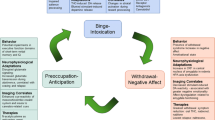
Abstract
Addiction is a complex disorder because many factors contribute to the development and maintenance of addiction. One factor is learning. For example, drug-context associations that develop during drug use could facilitate drug craving upon re-exposure to contexts previously associated with drugs. Additionally, deficits in cognitive processes associated with withdrawal could precipitate relapse in attempts to ameliorate those deficits. Because addiction and learning involve common neural areas and cell signaling cascades, addiction-related changes in processes underlying plasticity may contribute to addiction. This article examines similarities between addiction and learning at the behavioral, neural, and cellular levels, with emphasis on the neural substrates underlying the effects of acute nicotine, chronic nicotine, and withdrawal from chronic nicotine on hippocampus-dependent contextual, learning.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Peto R., Lopez A. D., Boreham J., Thun, M., Heath C. Jr., and Doll R. (1996) Mortality from smoking worldwide. Br. Med. Bull. 52, 12–21.
Corrigall W. A. (1999) Nicotine self-administration in animals as a dependence model. Nicotine. Tob. Res. 1, 11–20.
Rose J. E. and Corrigall W. A. (1997) Nicotine self-administration in animals and humans: similarities and differences. Psychopharmacology (Berl.) 130, 28–40.
Mathieu-Kia A. M., Kellogg S. H., Butelman E. R., and Kreek M. J. (2002) Nicotine addiction: insights from recent animal studies. Psychopharmacology (Berl.) 162, 102–118.
Malin D. H., Lake J. R., Newlin-Maultsby P., et al. (1992) Rodent model of nicotine abstinence syndrome. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 43, 779–784.
Damaj M. I., Kao W., and Martin B. R. (2003) Characterization of spontaneous and precipitated nicotine withdrawal in the mouse. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 307, 526–534.
Jonkman S., Henry B., Semenova S., and Markou A. (2005) Mild anxiogenic effects of nicotine withdrawal in mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 516, 40–45.
Epping-Jordan M. P., Watkins S. S., Koob G. F., and Markou A. (1998) Dramatic decreases in brain reward function during nicotine withdrawal. Nature 393, 76–79.
Semenova S., Bespalov A., and Markou A. (2003) Decreased prepulse inhibition during nicotine withdrawal in DBA/2J mice is reversed by nicotine self-administration. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 472, 99–110.
Hughes J. R., Gust S. W., Skoog K. Keenan R. M., and Fenwick J. W. (1991) Symptoms of tobacco withdrawal. A replication and extension. Arch. Gen Psychiatry 48, 52–59.
Kumari V. and Gray J. A. (1999) Smoking withdrawal, nicotine dependence and prepulse inhibition of the acoustic startle reflex. Psychopharmacology (Berl.) 141, 11–15.
Postma P., Kumari V., Sharma T., Hines M., and Gray J. A. (2001) Startle response during smoking and 24 h after withdrawal predicts successful smoking cessation. Psychopharmacology (Berl.) 156, 360–367.
Domino E. F. and Kishimoto T. (2002) Tobacco smoking increases gating of irrelevant and enhances attention to relevant tones. Nicotine. Tob. Res. 4, 71–78.
Snyder F. R. and Henningfield J. E. (1989) Effects of nicotine administration following 12 h of tobacco deprivation: assessment on computerized performance tasks. Psychopharmacology (Berl.) 97, 17–22.
Kleinman K. M., Vaughn R. L., and Christ T. S. (1973) Effects of cigarette smoking and smoking deprivation on paired-associated learning of high and low meaningful nonsense syllables. Psychol. Rep. 32, 963–966.
Bell S. L., Taylor R. C., Singleton E. G., Henningfield J. E., and Heishman S. J. (1999) Smoking after nicotine deprivation enhances cognitive performance and decreases tobacco craving in drug abusers. Nicotine. Tob. Res. 1, 45–52.
Baker T. B., Brandon T. H., and Chassin L. (2004) Motivational influences on cigarette smoking. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 55, 463–491.
Lerman C. and Niaura R. (2002) Applying genetic approaches to the treatment of nicotine dependence. Oncogene 21, 7412–7420.
Pomerleau C. S., Downey K. K., Snedecor S. M., Mehringer A. M., Marks J. L., and Pomerleau O. F. (2003) Smoking patterns and abstinence effects in smokers with no ADHD, childhood ADHD, and adult ADHD symptomatology. Add. Behav. 28, 1149–1157.
Adler L. E., Olincy A., Waldo M., et al. (1998) Schizophrenia, sensory gating, and nicotinic receptors. Schizophr. Bull. 24, 189–202.
Kreek M. J., Nielsen D. A., Butelman E. R., and Laforge K. S. (2005) Genetic influences on impulsivity, risk taking, stress responsivity and vulnerability to drug abuse and addiction. Nat. Neurosci. 8, 1450–1457.
Eichenbaum H. (1999) The hippocampus and mechanisms of declarative memory. Behav. Brain Res. 103, 123–133.
Setlow B. (1997) The nucleus accumbens and learning and memory. J. Neurosci. Res. 49, 515–521.
Blum S., Hebert A. E., and Dash P. K. (2006) A role for the prefrontal cortex in recall of recent and remote memories. Neuroreport 17, 341–344.
Pelletier J. G. and Pare D. (2004) Role of amygdala oscillations in the consolidation of emotional memories. Biol. Psychiatry 55, 559–562.
Takashima A., Petersson K. M., Rutters F., et al. (2006) Declarative memory consolidation in humans: a prospective functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103, 756–761.
Eichenbaum H. (1997) Declarative memory: insights from cognitive neurobiology. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 48, 547–572.
London E. D., Ernst M., Grant S., Bonson, K., and Weinstein A. (2000) Orbitofrontal cortex and human drug abuse: functional imaging. Cereb. Cortex 10, 334–342.
Mukhin A. G., Gundisch D., Horti A. G., et al. (2000) 5-lodo-A-85380, an alpha4beta2 subtype-selective ligand for nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Mol. Pharmacol. 57, 642–649.
Bechara A. (2005) Decision making, impulse control and loss of willpower to resist drugs: a neurocognitive perspective. Nat. Neurosci. 8, 1458–1463.
See R.E. (2002) Neural substrates of conditioned-cued relapse to drug-seeking behavior. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 71, 517–529.
Koob G. F. (1992) Drugs of abuse: anatomy, pharmacology and function of reward pathways. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 13, 177–184.
Di Chiara G., Tanda G., Bassareo, V., et al. (1999) Drug addiction as a disorder of associative learning—role of nucleus accumbens shell/extended amygdala dopamine. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 877, 461–485.
Cornish J. L. and Kalivas P. W. (2000) Glutamate transmission in the nucleus accumbens mediates relapse in cocaine addiction. J. Neurosci. 20, RC89.
Di Ciano P. and Everitt B. J. (2001) Dissociable effects of antagonism of NMDA and AMPA/KA receptors in the nucleus accumbens core and shell on cocaine-seeking behavior. Neuropsychopharmacology 25, 341–360.
Fuchs R. A., Evans K. A., Ledford C. C., et al. (2005) The role of the dorsomedial prefrontal cortex, basolateral amygdala, and dorsal hippocampus in contextual reinstatement of cocaine seeking in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 30, 296–309.
Vorel S. R., Liu X., Hayes R. J., Spector J. A., and Gardner E. L. (2001) Relapse to cocaineseeking after hippocampal theta burst stimulation. Science 292, 1175–1178.
Robbins T. W. and Everitt B. J. (2002) Limbic-Striatal Memory Systems and Drug Addiction. Neurobiol. Learning Mem. 78, 625–636.
Kalivas P. W. and Volkow N. D. (2005) The Neural Basis of Addiction: A Pathology of Motivation and Choice. Am. J. Psychiatry 162, 1403–1413.
Everitt B. J. and Robbins T. W. (2005) Neural systems of reinforcement for drug addiction: from actions to habits to compulsion. Nat. Neurosci. 8, 1481–1489.
Nestler E. J. (2002) Common Molecular and Cellular Substrates of Addiction and Memory. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 78, 637–647.
Pittenger C., Huang Y. Y., Paletzki R. F., et al. (2002) Reversible inhibition of CREB/ATF transcription factors in region CA1 of the dorsal hippocampus disrupts hippocampus-dependent spatial memory. Neuron 34, 447–462.
Abel T., Nguyen P. V., Barad M., Deuel T. A., Kandel E. R., and Bourtchouladze R. (1997) Genetic demonstration of a role for PKA in the late phase of LTP and in hippocampus-based long-term memory. Cell 88, 615–626.
Selcher J. C., Weeber E. J., Varga A. W., Sweatt J. D., and Swank M. (2002) Protein kinase signal transduction cascades in mammalian associative conditioning. Neuroscientist 8, 122–131.
Adams J. P. and Sweatt J. D. (2002) Molecular psychology: roles for the ERK MAP kinase cascade in memory. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 42, 135–163.
Silva A. J., Kogan J. H., Frankland P. W., and Kida S. (1998) CREB and memory. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 21, 127–148.
Cammarota M., Bevilaqua L. R., Viola H., et al. (2002) Participation of CaMKII in neuronal plasticity and memory formation. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 22, 259–267.
Self D. W., Genova L. M., Hope B. T., Barnhart W. J., Spencer J. J., and Nestler E. J. (1998) Involvement of cAMP-dependent protein kinase in the nucleus accumbens in cocaine self-administration and relapse of cocaine-seeking behavior. J. Neurosci. 18, 1848–1859.
Lynch W. J. and Taylor J. R. (2005) Persistent changes in motivation to self-administer cocaine following modulation of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase A (PKA) activity in the nucleus accumbens. Eur. J. Neurosci. 22, 1214–1220.
Hou J., Kuromi H., Fukasawa Y., Ueno K., Sakai T., and Kidokoro Y. (2004) Repetitive exposures to nicotine induce a hyper-responsiveness via the cAMP/PKA/CREB signal pathway in Drosophila. J. Neurobiol. 60, 249–261.
Pierce R. C., Quick E. A., Reeder D. C., Morgan Z. R., and Kalivas P. W. (1998) Calcium-Mediated Second Messengers Modulate the Expression of Behavioral Sensitization to Cocaine. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 286, 1171–1176.
Pierce R. C., Pierce-Bancroft A. F., and Prasad B. M. (1999) Neurotrophin-3 Contributes to the Initiation of Behavioral Sensitization to Cocaine by Activating the Ras/Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Signal Transduction Cascade. J. Neurosci. 19, 8685–8695.
Lu L., Hope B. T., Dempsey J., Liu S. Y., Bossert J. M., and Shaham Y. (2005) Central amygdala ERK signaling pathway is critical to incubation of cocaine craving. Nat. Neurosci. 8, 212–219.
Sanna P. P., Simpson C., Lutjens R., and Koob G. (2002) ERK regulation in chronic ethanol exposure and withdrawal. Brain Res. 948, 186–191.
Abel T. and Lattal K. M. (2001) Molecular mechanisms of memory acquisition, consolidation and retrieval. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 11, 180–187.
Carlezon J., Duman R. S., and Nestler E. J. (2005) The many faces of CREB. Trends Neurosci. 28, 436–445.
Pluzarev O. and Pandey S. C. (2004) Modulation of CREB expression and phosphorylation in the rat nucleus accumbens during nicotine exposure and withdrawal. J. Neurosci. Res 77, 884–891.
Carlezon W. A. Jr., Thome J., Olson V. G., et al. (1998). Regulation of Cocaine Reward by CREB. Science 282 2272–2275.
Widnell K. L., Self D. W., Lane S. B., et al. (1996) Regulation of CREB expression: in vivo evidence for a functional role in morphine action in the nucleus accumbens. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 276 306–315.
Risinger F. O. and Oakes R. A. (1995) Nicotine-induced conditioned place preference and conditioned place aversion in mice. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 51 457–461.
Horan B., Smith M., Gardner E. L., Lepore M., and Ashby C. R. Jr. (1997) (−)-Nicotine produces conditioned place preference in Lewis, but not Fischer 344 rats. Synapse 26 93, 94.
Vastola B. J., Douglas L. A., Varlinskaya E. I., and Spear L. P. (2002) Nicotine-induced conditioned place preference in adolescent and adult rats. Physiol. Behav. 77 107–114.
Belluzzi J. D., Lee A. G., Oliff H. S., and Leslie F. M. (2004) Age-dependent effects of nicotine on locomotor activity and conditioned place preference in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl.) 174 389–395.
Le Foll B. and Goldberg S. R. (2005) Nicotine induces conditioned place preferences over a large range of doses in rats. Psychopharmacology 178 481–492.
Grabus S., Martin B., Brown S., and Damaj M. (2006) Nicotine place preference in the mouse: influences of prior handling, dose and strain and attentuation by nicotinic receptor antagonists. Psychopharmacology 184 456–463.
Chaudhri N., Caggiula A., Donny E., Palmatier M., Liu X. and Sved A.(2006) Complex interactions between nicotine and nonpharmacological stimuli reveal multiple roles for nicotine in reinforcement. Psychopharmacology 184 353–366.
Caggiula A. R., Donny E. C., White A. R., et al. (2001) Cue dependency of nicotine self-administration and smoking. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 70 515–530.
Balfour D. J., Wright A. E., Benwell M. E., and Birrell C. E. (2000) The putative role of extrasynaptic mesolimbic dopamine in the neurobiology of nicotine dependence. Behav. Brain Res. 113 73–83.
Caggiula A. R., Donny E. C., White A. R., et al. (2002) Environmental stimuli promote the acquisition of nicotine self-administration in rats. Psychopharamcology (Berl.) 163 230–237.
Caggiula A. R., Donny E. C., Chaudhri N., Perkins K. A., Evans-Martin F. F., and Sved A. F. (2002) Importance of nonpharmacological factors in nicotine self-administration. Physiol. Behav. 77 683–687.
Chaudhri N., Caggiula A. R., Donny E. C., et a al. (2005) Sex differences in the contribution of nicotine and nonpharmacological stimuli to nicotine self-administration in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl.) 180 258–266.
Cohen C., Perrault G., Griebel G., and Soubrie P. (2005) Nicotine-associated cues maintain nicotine-seeking behavior in rats several weeks after nicotine withdrawal: reversal by the cannabinoid (CB1) receptor antagonist, rimonabant (SR141716). Neuropsychopharmacology 30, 145–155.
White N. M. (1996) Additive drugs as reinforces: multiple partial actions on memory systems. Addiction 91 921–949.
Logue S. F., Paylor R., and Wehner J. M. (1997) Hippocampal lesions cause learning deficits in inbred mice in the Morris water maze and conditioned-fear task. Behav. Neurosci. 111 104–113.
Phillips R. G. and Ledoux J. E. (1992) Differential contribution of amygdala and hippocampus to cued and contextual fear conditioning. Behav. Neurosci. 106 274–285.
Gould T. J. and Wehner J. M. (1999) Nicotine enhancement of contextual fear conditioning. Behav. Brain Res. 102 31–39.
Gould T. J. (2003) Nicotine produces a within subject enhancement of contextual fear conditioning in C57BL/6 mice independent of sex. Int. Physiol. Behav. Science 38 124–132.
Gould T. J. and Lommock J. A. (2003) Nicotine enhances contextual fear conditioning and ameliorates ethanol-induced deficits in contextual fear conditioning. Behav. Neurosci. 117, 1276–1282.
Gould T. J. and Higgins J. S. (2003) Nicotine enhances contextual fear conditioning in C57BL/6J mice at 1 and 7 days post-training. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 80 147–157.
Rossebo O. E. and Gould T. J. (2003) Nicotine enhancement of cued trace fear conditioning but not cued delay fear conditioning in C57BL/6J mice. Soc. Neurosci. Abs. 89 1.
Levin E. D. and Rose J. E. (1991) Nicotinc and muscarinic interactions and choice accuracy in the radial-arm maze. Brain Res. Bull. 27, 125–128.
Rush R., Kuryatov A., Nelson M. E., and Lindstrom J. (2002) First and second transmembrane segments of alpha3, alpha4, beta2, and beta4 nicotine acetylcholine receptor subunits influence the efficacy and potency of nicotine. Mol. Pharmacol. 61 1416–1422.
Lena C. and Changeux J. P. (1998) Allosteric nicotinic receptors, human pathologies. J. Physiol Paris 92 63–74.
le Novere N., Grutter T., and Changeux J. P. (2002) Models of the extracellular domain of the nicotinic receptors and of agonist- and Ca2+-binding sites. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99 3210–3215.
Cordero-Erausquin M., Marubio L. M., Klink R., and Changeux J. P. (2000) Nicotinic receptor function: new perspectives from knockout mice. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 21 211–217.
Broide R. S. and Leslie F. M. (1999) The alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor in neuronal plasticity. Mol. Neurobiol. 20 1–16.
Wonnacott S. (1997) Presynaptic nicotinic ACh receptors. Trends. Neurosci. 20 92–98.
Perry D. C., Xiao Y., Nguyen H. N., Musachio J. L., Davila-Garcia M. I., and Kellar K. J. (2002) Measuring nicotinic receptors with characteristics of alpha4beta2, alpha3beta2 and alpha3beta4 subtypes in rat tissues by autoradiography. J. Neurochem. 82 468–481.
Papke R. L., Sanberg R. P., and Shytle R. D. (2001) Analysis of mecamylamine stereoisomers on human nicotinic receptor subtypes. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 297 646–656.
Fenster C. P., Rains M. F., Noerager B., Quick M. W., and Lester R. A. (1997) Influence of subunit composition on desensitization of neuronal acetylcholine receptors at low concentrations of nicotine. J. Neurosci. 17 5747–5759.
Wooltorton J. R., Pidoplichko V. I., Broide R. S., and Dani J. A. (2003) Differential desensitization and distribution of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subtypes in midbrain dopamine areas. J. Neurosci. 23 3176–3185.
Orr-Urtreger A., Goldner F. M., Saeki M., et al. (1997) Mice deficient in the alpha7 neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor lack alpha-bungarotoxin binding sites and hippocampal fast nicotinic currents. J. Neurosci. 17 9165–9171.
Zhang Z. W., Coggan J. S., and Berg D. K. (1996) Synaptic currents generated by neuronal acetylcholine receptors sensitive to alpha-bungarotoxin. Neuron 17 1231–1240.
Berg D. K. and Conroy W. G. (2002) Nicotinic alpha 7 receptors: synaptic options and down-stream signaling in neurons. J. Neurobiol. 53, 512–523.
Sorenson E. M., Shiroyama T., and Kitai S. T. (1998) Postsynaptic nicotinic receptors on dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta of the rat. Neuroscience 87, 659–673.
Porter J. T., Cauli B., Tsuzuki K., Lambolez B., Rossier J., and Audinat E. (1999) Selective excitation of subtypes of neocortical interneurons by nicotinic receptors. J. Neurosci. 19, 5228–5235.
Nomikos G. G., Schilstrom B., Hildebrand B. E., Panagis G., Grenhoff J., and Svensson T. H. (2000) Role of alpha7 nicotinic receptors for psychiatric illness. Behav. Brain. Res. 113, 97–103.
Eilers H., Schaeffer E., Bickler P. E., and Forsayeth J. R. (1997) Functional deactivation of the major neuronal nicotinic receptor caused by nicotine and a protein kinase C-dependent mechanism. Mol. Pharmacol. 52, 1105–1112.
Dajas-Bailador, F. A., Mogg A. J., and Wonnacott S. (2002) Intracellular Ca2+ signals evoked by stimulation of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in SH-SY5Y cells: contribution of voltage-operated Ca2+ channels and Ca2+ stores. J. Neurochem. 81, 606–614.
Barrantes G. E., Murphy C. T., Westwick J., and Wonnacott S. (1995) Nicotine increases intracellular calcium in rat hippocampal neurons via voltage-gated calcium channels. Neurosci. Lett. 196, 101–104.
Barrantes G. E., Westwick J., and Wonnacott S. (1994) Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in primary cultures of hippocampal neurons: pharmacology and Ca++ permeability. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 22, 294S.
Sabban E. L. and Gueorguiev V. D. (2002) Effects of short- and long-term nicotine treatment on intracellular calcium and tyrosine hydroxylase gene expression. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 971, 39–44.
Nakayama H., Numakawa T., Ikeuchi T., and Hatanaka H. (2001) Nicotine-induced phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase and CREB in PC12h cells. J. Neurochem. 79, 489–498.
Grottick A. J. and Higgins G. A. (2000) Effect of subtype selective nicotinic compounds on attention as assessed by the five-choice serial reaction time task. Behav. Brain Res. 117, 197–208.
Grillner P. and Svensson T. H. (2000) Nicotine-induced excitation of midbrain dopamine neurons in vitro involves ionotropic glutamate receptor activation. Synapse 38, 1–9.
Fujii S., Ji Z., and Sumikawa K. (2000) Inactivation of alpha7 ACh receptors and activation of non-alpha7 ACh receptors both contribute to long term potentiation induction in the hippocampal CA1 region. Neurosci. Lett. 286, 134–138.
Maren S. (2001) Neurobiology of Pavlovian fear conditioning. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 24, 897–931.
Gould T. J., Feiro O., and Moore D. (2004) Nicotine enhancement of trace cued fear conditioning but not delay cued fear conditioning in C57BL/6J mice. Behav. Brain Res. 155, 167–173.
Feiro O. and Gould T. J. (2005) The interactive effects of nicotinic and muscarinic cholinergic receptor inhibition on fear conditioning in young and aged C57BL/6 mice. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 80, 251–262.
Caldarone B. J., Duman C. H., and Picciotto M. R. (2000) Fear conditioning and latent inhibition in mice lacking the high affinity subclass of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in the brain. Neuropharmacology 39, 2779–2784.
Paylor R., Nguyen M., Crawley J. N., Patrick J., Beaudet A., and Orr-Urtreger A. (1998) Alpha7 nicotinic receptor subunits are not necessary for hippocampal-dependent learning or sensorimotor gating: a behavioral characterization of Acra7-deficient mice. Learn. Mem. 5, 302–316. 302-316.
Wehner J. M., Keller J. J., Keller, A. B., et al. (2004) Role of neuronal nicotinic receptors in the effects of nicotine and ethanol on contextual fear conditioning. Neuroscience 129, 11–24.
Davis J. A. and Gould T. J. (2006) The effects of DHBE and MLA on nicotine-induced enhancement of contextual fear conditioning in C57BL/6 mice. Psychopharmacology 184, 345–352.
Wu M., Hajszan T., Leranth C., and Alreja M. (2003) Nicotine recuits a local glutamatergic circuit to excite septohippocampal GABAergic neurons. Eur. J. Neurosci. 18, 1155–1168.
Alkondon M., Pereira E. F. R., and Albuquerque E. X. (2003) NMDA and AMPA Receptors Contribute to the Nicotinic Cholinergic Excitation of CA1 Interneurons in the Rat Hippocampus. Neurophysiol. 90, 1613–1625.
Radcliffe K. A., Fisher J. L., Gray R., and Dani J. A. (1999) Nicotinic modulation of glutamate and GABA synaptic transmission of hippocampal neurons. Am. NY Acad. Sci. 868, 591–610.
Gould T. J. and Lewis M. C. (2005) Coan tagonism of glutamate receptors and nicotinic acetylcholinergic receptors disrupts fear conditioning and latent inhibition of fear conditioning. Learn. Mem. 12, 389–398.
Kim J. J., DeCola J. P., Landejra-Fernandez J., and Fanselow M. S. (1991) N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist APV blocks acquisition but not expression of fear conditioning. Behav. Neurosci. 105, 126–133.
Fanselow M. S., Kim J. J., Yipp J., and De O ca B. (1994) Differential effects of the N-methyl-D-asparate antagonist DL-2-amino-5-phosphonovalerate on acquisition of fear of auditory and contextual cues. Behav. Neurosci. 108, 235–240.
Fanselow M. S. and Kim J. J. (1994) Acquisition of contextual Pavlovian fear conditioning is blocked by application of an NMDA receptor antagonist D,L-2-amino-5-phosphonovaleric acid to the basolateral amygdala. Behav. Neurosci. 108, 210–212.
Gould T. J., McCarthy M. M., and Keith R. A. (2002) MK-801 disrupts acquisition of contextual fear conditioning but enhances memory consolidation of cued fear conditioning. Behav. Pharmacol. 13, 287–294.
Stiedl O., Birkenfeld K., Palve M., and Spiess J. (2000) Impairment of conditioned contextual fear of C57BL/6J mice by intracerebral injections of the NMDA receptor antagonist APV. Behav. Brain Res. 116, 157–168.
Alkondon M., Pereira E. F., and Albuquerque E. X. (1998) alpha-bungarotoxin- and methylly-caconitine-sensitive nicotinic receptors mediate fast synaptic transmission in interneurons of rat hippocampal slices. Brain Res. 810, 257–263.
Frazier C. J., Buhler A. V., Weiner J. L., and Dunwiddie T. V. (1998) Synaptic Potentials Mediated via alpha-Bungarotoxin-Sensitive Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors in Rat Hippocampal Interneurons. J. Neurosci. 18, 8228–8235.
Hefft S., Hulo S., Bertrand D., and Mullner D. (1999) Synaptic transmission at nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in rat hippocampal organotypic cultures and slices. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 515, 769–776.
Matsubayashi H., Inoue A., Amano T., et al. (2004) Involvement of (alpha)7- and (alpha)4(beta)2-type postsynaptic nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in nicotine-induced excitation of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra: a patch clamp and single-cell PCR study using acutely dissociated nigral neurons. Mol. Brain Res. 129, 1–7.
Matsubayashi H., Amano T., Seki T., Sasa M., and Sakai N. (2004) Postsynaptic (alpha)4-(beta)2 and (alpha)7 type nicotinic acetylcholine receptors contribute to the local and endogenous acetylcholine-mediated synaptic transmissions in nigral dopaminergic neurons. Brain Res. 1005, 1–8.
Chen Y., Sharples T. J. W., Phillips K. G., et al. (2003) The nicotinic (alpha)4(beta)2 receptor selective agonist TC-2559, increases dopamine neuronal activity in the ventral tegmental area of rat midbrain slices. Neuropharmacology 45, 334–344.
Ji D., Lape R., and Dani J. A. (2001) Timing and Location of Nicotinic Activity Enhances or Depresses Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity. Neuron 31, 131–141.
Roerig B., Nelson D. A., and Katz L. C. (1997) Fast Synaptic Signaling by Nicotinic Acetylcholine and Serotonin 5-HT3 Receptors in Developing Visual Cortex. J. Neurosci. 17, 8353–8362.
Chu Z. G., Zhou F. M., and Hablitz J. J. (2000) Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor-mediated synaptic potentials in rat neocortex. Brain Res. 887, 339–405.
Fabian-Fine R., Skehel P., Errington M. L., et al (2001) Ultrastructural Distribution of the α7 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Subunit in Rat Hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 21, 7993–8003.
Levy R. B. and Aoki C. (2002) Alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors occur at postsynaptic densities of AMPA receptor-positive and-negative excitatory synapses in rat sensory cortex. J. Neurosci. 22, 5001–5015.
Broide R. S. and Leslie F. M. (1999) The alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor in neuronal plasticity. Mol. Neurobiol. 20, 1–16.
Chavez-Noriega L. E., Gillespie A., Stauderman K. A., et al. (2000) Characterization of the recombinant human neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (alpha)3(beta)2 and (alpha)4(beta)2 stably expressed in HEK293 cells*1. Neuropharmacology 39, 2543–2560.
Karadsheh M. S., Shah M. S., Tang X., Macdonald R. L., and Stitzel J. A. (2004) Functional characterization of mouse alpha4beta2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors stably expressed in HEK293T cells. J. Neurochem. 91, 1138–1150.
Fujii S. and Sumikawa K. (2001) Acute and chronic nicotine exposure reverse age-related declines in the induction of long-term potentiation in the rat hippocampus. Brain Res. 894, 347–353.
Fujii S. and Sumikawa K. (2001) Nicotine accelerates reversal of long-term potentiation and enhances long-term depression in the rat hippocampal CA1 region. Brain Res. 894, 340–346.
Radcliffe K. A. and Dani J. A. (1998) Nicotinic stimulation produces multiple forms of increased glutamatergic synpatic transmission. J. Neurosci. 18, 7075–7083.
Fujii S., Jia Y., Yang A., and Sumikawa K. (2000) Nicotine reverses GABAergic inhibition of long-term potentiation induction in the hippocampal CA1 region. Brain Res. 863, 259–265.
Fisher, J. L. and Dani J. A. (2000) Nicotinic receptors on hippocampal cultures can increase synaptic glutamate recurrents while decreasing the NMDA-receptor component. Neuropharmacology 39, 2756–2769.
Alonso M., Bevilaqua L. R., Izquierdo I., Medina J. H., and Cammarota M. (2003) Memory formation requires p38MAPK activity in the rat hippocampus. Neuroreport 14, 1989–1992.
Atkins C. M., Selcher J. C., Petraitis J. L., Trzaskos J. M., and Sweatt J. D. (1998) The MAPK cascade is required for mammalian associative learning. Nat. Neurosci. 1, 602–609.
Waltereit R. and Weller M. (2003) Signaling from cAMP/PKA to MAPK and synaptic plasticity. Mol. Neurobiol. 27, 99–106.
Schafe G. E., Atkins C. M., Swank M. W., Bauer E. P., Sweatt J. D., and Ledoux J. E. (2000) Activation of ERK/MAP kinase in the amygdala is required for memory consolidation of pavlovian fear conditioning. J. Neurosci. 20, 8177–8187.
Selcher J. C., Atkins C. M., Trzaskos J. M., Paylor R., and Sweatt J. D. (1999) A necessity for MAP kinase activation in mammalian spatial learning. Learn. Mem. 6, 478–490.
Shalin S. C., Zirrgiebel U., Honsa K. J., et al. (2004) Neuronal MEK is important for normal fear conditioning in mice. J. Neurosci. Res. 75, 760–770.
Chang K. T. and Berg D. K. (2001) Voltage-gated channels block nicotinic regulation of CREB phosphorylation and gene expression in neurons. Neuron 32, 855–865.
Dajas-Bailador F. A., Soliakov L., and Wonnacott S. (2002) Nicotine activates the extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 via the alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor and protein kinase A in SH-SY5Y cells and hippocampal neurones. J. Neurochem. 80, 520–530.
Valjent E., Pages C., Herve D., Girault J. A., and Caboche J. (2004) Addictive and non-addictive drugs induce distinct and specific patterns of ERK activation in mouse brain Eur. J. Neurosci. 19, 1826–1836.
Zhang S. H., Day I. M., and Ye S. H. (2001) Microrray analysis of nicotine-induced changes in gene expression in endothelial cells. Physiol. Genom. 5, 187–192.
Konu O., Kane J. K., Barrett T., et al. (2001) Region-specific transcriptional response to chronic nicotine in rat brain. Brain Res. 909, 194–203.
Davis J. A., James J. R., Siegel S. J., and Gould T. J. (2005) Withdrawal from chronic nicotine administration impairs contextual fear conditioning in C57BL/6 mice. J. Neurosci. 25, 8708–8713.
Koob G. F. and Bloom F. E. (1988) Cellular and molecular mechanisms of drug dependence. Science 242, 715–723.
Benowitz N. L., Porchet H., and Jacob P., III (1989) Nicotine dependence and tolerance in man: pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic investigations. Prog. Brain Res. 79, 279–287.
Henningfield J. E. and Keenan R. M. (1993) Nicotine delivery kinetics and abuse liability. J. Consult. Clin. Psychol. 61, 743–750.
Brunzell D. H., Russell D. S., and Picciotto M. R. (2003) In vivo nicotine treatment regulates mesocorticolimbic CREB and ERK signaling in C57B1/6J mice. J. Neurochem. 84, 1431–1441.
Marks M. J., Burch J. B., and Collins A. C. (1983) Genetics of nicotine response in four inbred strains of mice. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 226, 291–302.
Marks M. J., Rowell P. P., Cao J. Z., Grady S. R., McCallum S. E., and Collins A. C. (2004) Subsets of acetylcholine-stimulated 86Rb+ efflux and (125I)-epibatidine binding sites in C57BL/6 mouse brain are differentially affected by chronic nicotine treatment. Neuropharmacology 46, 1141–1157.
Peng X., Gerzanich V., Anand R., Wang F., and Lindstrom J. (1997) Chronic nicotine treatment up-regulates alpha3 and alpha7 acetylcholine receptor subtypes expressed by the human neuroblastoma cell line SH-SY5Y. Mol. Pharmacol. 51, 776–784.
Marks M. J., Grady S. R., and Collins A. C. (1993) Downregulation of nicotinic receptor function after chronic nicotine infusion. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 266, 1268–1276.
Schwartz R. D. and Kellar K. J. (1985) In vivo regulation of (3H)acetylcholine recognition sites in brain by nicotinic cholinergic drugs. J. Neurochem. 45, 427–433.
Olale F., Gerzanich V., Kuryatov A., Wang F., and Lindstrom J. (1997) Chronic nicotine exposure differentially affects the function of human alpha3, alpha4, and alpha7 neuronal nicotinic receptor subtypes. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 283, 675–683.
Gentry C. L., Wilkins L. H. Jr., and Lukas R. J. (2003) Effects of Prolonged Nicotinic Ligand Exposure on Function of Heterologously Expressed, Human alpha 4beta 2- and alpha 4beta 4-Nicotinic Acetylcholine Recptors. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 304, 206–216.
Picciotto M. R., Caldarone B. J., King S. L., and Zachariou V. (2000) Nicotinic receptors in the brain. Links between molecular biology and behavior. Neuropsychopharmacology 22, 451–465.
McCallum S., Collins A. Paylor R., and Marks M. (2006) Deletion of the beta 2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunit alters development of tolerance to nicotine and eliminates receptor upregulation. Psychopharmacology 184, 314–327.
Tzavara E. T., Monory K., Hanoune J., and Nomikos G. G. (2002) Nicotine withdrawal syndrome: behavioural distress and selective up-regulation of the cyclic AMP pathway in the amygdala. Eur. J. Neurosci. 16, 149–153.
Pandey S. C., Roy A., Xu T., and Mittal N. (2001) Effects of protracted nicotine exposure and withdrawal on the expression and phosphorylation of the CREB gene transcription factor in rat brain. J. Neurochem. 77, 943–952.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gould, T.J. Nicotine and hippocampus-dependent learning. Mol Neurobiol 34, 93–107 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1385/MN:34:2:93
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/MN:34:2:93