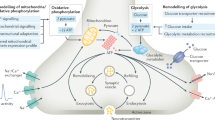
Abstract
As in other cells, neurons use adenosine triphosphate (ATP) as an energy source to drive biochemical processes involved in various cell functions, and produce reactive oxygen species (ROS) as “by products” of oxidative phosphorylation. However, the electrical excitability and structural and synaptic complexity of neurons present unusual demands upon cellular systems that produce or respond to ATP and ROS. Mitochondria in axons and presynaptic terminals provide sources of ATP to drive the ion pumps that are concentrated in these structures to rapidly restore ion gradients following depolarization and neurotransmitter release. Mitochondria may also play important roles in the regulation of synaptic function because of their ability to regulate calcium levels and ROS production. ROS generated in response to synaptic activity are now known to contribute to the regulation of long-term structural and functional changes in neurons, and the best-known example is the nitric oxide radical. The high-energy demands of synapses, together with their high levels of ROS production, place them at risk during conditions of increased stress, which occur in aging, neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases, and after acute traumatic and ischemic insults. Energy depletion and/or increased oxidative damage to various synaptic proteins can result in a local dysregulation of calcium homeostasis and synaptic degeneration. Accordingly, recent studies have shown that dietary and pharmacological manipulations that improve energy efficiency and reduce oxyradical production can prevent synaptic degeneration and neuronal death in experimental models of neurodegenerative disorders. A better understanding of the molecular control of subcellular energy production and utilization, and of the functional relationships between energy metabolism, ion homeostasis, and cytoskeletal and vesicular dynamics, will provide novel insight into mechanisms of neuronal plasticity and disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abeliovich A., Schmitz Y., Farinas I., Choi-Lundberg D., Ho W. H., Castillo P. E., et al. (2000) Mice lacking alpha-synuclein display functional deficits in the nigrostriatal dopamine system. Neuron 25, 239–252.
Auerbach J. M. and Segal M. (1997) Peroxide modulation of slow onset potentiation in rat hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 17, 8695–8701.
Bajjalieh S. M. and Scheller R. H. (1995) The biochemistry of neurotransmitter secretion. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 1971–1974.
Blanc E. M., Kelly J. F., Mark R. J., Waeg G., and Mattson M. P. (1997) 4-Hydroxynonenal, an aldehydic product of lipid peroxidation, impairs signal transduction associated with muscarinic acetylcholine and metabotropic glutamate receptors: possible action on G alpha(q/11). J. Neurochem. 69, 570–580.
Bohme G. A., Bon C., Stutzmann J. M., Doble A., and Blanchard J. C. (1991) Possible involvement of nitric oxide in long-term potentiation. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 199, 379–381.
Bohme G. A., Bon C., Lemaire M., Reibaud M., Piot O., Stutzmann J. M., et al. (1993) Altered synaptic plasticity and memory formation in nitric oxide synthase inhibitor-treated rats. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90, 9191–9194.
Boitier E., Rea R., and Duchen M. R. (1999) Mitochondria exert a negative feedback on the propagation of intracellular Ca2+ waves in rat cortical astrocytes. J. Cell Biol. 145, 795–808.
Bootman M. D., Lipp P., and Berridge M. J. (2001) The organisation and functions of local Ca(2+) signals. J. Cell Sci. 114, 2213–2222.
Braun N., Schikorski T., and Zimmermann H. (1993) Cytoplasmic segregation and cytoskeletal organization in the electric catfish giant electromotoneuron with special reference to the axon hillock region. Neuroscience 52, 745–756.
Brodin L., Bakeeva L., and Shupliakov O. (1999) Presynaptic mitochondria and the temporal pattern of neurotransmitter release. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 354, 365–372.
Brorson J. R., Schumacker P. T., and Zhang H. (1999) Nitric oxide acutely inhibits neuronal energy production. The Committees on Neurobiology and Cell Physiology. J. Neurosci. 19, 147–158.
Bruce-Keller A. J., Umberger G., McFall R., and Mattson M. P. (1999) Food restriction reduces brain damage and improves behavioral outcome following excitotoxic and metabolic insults. Ann. Neurol. 45, 8–15.
Buckman J. F. and Reynolds I. J. (2001) Spontaneous changes in mitochondrial membrane potential in cultured neurons. J. Neurosci. 21, 5054–5065.
Carelli V., Ross-Cisneros F. N., and Sadun A. A. (1999) Optic nerve degeneration and mitochondrial dysfunction: genetic and acquired optic neuropathies. Neurochem. Int. 40, 573–584.
Cattaneo E., Rigamonti D., Goffredo D., Zuccato C., Squitieri F., and Sipione S. (2001) Loss of normal huntingtin function: new developments in Huntington’s disease research. Trends Neurosci. 24, 182–188.
Chapman P. F., Atkins C. M., Allen M. T., Haley J. E., and Steinmetz J. E. (1992) Inhibition of nitric oxide synthesis impairs two different forms of learning. Neuroreport 3, 567–570.
Cheng B. and Mattson M. P. (1992) Glucose deprivation elicits neurofibrillary tangle-like antigenic changes in hippocampal neurons: Prevention by NGF and bFGF. Exp. Neurol. 117, 114–123.
Cheng G., Yu Z., Zhou D., and Mattson M. P. (2002) Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase—Akt and p42/p44 mitogen-activated protein kinases mediate neurotrophic and excitoprotective actions of a secreted form of amyloid precursor protein. Exp. Neurol. 175, 407–414.
Chinopoulos C., Tretter L., Rozsa A., and Adam-Vizi V. (2000) Exacerbated responses to oxidative stress by an Na(+) load in isolated nerve terminals: the role of ATP depletion and rise of [Ca(2+)](i). J. Neurosci. 20, 2094–2103.
Chinopoulos C. and Adam-Vizi V. (2001) Mitochondria deficient in complex I activity are depolarized by hydrogen peroxide in nerve terminals: relevance to Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurochem. 76, 302–306.
Colton C. A., Fagni L., and Gilbert D. (1989) The action of hydrogen peroxide on paired pulse and long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 7, 3–8.
Cutler R. G., Pedersen W. A., Camandola S., Rothstein J. D., and Mattson M. P. (2002) Evidence that accumulation of ceramides and cholesterol esters mediates oxidative stress-induced death of motor neurons in ALS. Ann. Neurol. 52, 448–457.
Davey G. P., Peuchen S., and Clark J. B. (1998) Energy thresholds in brain mitochondria. Potential involvement in neurodegeneration. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 12,753–12,757.
Dedov V. N., Armati P. J., and Roufogalis B. D. (2000) Three-dimensional organisation of mitochondrial clusters in regenerating dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons from neonatal rats: evidence for mobile mitochondrial pools. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 5, 3–10.
Duan W. and Mattson M. P. (1999) Dietary restriction and 2-deoxyglucose administration improve behavioral outcome and reduce degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in models of Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurosci. Res. 57, 195–206.
Duan W., Rangnekar V., and Mattson M. P. (1999a) Par-4 production in synaptic compartments following apoptotic and excitotoxic insults: evidence for a pivotal role in mitochondrial dysfunction and neuronal degeneration. J. Neurochem. 72, 2312–2322.
Duan W., Zhang Z., Gash D. M., and Mattson M. P. (1999b) Participation of prostate apoptosis response-4 in degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in models of Parkinson’s disease. Ann. Neurol. 46, 587–597.
Farrell C. M., Mackey A. T., Klumpp L. M., and Gilbert S. P. (2002) The role of ATP hydrolysis for kinesin processivity. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 17,079–17,087.
Friel, D. D. (1999) Mitochondria as regulators of stimulus-evoked calcium signals in neurons. Cell Calcium 28, 307–316.
Gary, D. S. and Mattson, M. P. (2001) Integrin signaling via the PI3-kinase-Akt pathway increases neuronal resistance to glutamate-induced apoptosis. J. Neurochem. 76, 1485–1496.
Geibel S., Barth A., Amslinger S., Jung A. H., Burzik C., Clarke R. J., et al. (2000) P(3)-[2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-oxo]ethyl ATP for the rapid activation of the Na(+),K(+)-ATPase. Biophys. J. 79, 1346–1357.
Gioio A. E., Eyman M., Zhang H., Lavina Z. S., Giuditta A., and Kaplan B. B. (2001) Local synthesis of nuclear-encoded mitochondrial proteins in the presynaptic nerve terminal. J. Neurosci. Res. 64, 447–453.
Glazner G. W., Chan S. L., Lu C., and Mattson M. P. (2000) Caspase-mediated degradation of AMPA receptor subunits: a mechanism for preventing excitotoxic necrosis and ensuring apoptosis. J. Neurosci. 20, 3641–3649.
Gunawardena S. and Goldstein L. S. (2001) Disruption of axonal transport and neuronal viability by amyloid precursor protein mutations in Drosophila. Neuron 32, 389–401.
Guo Z. H. and Mattson M. P. (2000) Neurotrophic factors protect cortical synaptic terminals against amyloid and oxidative stress-induced impairment of glucose transport, glutamate transport and mitochondrial function. Cereb. Cortex 10, 50–57.
Guo Z. H., Ersoz A., Butterfield D. A., and Mattson M. P. (2000) Beneficial effects of dietary restriction on cerebral cortical synaptic terminals: preservation of glucose and glutamate transport and mitochondrial function after exposure to amyloid beta-peptide, iron, and 3-nitropropionic acid. J. Neurochem. 75, 314–320.
Guo Z. H. and Mattson M. P. (2000) In vivo 2-deoxyglucose administration preserves glucose and glutamate transport and mitochondrial function in cortical synaptic terminals after exposure to amyloid beta-peptide and iron: evidence for a stress response. Exp. Neurol. 166, 173–179.
Gurney M. E., Pu H., Chiu A. Y., Dal Canto M. C., Polchow C. Y., Alexander D. D., et al. (1994) Motor neuron degeneration in mice that express a human Cu,Zn superoxide dismutase mutation. Science 264, 1772–1775.
Gurney M. E., Cutting F. B., Zhai P., Doble A., Taylor C. P., Andrus P. K., et al. (1996) Benefit of vitamin E, riluzole, and gabapentin in a transgenic model of familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ann. Neurol. 39, 147–157.
Herrera A. A., Grinnell A. D., and Wolowske B. (1985) Ultrastructural correlates of naturally occurring differences in transmitter release efficacy in frog motor nerve terminals. J. Neurocytol. 14, 193–202.
Hollenbeck P. J. (1996) The pattern and mechanism of mitochondrial transport in axons. Front. Biosci. 1, d91-d102.
Ishida A., Furukawa K., Keller J. N., and Mattson M. P. (1997) Secreted form of beta amyloid precursor protein shifts the frequency dependency for induction of LTD, and enhances LTP in hippocampal slices. Neuroreport 8, 2133–2137.
Jankowsky J. L. and Patterson P. H. (1999) Cytokine and growth factor involvement in long-term potentiation. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 14, 273–286.
Jarvis S. E. and Zamponi G. W. (2001) Interactions between presynaptic Ca2+ channels, cytoplasmic messengers and proteins of the synaptic vesicle release complex. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 22, 519–525.
Jenner P. and Olanow C. W. (1998) Understanding cell death in Parkinson’s disease. Ann. Neurol. 44, S72-S84.
Kater S. B. and Mattson M. P. (1988) Calcium regulation of the neuronal growth cone. Trends Neurosci. 11, 315–321.
Keller J. N., Mark R. J., Bruce A. J., Blanc E., Rothstein J. D., Uchida K., et al. (1997) 4-Hydroxynonenal, an aldehydic product of membrane lipid peroxidation, impairs glutamate transport and mitochondrial function in synaptosomes. Neuroscience 80, 685–696.
Kim-Han J. S., Reichert S. A., Quick K. L., and Dugan L. L. (2001) BMCP1: a mitochondrial uncoupling protein in neurons which regulates mitochondrial function and oxidant production. J. Neurochem. 79, 658–668.
Kitagawa K., Matsumoto M., Kuwabara K., Takasawa K., Tanaka S., Sasaki T., et al. (2002) Protective effect of apolipoprotein E against ischemic neuronal injury is mediated through antioxidant action. J. Neurosci. Res. 68, 226–232.
Knapp L. T. and Klann E. (2002) Potentiation of hippocampal synaptic transmission by superoxide requires the oxidative activation of protein kinase C. J. Neurosci. 22, 674–683.
Kruman I. I., Pedersen W. A., Springer J. E., and Mattson M. P. (1999) ALS-linked Cu/Zn-SOD mutation increases vulnerability of motor neurons to excitotoxicity by a mechanism involving increased oxidative stress and perturbed calcium homeostasis. Exp. Neurol. 160, 28–39.
Liu R., Althaus J. S., Ellerbrock B. R., Becker D. A., and Gurney M. E. (1998) Enhanced oxygen radical production in a transgenic mouse model of familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ann. Neurol. 44, 763–770.
Liu D., Lu C., Wan R., Auyeung W. W., and Mattson M. P. (2002) Activation of mitochondrial ATP-dependent potassium channels protects neurons against ischemia-induced death by a mechanism involving suppression of Bax translocation and cytochrome c release. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 22, 431–443.
Lu C., Fu W., and Mattson M. P. (2002) Direct cleavage of AMPA receptor subunit GluR1 and suppression of AMPA currents by caspase-3: implications for synaptic plasticity and excitotoxic neuronal death. NeuroMolecular Med. 1, 69–79.
Mark R. J., Hensley K., Butterfield D. A., and Mattson M. P. (1995) Amyloid beta-peptide impairs ion-motive ATPase activities: evidence for a role in loss of neuronal Ca2+ homeostasis and cell death. J. Neurosci. 15, 6239–6249.
Mark R. J., Pang Z., Geddes J. W., Uchida K., and Mattson M. P. (1997) Amyloid beta-peptide impairs glucose transport in hippocampal and cortical neurons: involvement of membrane lipid peroxidation. J. Neurosci. 17, 1046–1054.
Mattson M. P. (1992) Calcium as sculptor and destroyer of neural circuitry. Exp. Gerontol. 27, 29–49.
Mattson M. P., Zhang Y., and Bose S. (1993) Growth factors prevent mitochondrial dysfunction, loss of calcium homeostasis, and cell injury, but not ATP depletion in hippocampal neurons deprived of glucose. Exp. Neurol. 121, 1–13.
Mattson M. P. (1997) Cellular actions of beta-amyloid precursor protein and its soluble and fibrillogenic derivatives. Physiol. Rev. 77, 1081–1132.
Mattson M. P., Fu W., Waeg G., and Mattson M. P. (1997) 4-hydroxynonenal, a product of lipid peroxidation, inhibits dephosphorylation of the microtubule-associated protein tau. NeuroReport 8, 2275–2281.
Mattson M. P. (1998) Modification of ion homeostasis by lipid peroxidation: roles in neuronal degeneration and adaptive plasticity. Trends Neurosci. 21, 53–57.
Mattson M. P., Keller J. N., and Begley J. G. (1998a) Evidence for synaptic apoptosis. Exp. Neurol. 153, 35–48.
Mattson M. P., Partin J., and Begley J. G. (1998b) Amyloid beta-peptide induces apoptosis-related events in synapses and dendrites. Brain Res. 807, 167–176.
Mattson M. P. and Partin J. (1999) Evidence for mitochondrial control of neuronal polarity. J. Neurosci. Res. 56, 8–20.
Mattson M. P., Guo Z. H., and Geiger J. D. (1999) Secreted form of amyloid precursor protein enhances basal glucose and glutamate transport, and protects against oxidative impairment of glucose and glutamate transport in synaptosomes by a cyclic GMP-mediated mechanism. J. Neurochem. 73, 532–537.
Mattson M. P. (2000) Apoptosis in neurodegenerative disorders. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 1, 120–129.
Mattson M. P. (2002) Accomplices to neuronal death. Nature 415, 377–379.
Mattson M. P., Duan W., and Maswood N. (2002) How does the brain control lifespan? Ageing Res. Rev. 1, 155–165.
McCracken E., Valeriani V., Simpson C., Jover T., McCulloch J., and Dewar D. (2000) The lipid peroxidation by-product 4-hydroxynonenal is toxic to axons and oligodendrocytes. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 20, 1529–1536.
Medler K. and Gleason E. L. (2002) Mitochondrial ca(2+) buffering regulates synaptic transmission between retinal amacrine cells. J. Neurophysiol. 87, 1426–1439.
Morris R. L. and Hollenbeck P. J. (1993) The regulation of bidirectional mitochondrial transport is coordinated with axonal outgrowth. J. Cell Sci. 104, 917–927.
Muller D., Toni N., and Buchs P. A. (2000) Spine changes associated with long-term potentiation. Hippocampus 10, 596–604.
Murphy M. P. (2001) How understanding the control of energy metabolism can help investigation of mitochondrial dysfunction, regulation and pharmacology. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1504, 1–11.
Neely M. D., Sidell K. R., Graham D. G., and Montine T. J. (1999) The lipid peroxidation product 4-hydroxynonenal inhibits neurite outgrowth, disrupts neuronal microtubules, and modifies cellular tubulin. J. Neurochem. 72, 2323–2333.
Nguyen P. V., Marin L., and Atwood H. L. (1997) Synaptic physiology and mitochondrial function in crayfish tonic and phasic motor neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 78, 281–294.
Nicotera P., Leist M., Fava E., Berliocchi L., and Volbracht C. (2000) Energy requirement for caspase activation and neuronal cell death. Brain Pathol. 10, 276–282.
Nobler M. S., Pelton G. H., and Sackeim H. A. (1999) Cerebral blood flow and metabolism in late-life depression and dementia. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry Neurol. 12, 118–127.
O’Dell T. J., Hawkins R. D., Kandel E. R., and Arancio O. (1991) Tests of the roles of two diffusible substances in long-term potentiation: evidence for nitric oxide as a possible early retrograde messenger. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88, 11,285–11,289.
Pantaloni D., Le Clainche C., and Carlier M. F. (2001) Mechanism of actin-based motility. Science 292, 1502–1506.
Pedersen W. A., Fu W., Keller J. N., Markesbery W. R., Appel S., Smith R. G., et al. (1998) Protein modification by the lipid peroxidation product 4-hydroxynonenal in the spinal cords of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients. Ann. Neurol. 44, 819–824.
Persky A. M. and Brazeau G. A. (2001) Clinical pharmacology of the dietary supplement creatine monohydrate. Pharmacol. Rev. 53, 161–176.
Pfefferbaum A. and Zipursky R. B. (1991) Neuroimaging studies of schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 4, 193–208.
Pfister K. K. (1999) Cytoplasmic dynein and microtubule transport in the axon: the action connection. Mol. Neurobiol. 20, 81–91.
Pollard T. D., Blanchoin L., and Mullins R. D. (2000) Molecular mechanisms controlling actin filament dynamics in nonmuscle cells. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 29, 545–576.
Prolla T. A. and Mattson M. P. (2001) Molecular mechanisms of brain aging and neurodegenerative disorders: lessons from dietary restriction. Trends Neurosci. 24, S21-S31.
Rabinovic A. D., Lewis D. A., and Hastings T. G. (2000) Role of oxidative changes in the degeneration of dopamine terminals after injection of neurotoxic levels of dopamine. Neuroscience 101, 67–76.
Raff M. C., Barres B. A., Burne J. F., Coles H. S., Ishizaki Y., and Jacobson M. D. (1993) Programmed cell death and the control of cell survival: lessons from the nervous system. Science 262, 695–700.
Robb-Gaspers L. D., Rutter G. A., Burnett P., Hajnoczky G., Denton R. M., and Thomas A. P. (1998) Coupling between cytosolic and mitochondrial calcium oscillations: role in the regulation of hepatic metabolism. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1366, 17–32.
Rothstein J. D., VanKammen B. A., Levey A. I., Martin L. J., and Kuncl R. W. (1995) Selective loss of glial glutamate transporter GLT-1 in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ann. Neurol. 38, 73–84.
Saraste M. (1999) Oxidative phosphorylation at the fin de siecle. Science 283, 1488–1493.
Schuman E. M. and Madison D. V. (1991) A requirement for the intercellular messenger nitric oxide in long-term potentiation. Science 254, 1503–1506.
Stanton P. K. and Schanne F. A. (1986) Hippocampal long-term potentiation increases mitochondrial calcium pump activity in rat. Brain Res. 382, 185–188.
Strakowski S. M., DelBello M. P., Adler C., Cecil D. M., and Sax K. W. (2000) Neuroimaging in bipolar disorder. Bipolar Disord. 2, 148–164.
Sullivan P. G., Geiger J. D., Mattson M. P., and Scheff S. W. (2000) Dietary supplement creatine protects against traumatic brain injury. Ann. Neurol. 48, 723–729.
Tarnopolsky M. A. and Beal M. F. (2001) Potential for creatine and other therapies targeting cellular energy dysfunction in neurological disorders. Ann. Neurol. 49, 561–574.
Tartaglia N., Du J., Tyler W. J., Neale E., Pozzo-Miller L., and Lu B. (2001) Protein synthesis-dependent and -independent regulation of hippocampal synapses by brain-derived neurotrophic factor. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 37,585–37,593.
Tesseur I., Van Dorpe J., Bruynseels K., Bronfman F., Sciot R., Van Lommel A., et al. (2000) Prominent axonopathy and disruption of axonal transport in transgenic mice expressing human apolipoprotein E4 in neurons of brain and spinal cord. Am. J. Pathol. 157, 1495–1510.
Thiels E., Urban N. N., Gonzalez-Burgos G. R., Kanterewicz B. I., Barrionuevo G., Chu C. T., et al. (2000) Impairment of long-term potentiation and associative memory in mice that overexpress extracellular superoxide dismutase. J. Neurosci. 20, 7631–7639.
Tolkovsky A. M. and Suidan H. S. (1987) Adenosine 5′-triphosphate synthesis and metabolism localized in neurites of cultured sympathetic neurons. Neuroscience 23, 1133–1142.
Tsujimoto Y. and Shimizu S. (2002) The voltage-dependent anion channel: an essential player in apoptosis. Biochimie 9, 187–193.
Wataya T., Nunomura A., Smith M. A., Siedlak S. L., Harris P. L., Shimohama S., et al. (2002) High molecular weight neurofilament proteins are physiological substrates of adduction by the lipid peroxidation product hydroxynonenal. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 4644–4648.
Weeber E. J., Levy M., Sampson M. J., Anflous K., Armstrong D. L., Brown S. E., et al. (2002) The role of mitochondrial porins and the permeability transition pore in learning and synaptic plasticity. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 18,891–18,897.
Williams J. M., Thompson V. L., Mason-Parker S. E., Abraham W. C., and Tate W. P. (1998) Synaptic activity-dependent modulation of mitochondrial gene expression in the rat hippocampus. Mol. Brain Res. 60, 50–56.
Williamson T. L. and Cleveland D. W. (1999) Slowing of axonal transport is a very early event in the toxicity of ALS-linked SOD1 mutants to motor neurons. Nat. Neurosci. 2, 50–56.
Yu Z. F. and Mattson M. P. (1999) Dietary restriction and 2-deoxyglucose administration reduce focal ischemic brain damage and improve behavioral outcome: evidence for a preconditioning mechanism. J. Neurosci. Res. 57, 830–839.
Yuste R. and Bonhoeffer T. (2001) Morphological changes in dendritic spines associated with long-term synaptic plasticity. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 24, 1071–1089.
Zenisek D. and Matthews G. (2000) The role of mitochondria in presynaptic calcium handling at a ribbon synapse. Neuron 25, 229–237.
Zhu H., Guo Q., and Mattson M. P. (1999) Dietary restriction protects hippocampal neurons against the death-promoting action of a presenilin-1 mutation. Brain Res. 842, 224–229.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mattson, M.P., Liu, D. Energetics and oxidative stress in synaptic plasticity and neurodegenerative disorders. Neuromol Med 2, 215–231 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1385/NMM:2:2:215
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/NMM:2:2:215