Abstract
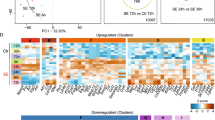
Unlike adults, kainic acid (KA)-induced status epilepticus (SE) in immature rats causes neither cell death nor recurrent spontaneous seizures. To elucidate the mechanisms of these distinct responses, transcriptional changes in neuropeptides were examined following KA-induced SE. We aimed to determine whether neuropeptides with anticonvulsant/neuroprotective properties were preferentially increased in immature rats while those with a proconvulsant/neurotoxic role were elevated to a greater extent in mature rats. We used high-density oligonucleotide gene arrays and directly compared transcriptional regulation of seven select neuropeptides at P15 and P30 over five time points. Total RNAs were isolated from hippocampi of 12 animals and pooled to hybridize to triplicate Affymetrix Genechips. Microarray results were validated by real-time quantitative RT-PCR (qRT-PCR). Independent individual RNA samples were purified for triplicate runs of qRT-PCR. Neuropeptides are significantly regulated by seizures in both immature and mature hippocampus. The magnitude of increase is significantly higher at P30 compared with that at P15, not only for neuropeptides with neurotoxic/proconvulsant properties but also for those with neuroprotective/anticonvulsant properties. Galanin is induced at 24 h only in P30 rats. CST shows high expression in immature hippocampus and is further increased after KA-induced SE only in P15. The expression trends seen in the microarray data are confirmed by qRT-PCR for all six neuropeptides analyzed. CST might play a neuroprotective role in immature rats, and its overexpression might prevent neuronal loss after seizure in adults. Also, suppression of tachykinin and corticotropin-releasing hormone might be effective in alleviating seizure-induced neuronal damage.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albala B. J., Moshe S. L., and Okada R. (1984) Kainic-acid-induced seizures: a developmental study. Brain Res. 315, 139–148.
Avishai-Eliner S., Brunson K. L., Sandman C. A., and Baram T. Z. (2002) Stressed-out, or in (utero)? Trends Neurosci. 25, 518–524.
Baraban S. C., Hollopeter G., Erickson J. C., Schwartzkroin P. A., and Palmiter R. D. (1997) Knock-out mice reveal a critical antiepileptic role for neuropeptide Y. J. Neurosci. 17, 8927–8936.
Baram T. Z. and Hatalski C. G. (1998) Neuropeptide-mediated excitability: a key triggering mechanism for seizure generation in the developing brain. Trends Neurosci. 21, 471–476.
Behan D. P., De Souza E. B., Lowry P. J., Potter E., Sawchenko P., and Vale W. W. (1995) Corticotropin releasing factor (CRF) binding protein: a novel regulator of CRF and related peptides. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 16, 362–382.
Bellmann R., Widmann R., Olenik C., Meyer D. K., Maas D., Marksteiner J., and Sperk G. (1991) Enhanced rate of expression and biosynthesis of neuropeptide Y after kainic acid-induced seizures. J. Neurochem. 56, 525–530.
Ben-Ari Y. (1985) Limbic seizure and brain damage produced by kainic acid: mechanisms and relevance to human temporal lobe epilepsy. Neuroscience 14, 375–403.
Bengzon J., Mohapel P., Ekdahl C. T., and Lindvall O. (2002) Neuronal apoptosis after brief and prolonged seizures. Prog. Brain Res. 135, 111–119.
Braun H., Schulz S., Becker A., Schroder H., and Hollt V. (1998) Protective effects of cortistatin (CST-14) against kainate-induced neurotoxicity in rat brain. Brain Res. 803, 54–60.
Buckmaster P. S., Otero-Corchon V., Rubinstein M., and Low M. J. (2002) Heightened seizure severity in somatostatin knockout mice. Epilepsy Res. 48, 43–56.
Calbet M., Guadano-Ferraz A., Spier A. D., Maj M., Sutcliffe J. G., Przewlocki R., and de Lecea L. (1999) Cortistatin and somatostatin mRNAs are differentially regulated in response to kainate. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 72, 55–64.
Cavalheiro E. A., Silva D. F., Turski W. A., Calderazzo-Filho L. S., Bortolotto Z. A., and Turski L. (1987) The susceptibility of rats to pilocarpine-induced seizures is age-dependent. Brain Res. 465, 43–58.
Chen Y., Bender R. A., Frotscher M., and Baram T. Z. (2001) Novel and transient populations of corticotropin-releasing hormone-expressing neurons in developing hippocampus suggest unique functional roles: a quantitative spatiotemporal analysis. J. Neurosci. 21, 7171–7181.
Chepurnov S. A., Chepurnova N. E., and Berdiev R. K. (1998) Galanin controls excitability of the brain. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 865, 547–550.
Cortes R., Ceccatelli S., Schalling M., and Hokfelt T. (1990) Differential effects of intracerebroventricular colchicine administration on the expression of mRNAs for neuropeptides and neurotransmitter enzymes, with special emphasis on galanin: an in situ hybridization study. Synapse 6, 369–391.
Drake C. T., Terman G. W., Simmons M. L., Milner T. A., Kunkel D. D., Schwartzkroin P. A., and Chavkin C. (1994) Dynorphin opioids present in dentate granule cells may function as retrograde inhibitory neurotransmitters. J. Neurosci. 14, 3736–3750.
Ehlers C. L., Henriksen S. J., Wang M., Rivier J., Vale W., and Bloom F. E. (1983) Corticotropin releasing factor produces increases in brain excitability and convulsive seizures in rats. Brain Res. 278, 332–336.
Elliott-Hunt C. R., Marsh B., Bacon A., Pope R., Vanderplank P., and Wynick D (2004) Galanin acts as a neuroprotective factor to the hippocampus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 10, 5105–5110.
Gibson U. E., Heid C. A., and Williams P. M. (1996) A novel method for real time quantitative RT-PCR. Genome Res. 6, 9951001.
Hashimoto T. and Obata K. (1991) Induction of somatostatin by kainic acid in pyramidal and granule cells of the rat hippocampus. Neurosci. Res. 12, 514–527.
Hatalski C. G., Brunson K. L., Tantayanubutr B., Chen Y., and Baram T. Z. (2000) Neuronal activity and stress differentially regulate hippocampal and hypothalamic corticotropin-releasing hormone expression in the immature rat. Neuroscience 101, 571–580.
Haut S. R., Veliskova J., and Moshe S. L. (2004) Susceptibility of immature and adult brains to seizure effects. Lancet Neurol. 3, 608–617.
Heid C. A., Stevens J., Livak K. J., and Williams P. M. (1996) Real time quantitative PCR. Genome Res. 6, 986–994.
Hellier J. L., Patrylo P. R., Buckmaster P. S., and Dudek F. E. (1998) Recurrent spontaneous motor seizures after repeated low-dose systemic treatment with kainate: assessment of a rat model of temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsy Res. 31, 73–84.
Holland P. M., Abramson R. D., Watson R., and Gelfand D. H. (1991) Detection of specific polymerase chain reaction product by utilizing the 5′—3′ exonuclease activity of Thermus aquaticus DNA polymerase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 88, 7276–7280.
Jokeit H. and Ebner A. (1999) Long term effects of refractory temporal lobe epilepsy on cognitive abilities: a cross sectional study. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 67, 44–50.
Knoblach S. M. and Kubek M. J. (1997) Changes in thyrotropin-releasing hormone levels in hippocampal subregions induced by a model of human temporal lobe epilepsy: effect of partial and complete kinding. Neuroscience 76, 97–104.
Kotloski R., Lynch M., Lauersdorf S., and Sutula T. (2002) Repeated brief seizures induce progressive hippocampal neuron loss and memory deficits. Prog. Brain Res. 135, 95–110.
Leite J. P., Garcia-Cairasco N., and Cavalheiro E. A. (2002) New insights from the use of pilocarpine and kainate models. Epilepsy Res. 50, 93–103.
Lin E. J., Richichi C., Young D., Baer K., Vezzani A., and During M. J. (2003) Recombinant AAV-mediated expression of galanin in rat hippocampus suppresses seizure development. Eur. J. Neurosci. 18, 2087–2092.
Liu H., Mazarati A. M., Katsumori H., Sankar R., and Wasterlain C. G. (1999) Sustance P is expressed in hippocampal principal neurons during status epilepticus and plays a critical role in the maintenance of status epilepticus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 96, 5286–5291.
Liu H., Sankar R., Shin D. H., Mazarati A. M., and Wasterlain C. G. (2000) Patterns of status epilepticus-induced substance P expression during development. Neuroscience 101, 297–304.
Maecker H., Desai A., Dash R., Rivier J., Vale W., and Sapolsky R. (1997) Astressin, a novel and potent CRF antagonist, is neuroprotective in the hippocampus when administered after a seizure. Brain Res. 744, 166–170.
Mazarati A. M., Hohmann J. G., Bacon A., Liu H., Sankar R., Steiner R. A., et al. (2000) Modulation of hippocampal excitability and seizures by galanin. J. Neurosci. 20, 6276–6281.
Mazarati A. M., Liu H., Soomets U., Sankar R., Shin D., Katsumori H., et al. (1998) Galanin modulation of seizures and seizure modulation of hippocampal galanin in animal models of status epilepticus. J. Neurosci. 18, 10070–10077.
Merchenthaler I., Lopez F. J., and Negro-Vilar A. (1993) Anatomy and physiology of central galanin-containing pathways. Prog. Neurobiol. 40, 711–769.
Nadler J. V. (1981) Minireview. Kainic acid as a tool for the study of temporal lobe epilepsy. Life Sci. 29, 2031–2042.
Nitecka L., Tremblay E., Charton G., Bouillot J. P., Berger M. L., and Ben-Ari Y. (1984) Maturation of kainic acid seizure-brain damage syndrome in the rat. II. Histopathological sequelae. Neuroscience 13, 1073–1094.
Perez J., Vezzani A., Civenni G., Tutka P., Rizzi M., Schupbach E., and Hoyer D. (1995) Functional effects of D-Phe-c[Cys-Tyr-D-Trp-Lys-Val-Cys]-Trp-NH2 and differential changes in somatostatin receptor messenger RNAs, binding sites and somatostatin release in kainic acid-treated rats. Neuroscience 65, 1087–1097.
Piekut D. T. and Phipps B. (1998) Increased corticotropin-releasing factor immunoreactivity in select brain sites following kainate elicited seizures. Brain Res. 781, 100–113.
Poirier J. L., Capek R., and De Koninck Y. (2000) Differential progression of Dark Neuron and Fluoro-Jade labelling in the rat hippocampus following pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus. Neuroscience 97, 59–68.
Ribak C. E. and Baram T. Z. (1996) Selective death of hippocampal CA3 pyramidal cells with mossy fiber afferents after CRH-induced status epilepticus in infant rats. Brain Res. Dev. Brain Res. 91, 245–251.
Richichi C., Lin E. J., Stefanin D., Colella D., Ravizza T., Grignaschi G., et al. (2004) Anticonvulsant and antiepileptogenic effects mediated by adeno-associated virus vector neuropeptide Y expression in the rat hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 24, 3051–3059.
Romijn H. J., Hofman M. A., and Gramsbergen A. (1991) At what age is the developing cerebral cortex of the rat comparable to that of the full-term newborn human baby? Early Hum. Dev. 26, 61–67.
Sadzot B. (1997) Epilepsy: a progressive disease? BMJ 314, 391,392.
Sayin U., Osting S., Hagen J., Rutecki P., and Sutula T. (2003) Spontaneous seizures and loss of axo-axonic and axo-somatic inhibition induced by repeated brief seizures in kindled rats. J. Neurosci. 23, 2759–2768.
Schwarzer C., Sperk G., Samanin R., Rizzi M., Gariboldi M., and Vezzani A. (1996) Neuropeptides—immunoreactivity and their mRNA expression in kindling: functional implications for limbic epileptogenesis. Brain Res. Brain Res. Rev. 22, 27–50.
Senut M. C., Menetrey D., and Lamour Y. (1989) Cholinergic and peptidergic projections from the medial septum and the nucleus of the diagonal band of Broca to dorsal hippocampus, cingulate cortex and olfactory bulb: a combined wheatgerm agglutinin-apohorseradish peroxidase-gold immunohistochemical study. Neuroscience 30, 385–403.
Smialowska M., Bijak M., Sopala M., and Tokarski K. (1996) Inhibitory effect of NPY on the picrotoxin-induced activity in the hippocampus: a behavioural and electrophysiological study. Neuropeptides 30, 7–12.
Smialowska M., Wieronska J. M., and Szewczyk B. (2003) Neuroprotective effect of NPY on kainate neurotoxicity in the hippocampus. Pol. J. Pharmacol. 55, 979–986.
Sperber E. F., Haas K. Z., Stanton P. K., and Moshe S. L. (1991) Resistance of the immature hippocampus to seizure-induced synaptic reorganization. Brain Res. Dev. Brain Res. 60, 88–93.
Sperk G., Marksteiner J., Gruber B., Bellmann R., Mahata M., and Ortler M. (1992) Functional changes in neuropeptide Y- and somatostatin-containing neurons induced by limbic seizures in the rat. Neuroscience 50, 831–846.
Stafstrom C. E., Thompson J. L., and Holmes G. L. (1992) Kainic acid seizures in the developing brain: status epilepticus and spontaneous recurrent seizures. Brain Res. Dev. Brain Res. 65, 227–236.
Storey J. D. and Tibshirani R. (2003) Statistical significance for genomewide studies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 100, 9440–9445.
Toth Z., Yan X. X., Haftoglou S., Ribak C. E., and Baram T. Z. (1998) Seizure-induced neuronal injury: vulnerability to febrile seizures in an immature rat model. J. Neurosci. 18, 4285–4294.
Vezzani A. and Hoyer D. (1999) Brain somatostatin: a candidate inhibitory role in seizures and epileptogenesis. Eur. J. Neurosci. 11, 3767–3776.
Vezzani A., Michalkiewicz M., Michalkiewicz T., Moneta D., Ravizza T., Richichi C., et al. (2002) Seizure susceptibility and epileptogenesis are decreased in transgenic rats overexpressing neuropeptide Y. Neuroscience 110, 237–243.
Woldbye D. P., Larsen P. J., Mikkelsen J. D., Klemp K., Madsen T. M., and Bolwig T. G. (1997) Powerful inhibition of kainic acid seizures by neuropeptide Y via Y5-like receptors. Nat. Med. 3, 761–764.
Woldbye D. P., Madsen T. M., Larsen P. J., Mikkelsen J. D., and Bolwig T. G. (1996) Neuropeptide Y inhibits hippocampal seizures and wet dog shakes. Brain Res. 737, 162–168.
Zachrisson O., Lindefors N., and Brene S. (1998) A tachykinin NK1 receptor antagonist, CP-122,721-1, attenuates kainic acid-induced seizure activity. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 60, 291–295.
Zhang X., Cui S. S., Wallace A. E., Hannesson D. K., Schmued L. C., Saucier D. M., et al. (2002) Relations between brain pathology and temporal lobe epilepsy. J. Neurosci. 22, 6052–6061.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wilson, D.N., Chung, H., Elliott, R.C. et al. Microarray analysis of postictal transcriptional regulation of neuropeptides. J Mol Neurosci 25, 285–298 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1385/JMN:25:3:285
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/JMN:25:3:285