Abstract
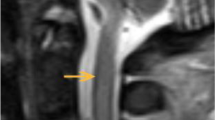
Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome (RPLS) is characterized radiographically by magnetic resonance imaging as white matter hyperintensities, which reflect cerebral edema. These changes are typically restricted to the parietal and occipital lobes, and are usually quite symmetric. We report a case of asymmetric RPLS involving only one frontal lobe in a patient with severe hypertension chronic internal carotid artery stenosis, and ipsilateral vasogenic edema.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chester EM, Agamanolis DP, Banker BQ, et al. Hypertensive encephalopathy: a clinicopathologic study of 20 cases. Neurology 1978;28:928–939.
Singhal AB. Postpartum angiopathy with reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy. Arch Neurol 2004;61:411–416.
Stott VL, Hurrell MA, Anderson TJ. Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome: a misnomer reviewed. Int Med J 2005;35:83–90.
Schaefer PW, Buonanno FS, Gonzales RG, et al. Diffusion-weighted imaging discriminates between cytotoxic and vasogenic edema in a patient with eclampsia Stroke 1997;28:1082–1085.
Lamy C, Oppenheim C, Méder JF, et al. Neuromaging in posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome. J Neuroimaging 2004;14:89–96.
Ahn KJ, You WJ, Jeong SL. Atypical manifestations of reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome: findings on diffusion imaging and ADC mapping. Neuroradiology 2004;46:978–983.
Karapanayiotides T, Meuli R, Devuyst G, et al. Postcarotid endarterectomy hyperperfusion or reperfusion syndrome. Stroke 36: 21–26.
Jorgensen LG, Schroeder TV. Defective cerebrovascular autoregulation after carotid endarterectomy Eur J Vasc Surg 1993;7:370–379.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schambra, H.M., Greer, D.M. Asymmetric reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome. Neurocrit Care 4, 245–247 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1385/NCC:4:3:245
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/NCC:4:3:245