Abstract
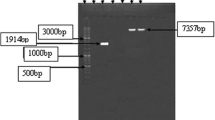
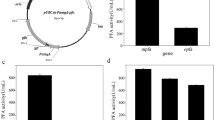
Pyrococcus woesei (DSM 3773) α-amylase gene was cloned into pET21d(+) and pYTB2 plasmids, and the pET21d(+)α-amyl and pYTB2α-amyl vectors obtained were used for expression of thermostable α-amylase or fusion of α-amylase and intein in Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) or BL21(DE3)pLysS cells, respectively. As compared with other expression systems, the synthesis of α-amylase in fusion with intein in E. coli BL21(DE3)pLysS strain led to a lower level of inclusion bodies formation—they exhibit only 35% of total cell activity—and high productivity of the soluble enzyme form (195,000 U/L of the growth medium). The thermostable α-amylase can be purified free of most of the bacterial protein and released from fusion with intein by heat treatment at about 75°C in the presence of thiol compounds. The recombinant enzyme has maximal activity at pH 5.6 and 95°C. The half-life of this preparation in 0.05 M acetate buffer (pH 5.6) at 90°C and 110°C was 11 h and 3.5 h, respectively, and retained 24% of residual activity following incubation for 2 h at 120°C. Maltose was the main end product of starch hydrolysis catalyzed by this α-amylase. However, small amounts of glucose and some residual unconverted oligosaccharides were also detected. Furthermore, this enzyme shows remarkable activity toward glycogen (49.9% of the value determined for starch hydrolysis) but not toward pullulan.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Koch, R., Spreinat, A., Lemke, K., and Antranikian, G. (1991) Purification and properties of a hyperthermoactive α-amylase from the archaebacterium P. woesei. Arch. Microbiol. 155, 572–578.
Linden, A., Niehaus F., and Antranikian, G. (2000) Single-step purification of a recombinant thermostable α-amylase after solubilization of the enzyme from insoluble aggregates. J. Chromatogr. 737, 253–259.
Fischer, B., Sumner, I., and Goodenough, P. (1993) Isolation, renaturation, and formation of disulfide bonds of eukaryotic proteins expressed in Escherichia coli as inclusion bodies. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 41, 3–13.
Uemori, T., Ishino, Y., Toh, H., Asada, K., and Kato, I. (1993) Organization and nucleotide sequence of the DNA polymerase from the archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus. Nucleic Acids Res. 21, 259–265.
Bernfeld, P. (1955) Amylases α and β. Methods Enzymol. 1, 149–158.
Bradford, M. M. (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for quantication of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72, 248–254.
Laemmli, U. K. (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227, 680–685.
Hansen, S. A. (1975) Thin-layer chromatography method for identification of oligosaccharides in starch hydrolysates. J. Chromatogr. 105, 388–390.
Laderman, K. A., Asada, K., Uemori, T., et al. (1993) α-Amylase from the hyperthermophilic archaebacterium Pyrococcus furiosus. J. Biol. Chem. 268, 24,402–24,407.
Dong, G., Vieille, C., Savchenko, A., and Zeikus, J. G. (1997) Cloning, sequencing, and expression of the gene encoding extracellular α-amylase from Pyrococcus furiosus and biochemical characterization of the recombinant enzyme. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 63, 3569–3576.
Pisani, F. M., Rella, R., Raja, C. A., et al. (1990) Thermostable β-galactosidase from the archaebacterium sulfolobus solfatoricus: purification and porperties. Eur. J. Blochem. 187, 321–328.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grzybowska, B., Szweda, P. & Synowiecki, J. Cloning of the thermostable α-amylase gene from Pyrococcus woesei in Escherichia coli . Mol Biotechnol 26, 101–109 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1385/MB:26:2:101
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/MB:26:2:101