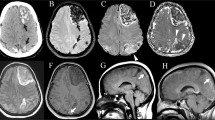
Abstract
Multiple simultaneous intracerebral hemorrhages are rare and varied in etiology. In the absence of known risk factors or obvious underlying disease, determining the cause may be problematic. We outline a diagnostic approach to multiple simultaneous intracerebral hemorrhages in the context of three case studies. We conclude that when there are no apparent risk factors, neuroimaging and identification of underlying diseases are central to determining the cause of multiple simultaneous intracerebral hemorrhage.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
McCormick WF, Rosenfield DB. Massive brain hemorrhage: a review of 144 cases and an examination of their causes. Stroke 1973;4:946–954.
Weisberg L. Multiple spontaneous intracerebral hematoma: clinical and computed homographic correlations. Neurol 1981;31:897–900.
Seijo M, Ucles A, Gil-Nagel A, Balseiro J, Calandre L. Hemotomas cerebrales multiples: revision de siete casas. Rev Neurol 1996;24:549–553.
Norrving B. Cerebral hemorrhage, In: Ginsberg MD, Bogousslavsky J, ed. Cerebrovascular Disease: Pathophysiology Diagnosis and Management, vol. 2, Malden: Blackwell Science, 1998:1466.
Maurino J, Saposnik G, Lepera S, Rey RC, Sica RE. Multiple simultaneous intracerebral hemorrhages. Clinical features and outcome. Arch Neurol 2001;58:629–632.
Mandybur TI. Intracranial hemorrhage caused by metastatic tumors. Neurol 1977;27:650–655.
Weisberg LA. Hemorrhagic metastatic intracranial neoplasms: clinical-computed tomographic correlations. Comput Radiol 1985;9:105–114.
Hill MD, Silver FL, Austin PC, Tu JV. Rate of stroke recurrence in patients with primary intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke 2000;31:123–127.
Kase CS. Vascular Disease of the Nervous System. Intracerebral Hemorrhage. In: Bradley WG, Daroff RB, Fenichel GM, Jankovic J, eds. Neurology In Clinical Practice, Philadelphia: Butterworth-Heinemann, 2004:1251–1267.
Yuh WTC, Fisher DJ, Runge VM, et al. Phase III multicenter trial of high-dose gadoteridol in MR evaluation of brain metastases. AJNR 1994;15:1037–1051.
Hermier M, Nighoghossian N. Contribution of susceptibility-weighted imaging to acute stroke assessment. Stroke 2004;351: 1989–1994.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Finelli, P.F. A diagnostic approach to multiple simultaneous intracerebral hemorrhages. Neurocrit Care 4, 267–271 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1385/NCC:4:3:267
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/NCC:4:3:267