Abstract
Introduction: Standard therapy for recurrent or metastatic renal carcinoma includes the biologic response modifiers interferon-alpha (IFN-α) and interleukin-2 (IL-2). The response rate for both agents is modest and toxicity is significant. New agents are needed. Interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) is a type II interferon that demonstrated promising activity in renal carcinoma in early clinical trials. In vitro data suggested synergistic activity when IFN-γ was combined with IFN-α. The Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group conducted a randomized phase II trial to confirm the efficacy of IFN-γ as a single agent and to evaluate the efficacy and toxicity of IFN-γ in combination with IFN-α in the treatment of patients with metastatic or recurrent renal carcinomas.
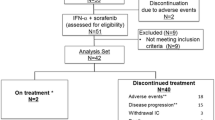
Materials and Methods: Ninety-five patients with recurrent or metastatic renal carcinoma were entered on trial. Patients were stratified based on risk assessment using the Elson method. Patients were randomly assigned to receive either IFN-γ 0.1 mg/m2 weekly (arm A) or IFN-γ 0.3 mg/m2 iv daily × 5 every 3 wk plus IFN-α 10 MU/m2 daily (arm B). Treatment efficacy was evaluated every 6 weeks.
Results: Toxicity in the arm A was minimal. Significant toxicity was noted in arm B, with four cases of grade 4 neurotoxicity. No responses were seen with IFN-γ alone. Five responses (two CR and three PR) were noted in the combination arm for an overall response rate of 10%. Four of five responders were classified as “good risk.” Median survival for arm A was 7.0 mo vs 10.4 mo for arm B. Risk stratification was significant in arm B.
Conclusion: IFN-γ at this dose and schedule failed to demonstrate activity in metastatic/recurrent renal carcinoma. The combination of IFN-γ and IFN-α demonstrated a response rate similar to IFN-α alone. There was no evidence of synergy between IFN-γ and IFN-α.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Murray T, Samuels A, Ghafoor A, Ward E, Thun MJ. Cancer Statistics—2003. CA-A Cancer Journal for Clinicians 2003; 53:5–26.
Slaton JW, Swanson DA. Radical nephrectomy for localized renal cell carcinoma. In: Vogelzang NJ, Scardino PT, Shipley WU, Coffey DS (eds). Comprehensive Textbook of Genitourinary Oncology, Second Edition, Lippincott-Williams and Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, 2000. pp 166–175.
Nelson JB, Marshall FF. Surgical treatment of locally advanced renal cell cancer. In: Vogelzang NJ, Scardino PT, Shipley WU, Coffey DS (eds). Comprehensive Textbook of Genitourinary Oncology, Second Edition, Lippincott-Williams and Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, 2000. pp 183–200.
Messing EM, Manola J, Wilding G, et al. Phase III study of interferon alfa NL as adjuvant treatment for resectable renal cell carcinoma: An Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group/Intergroup Trial. J Clin Oncol 2003; 21:1214–1222.
Pizzocaro G, Piva L, Colavita M, et al. Interferon adjuvant to radical nephrectomy in Robson stages II and III renal cell carcinoma: A multicentric randomized study. J Clin Oncol 2001; 19:425–431.
Clark J, Atkins MB, Urba W, et al. Adjuvant high dose bolus interleukin-2 (HD IL2) for patients with high-risk renal cell carcinoma—A Cytokine Working Group randomized trial. Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 2003; 22:164.
Krown SE. Interferon treatment of renal cell carcinoma. Cancer 1987; 59:647–651.
Elson P, Witte R, Trump D. Prognostic factors for survival in patients with recurrent or metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Res 1988; 48:7310–7313.
Mani S, Todd MB, Katz K, Poo WJ. Prognostic factors for survival in patients with metastatic renal cancer treated with biological respnse modifiers. J Urol 1995; 154:35–40.
Motzer RJ, Mazumdar M, Bacik J, Berg W, Amsterdam A, Ferrara J. Survival and prognostic stratification of 670 patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 1999; 17:2530–2540.
Zisman A, Pantuck AJ, Dorey F, et al. Improved prognostication of renal cell carcinoma using an integrated system. J Clin Oncol 2001; 19:1649–1657.
Fossa S, Jones M, Johnson P, et al. Interferon-alpha and survival in renal cell cancer. Br J Urol 1995; 76:286–290.
Dutcher JP. Interleukin-2 as a single agent in advanced renal cell carcinoma. In: Renal Cell Carcinoma Immunotherapy and Cellular Biology, Klein EA, Bukowski RM Finke JH (eds). Marcel Dekker Inc, New York, 1993, pp. 195–200.
Negrier S, Escudier B, Lasset C, et al. Recombinant human interleukin-2, recombinant human interferon alfa-2a, or both in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 1998; 338:1272–1278.
Fyfe G, Fisher RI, Rosenberg SA, Sznol M, Parkinson DR, Louie AC. Results of treatment of 255 patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma who received high-dose recombinant interleukin-2 therapy. J Clin Oncol 1995; 13:688–696.
Saito T, Berens ME, Welander CE. Direct and indirect effects of human recombinant γ-interferon on tumor cells in a clongenic assay. Cancer Res 1986; 46:1142–1147.
Kirkwood JM, Bryant J, Schiller JH, Oken MM, Borden EC, Whiteside TL. Immunomodulatory function of interferon gamma in patients with metastatic melanoma: Results of a phase II-B trial in subjects with metastatic melanoma, ECOG Study E4987. J Immunotherapy 1997; 20:146–157.
Ernstoff MS, Gooding W, Nair S, et al. Immunological effects of treatment with sequential administration of recombinant interferon gamma and alpha in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma during a phase I trial. Cancer Res 1992; 52:851–856.
Aulitzky W, Gastl G, Aulitzky W, et al. Successful treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma with a biologically active dose of recombinant interferon-gamma. J Clin Oncol 1989; 12:1875–1884.
Ellerhorst JA, Kilbourn RG, Amato RJ, Zukiwski AA, Jones E, Logisthetis CJ: Phase II trial of low dose γ-interferon in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J Urol 1994; 152:841–845.
Ernstoff MS, Nair S, Bahnson RR, et al. A phase IA trial of sequential administration of recombinant DNA-produced interferon: Combination recombinant interferon gamma and recombinant interferon alpha in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 1990; 8:1637–1649.
Mehta CR, Patel NR, Tsiatis AA. Exact significance testing to establish treatment equivalence with ordered categorical data. Biometrics 1984; 40:819–825.
Kaplan EL, Meier P. Nonparametric estimation of incomplete observations. J Am Statistical Assoc 1958; 53:457–481.
Mantel N. Evaluation of survival data and two new rank order statistics arising in its consideration. Cancer Chemother Rep 1966; 50:163–170.
Weiner LM, Steplewski Z, Koprowski H, Litwin S, Comis RL. Divergent dose-related effects of gamma-interferon therapy on in vitro antibody-dependent cellular and non-specific cytotoxicity by human peripheral blood monocytes. Cancer Res 1988; 48:1042–1046.
Aulitzky W, Gastl G, Aulitzky WE, et al. Interferon-gamma for the treatment of metastatic renal cancer: Dose-dependent stimulation and downregulation of β2 microglobulin and neopterin responses. Immunobiology 1987; 176:85–95.
Small EJ, Weiss FG, Malik UK, et al. The treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma patients with recombinant human gamma interferon. Cancer J Sci Amer 1998; 4:162–167.
Gleave ME, Elhilali M, Fradet Y, et al. Interferon gamma-1b compared with placebo in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 1998; 338:1265–1271.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
deceased
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dutcher, J.P., Fine, J.P., Krigel, R.L. et al. Stratification by risk factors predicts survival on the active treatment arm in a randomized phase II study of interferon-gamma plus/minus interferon-alpha in advanced renal cell carcinoma (E6890). Med Oncol 20, 271–281 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1385/MO:20:3:271
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/MO:20:3:271