatory approach using a novel broad-spectrum chemokine inhibitor. J. Cereb. Blood flow Metab. 21, 683–689.
Chapman G. A., Moores K., Harrison D., Campbell C. A., Stewart B. R., and Strijbos P. J. (2000) Fractalkine cleavage from neuronal membranes represents an acute event in the inflammatory response to excitotoxic brain damage. J. Neurosci. 20, RC87.
Chen Y., Hallenbeck J. M., Ruetzler C., et al. (2003) Overexpression of monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 in the brain exacerbates ischemic brain injury and is associated with recruitment of inflammatory cells. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 23, 748–755.
Dzenko K. A., Andjelkovic A. V., Kuziel W. A., and Pachter J. S. (2001) The chemokine receptor CCR2 mediates the binding and internalization of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 along brain microvessels. J. Neurosci. 21, 9214–9223.
Etienne-Mannevilla S. and Hall A. (2002) Rho GTPases on cell biology. Nature 420, 629–635.
Gregersen R., Lambertsen K., and Finsen B. (2000) Microglia and macrophages are the major source of tumor necrosis factor in permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion in mice. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 20, 53–65.
Harrison J. K., Jiang Y., Chen S., et al. (1998) Role for neuronally derived fractalkine in mediating interactions between neurons and CX3 CR1-expressing microglia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 10,896–10,901.
Honda S., Sasaki Y., Ohsawa K., et al. (2001) Extracellular ATP or ADP induce chemotaxis of cultured microglia though Gi/o—coupled P2Y receptors. J. Neurosci. 21, 1975–1982.
Hughes P. M., Allegrini P. R., Rudin M., Perry V. H., Mir A. K., and Wiessner C. (2002) Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 deficiency is protective in a murine stroke model. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 22, 308–317.
Katayama T., Minami M., Nakamura M., et al. (2002) Excitotoxic injury induces production of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in rat corticostriatal slice cultures. Neurosci. Lett. 328, 277–280.
Kim J. S., Gautam S. C., Chopp M., et al. (1995) Expression of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 and macrophage inflammatory protein-1 after focal cerebral ischemia in the rat. J. Neuroimmunol. 56, 127–134.
Liu T., Young P. R., McDonnell P. C., White R. F., Barone F. C., and Feuerstein G. Z. (1993) Cytokine-induced neutrophil chemoattractant mRNA expressed in cerebral ischemia. Neurosci. Lett. 164, 125–128.
Love S. (1999) Oxidative stress in brain ischemia. Brain Pathol. 9, 119–131.
Mabuchi T., Kitagawa K., Ohtsuki T., et al. (2000) Contribution of microglia/macrophages to expansion of infarction and response of oligodendrocytes after focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Stroke 31, 1735–1743.
Matsumoto T., Ikeda K., Mukaida N., et al. (1997) Prevention of cerebral edema and infarct in cerebral reperfusion injury by an antibody to interleukin-8. Lab. Invest. 77, 119–125.
Middleton J., Patterson A. M., Gardner L., Schmutz C., and Ashton B. A. (2002) Leukocytes extravasation: chemokine transport and presentation by the endothelium. Blood 100, 3853–3860.
Minami M. and Satoh M. (2003) Chemokine and their receptors in the brain: pathophysiological roles in ischemic brain injury. Life Sci. 74, 321–327.
Murphy P. M., Baggiolini M., Charo I. F., et al. (2000) International union of pharmacology. XXII. Nomenclature for chemokine receptors. Pharmacol. Rev. 52, 145–176.
Namura S., Iihara K., Takami S., et al. (2001) Intravenous administration of MEK inhibitor U0126 affords brain protection against forebrain ischemia and focal cerebral ischemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 11569–11574.
Nishiyori A., Minami M., Ohtani Y., et al. (1998) Localization of fractalkine and CX3CR1 mRNAs in rat brain: does fractalkine play a role in signaling from neuron to microglia? FEBS Lett. 429, 167–172.
Rollins B. J. (1997) Chemokines. Blood 90, 909–928.
Soriano S. G., Amaravadi L. S., Wang Y. F., et al. (2002) Mice deficient in fractalkine are less susceptible to cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. J. Neuroimmunol. 125, 59–65.
Stamatovic S. M., Keep R. F., Kunkel S. L., and Andjelkovic A. V. (2003) Potential role of MCP-1 in endothelial cell tight junction opening: signaling via Rho and Rho kinase. J. Cell Sci. 116, 4615–4628.
Takai Y., Sasaki T., and Matozaki T. (2001) Small GTP-binding proteins. Physiol. Rev. 81, 135–208.
Takami S., Minami M., Katayama T., Nagata I., Namura S., and Satoh M. (2002) TAK-779, a non-peptide CC chemokine receptor antagonist, protects the brain against focal cerebral ischemia in mice. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 22, 780–784.
Takami S., Minami M., Nagata I., Namura S., and Satoh M. (2001) Chemokine receptor antagonist peptide, viral MIP-II, protects the brain against focal cerebral ischemia in mice. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 21, 1430–1435.
Takami S., Nishikawa H., Minami M., et al. (1997) Induction of macrophage inflammatory protein MIP-1alpha mRNA on glial cells after focal cerebralischemia in the rat. Neurosci. Lett. 227, 173–176.
Tarozzo G., Campanella M., Ghiani M., Bulfone A., and Beltramo M. (2002) Expression of fractalkine and its receptor, CX3CR1, in response to ischaemia-reperfusion brain injury in the rat. Eur. J. Neurosci. 15, 1663–1668.
Wang Z. Q., Wu D. C., Huang F. P., and Yang G. Y. (2004) Inhibition of MEK/ERK 1/2 pathway reduces proinflammatory cytokine interleukin-1 expression in focal cerebral ischemia. Brain Res. 996, 55–66.
Wang X., Yue T. -L., Barone F. C., and Feuerstein G. Z. (1995) Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 messenger RNA expression in rat ischemic cortex. Stroke 26, 661–666.
Worthylake R. A. and Burridge K. (2001) Leukocyte transendothelial migration: orchestrating the underlying molecular machinery. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 13, 569–577.
Yamagami S., Tamura M., Hayashi M., et al. (1999) Differential production of MCP-1 and cytokine-induced neutrophil chemoattractant in the ischemic brain after transient focal ischemia in rats. J. Leukoc. Biol. 65, 744–749.
Yamasaki Y., Matsuo Y., Zagorski J., et al. (1997) New possibility of blocking cytokine-induced neutrophil chemoattractant on transient ischemic brain damage in rats. Brain Res. 759, 103–111.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Minami, M., Satoh, M. Role of chemokines in ischemic neuronal stress. Neuromol Med 7, 149–155 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1385/NMM:7:1-2:149
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/NMM:7:1-2:149