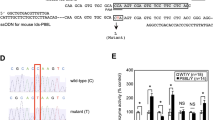
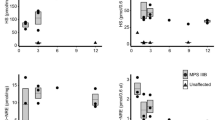
Abstract
Mucopolysaccharidosis IIID (MPS IIID) is a lysosomal storage disease associated with deficient activity of the enzyme N-acetylglucosamine 6-sulfatase (EC 3.1.6.14), a lysosomal hydrolase in the heparan sulfate glycosaminoglycan (HS-GAG) degradation pathway. In caprine MPS IIID, enzyme replacement therapy reversed early postnatal systemic but not primary or secondary central nervous system (CNS) substrate accumulations. The caprine MPS IIID large animal model system was used in this investigation to define the developmental profile of morphological and biochemical perturbations to estimate a time frame for therapeutic intervention. Light and electron microscopy were used to compare the CNS, liver, and kidney of normal +/+, MPS IIID carrier +/-, and MPS IIID-affected -/- goat kids (kids), at 60, 113–114, 128–129, and 135 d gestation (dg) of a 150-d gestational period, at birth, and at 59–64 d of postnatal (d-pn) age. In the CNS of -/- kids, morphological correlations of HS-GAG and glycolipid accumulations were evident in early differentiating neurons at 60 dg. CNS and systemic developmental, regional, and cellular differences in -/-kids at all time points included more prominent and earlier accumulation of lucent, putative HS-GAG substrates in lysosomes of meningeal and perivascular macrophages and hepatic sinusoidal cells than in CNS, hepatic, or renal parenchymal cells. The amounts and compositions of HS-GAG substrates in the brain and liver of +/+, +/-, and -/- kids were determined at 60, 65, 113–114, and 128–135 dg, at birth, and 53–78 d-pn. In the CNS of -/- kids, HS-GAG concentrations were variable and exceeded those of age-matched control tissue samples in the third but not the second trimester. In contrast, hepatic HS-GAG levels in -/- kids exceeded control values at all time points evaluated and paralleled the progressive morphological alterations. CNS and hepatic HS-GAG compositions in -/- kids were similar to each other and were more complex at all pre- and postnatal ages than those from control kids. Based on the time frame of development of CNS lesions and biochemical perturbations, prenatal therapeutic intervention in caprine MPS IIID is likely to be necessary to prevent or ameliorate substantive CNS and systemic lesions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ando S. (1983) Gangliosides in the nervous system. Neurochem. Int. 5, 507–537.
Auclair D., Hopwood J. J., Brooks D. A., Lemontt J. A., and Crawley A. C. (2003) Replacement therapy in mucopolysaccharidosis type VI: advantages of early onset of therapy. Mol. Genet. Metab. 78, 163–174.
Avila J. L. and Convit J. (1975) Inhibition of leucocytic lysosomal enzymes by glycosaminoglycans in vitro Biochem. J. 152, 57–64.
Baumkotter J. and Cantz M. (1983) Decreased ganglioside neuraminidase activity in fibroblasts from mucopolysaccharidosis patients. Inibition of the activity in vitro by sulfated glycosaminoglycans and other compounds. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 761, 163–170.
Blumenkrantz N. and Asboe-Hansen G. (1973) New method for quantitative determination of uronic acid. Anal. Biochem. 54, 484–489.
Byers S., Rolazkis T., Brumfield L. K., Ranieri E., and Hopwood, J. J. (1998). Glycosaminoglycan accumulation and excretion in the mucopolysaccharidoses: characterization and basis of a diagnostic test for MPS. Mol. Gene Met. 65, 282–290.
Casal M. L. and Wolfe J. H. (2000) Mucopolysaccharidosis type VII in the developing mouse fetus. Pediatr. Res. 47, 750–756.
Castagnaro M., Alroy J., Ucci A. A., and Glew R. H. (1987) Lectin histochemistry and ultrastructure of feline kidneys from six different storage diseases. Virchows Arch. B. 54, 16–26.
Cavanagh K. T., Leipprandt J. R., Jones M. Z., and Friderici K. (1995) Molecular defect of caprine N-acetylglucosamine-6-sulphatase deficiency. A single base substitution creates a stop codon in the 5′-region of the coding sequence. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 18, 96.
Ceuterick C., Martin J. J., Libert J., and Farriaux J. P (1980) Sanfilippo A disease in the fetus-comparison with pre- and postnatal cases. Neuropadiatrie 11(2), 176–185.
Downs-Kelly E., Jones M. Z., Alroy J., Cavanagh K. T., King B., Lucas R. E., et al. (2000) Caprine mucopolysaccharidosis IIID: A preliminary trial of enzyme replacement therapy. J. Mol. Neurosci. 15, 251–262.
Friderici K., Cavanagh K. T., Leipprandt J. R., Traviss C. E., Anson D. S., Hopwood J. J., and Jones M. Z. (1995) Cloning and sequence analysis of caprine N-acetylglucosamine 6-sulfatase cDNA. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1271, 369–373.
Fu H., Samulski R. J., McCown T. J., Picornell Y. J., Fletcher D., and Muenzer J. (2002) Neurological correction of lysosomal storage in a mucopolysaccharidosis IIIB mouse model by adeno-associated virus-mediated gene delivery. Mol. Ther. 5, 42–49.
Ginsberg S. D., Galvin J. E., Lee V. M. Y., Rorke L. B., Dickson D. W., Wolfe J. H., et al. (1999) Accumulation of intracellular amyloid-β peptides (Aβ1-40) in mucopolysaccharidosis brains. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 58, 815–824.
Gliddon B. L. and Hopwood J. J. (2004) Enzyme replacement therapy from birth delays the development of behavior and learning problems in mucopolysaccharidosis type-IIIA mice. Pediatr. Res. 56, 65–72.
Greenwood R. S., Hillman R. E., Alcala H., and Sly W. S. (1978) Sanfilippo A syndrome in the fetus. Clin. Genet. 13, 241–250.
Hannun Y. A. and Bell R. M. (1987) Lysosphingolipids inhibit protein kinase C: implications for the sphingolipidoses. Science 235, 670–674.
Harper P. S., Laurence K. M., Parkes A., Wusteman F. S., Kresse H., von Figura K., et al. (1974) Sanfilippo A disease in the fetus. J. Med. Genet. 11, 123–132.
Haskins M. E., Otis E. J., Hayden J. E., Jezyk P. F., and Stramm L. (1992) Hepatic storage of glycosaminoglycans in feline and canine models of mucopolysaccharidosis I, VI, and VII. Vet. Pathol. 29, 112–119.
Ho T. T., Maguire A. M. Aguirre G. D., Surace E. M., Anand V., Zeng Y., et al. (2002) Phenotypic rescue after adenoassociate virus-mediated delivery of 4-sulfatase to the retinal pigment epithelium of feline mucopolysaccharidosis VI. J. Genet. Med. 4, 613–621.
Ikeno T., Minami R., Tsugawa S., and Nakao T. (1982) Acidic glycosaminoglycans and gangliosides in the brains from four patients with genetic mucopolysaccharidosis. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 137, 253–260.
Instani M., Irie F., Plump A. S., Tessier-Lavigne M., and Yamaguchi Y. (2003) Mammalian brain morphogenesis and midline axon guidance require heparan sulfate. Science 302, 1044–1046.
Jones M. Z., Alroy J., Boyer P. J., Cavanagh K. T., Johnson K., Gage D., et al. (1998) Caprine mucopolysaccharidosis-IIID: clinical, biochemical, morphological and immunohistochemical characteristics. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 57, 148–157.
Jones M. Z., Alroy J., Rutledge J. C., Taylor J. W., Alvord E. C., Jr., Toone J., et al. (1997) Human mucopolysaccharidosis IIID: clinical, biochemical, morphological and immunohistochemical characteristics. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 56, 1158–1167.
Jones M. Z., Rathke E. J. S., Cavanagh K., and Hancock L. W. (1984) β-Mannosidosis: Prenatal biochemical and morphological characteristics. J. Inher. Metab. Dis. 7, 80–85.
Leipprandt J. R., Friderici K., Sprecher D. J., and Jones M. Z. (1995) Prenatal testing for caprine N-acetylglucosamine-6-sulphatase deficiency and sex identification. J. Inher. Metab. Dis. 18, 647–648.
Liour S. S., Jones M. Z., Suzuki M., Bieberich E., and Yu, R. K. (2001) Metabolic studies of glycosphingolipid accumulation in mucopolysaccharidosis IIID. Mol. Genet. Metab. 72, 239–247.
Lovell K. L., Kraemer S. A., Leipprandt J. R., Sprecher D. J., Ames N. K., Nichols-Torrez J., et al. (2001) In utero hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a caprine model for prenatal therapy in inherited metabolic diseases. Fetal Diagn. Ther. 16, 13–17.
Lovell K. L., Matsuura F., Patterson J., Baeverfjord G., Ames N. K., and Jones M. Z. (1997) Biochemical and morphological expression of early prenatal caprine β-mannosidosis. Prenat. Diagn. 1, 551–557.
Lovell K. L., Mitchell-Herpolsheimer C., Ames N. K., and Snyder E. Y. (1996) Prenatal engraftment of CNS stem-like cells: an approach to therapy for caprine β-mannosidosis. Soc. Neurosci. Abstr. 22, 577–577.
Meier C., Wiesmann U., Herschkowitiz N., and Bischoff A. (1979) Morphological observations in the nervous system of prenatal mucopolysaccharidosis II (M. Hunter) Acta Neuropathol. 48, 139–143.
Meertens L., Zhao Y., Rosic-Kablar S., Li L., Chan K., Dobson H., et al. (2002) In utero injection of α-L-iduronidase-carrying retrovirus in canine mucopolysaccharidosis type I: infection of multiple tissues and neonatal gene expression. Hum. Gene Ther. 13, 1809–1820.
Mito T., Nakano C. Yoshino K., Takashima S., Hashimoto K., Yumoto T., and Tanaka J. (1984) Histopathological study on the fetus of Sanfilippo B Disease. No To Hattatsu 16, 481–486.
Neufeld E. F. and Muenzer J. (2001) The mucopolysaccharidoses in The Metabolic and Molecular Bases of Inherited Disease, Scriver, C. R., Beaudet, A. L., Sly, W. S., Valle, D., Childs B., Kinzler K. W., and Vogelstein B., eds., McGraw-Hill, New York, pp. 3421–3452.
Obeid L. M., Linardic C. M., Karolak L. A., and Hannun Y. A. (1993) Programmed cell death induced by ceramide. Science 259, 1769–1771.
Ogawa-Goto K., Funamoto N., Abe T., and Nagashima K. (1990) Different ceramide compositions of gangliosides between human motor and sensory nerves. J. Neurochem. 55, 1486–1493.
Perrimon N. and Bernfield M. (2000) Specificities of heparan sulphate proteoglycans in developmental processes. Nature 404, 725–728.
Prasad A., Kaye E. M., and Alroy J. (1996) Electron microscopic examination of skin biopsy as a cost-effective tool in the diagnosis of lysosomal storage diseases. J. Child. Neurol. 11, 301–308.
Salmivirta M., Lidholt K., and Lindahl U. (1996) Heparan sulfate: a piece of information. FASEB J. 10, 1270–1279.
Sands M. S., Vogler C., Kyle J. W., Grubb J. H., Levy B., Galvin N., Sly W. S., and Birkenheimer G. H. (1994) Enzyme replacement therapy for murine mucopolysaccharidosis type VII. J. Clin. Invest. 93, 2324–2331.
Selleck S. B. (2000) Proteoglycans and pattern formation: sugar biochemistry meets developmental genetics. Trends Genet. 16, 206–212.
Selznick L. A., Zheng T. S., Flavell R. A., Rakic P., and Roth K. A. (2000) Amyloid beta-induced neuronal death is bax-dependent but caspase-independent. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 59, 271–279.
Thompson J. N., Jones M. Z., Dawson G., and Huffman P. S. (1992) N-acetylglucosamine 6-sulphatase deficiency in a Nubian goat: a model of Sanfilippo syndrome type D (mucopolysaccharidosis IIID). J. Inher. Metab. Dis. 15, 760–768.
Tumova S., Woods A., and Couchman J. R. (2000) Heparan sulfate proteoglycans on the cell surface: versatile coordinators of cellular functions. Int. J. Biochem. Cell. Biol. 32, 269–288.
Vogler C., Levy B., Galvin N. J., Thorpe C., Sands M. S., Barker J. E., et al. (1999) Enzyme replacement in murine mucopolysaccharidosis type VII: neuronal and glial response to beta-glucuronidase requires early initiation of enzyme replacement therapy. Pediatr. Res. 45, 838–844.
Wiesmann U., Spycher M. A., Meier C., Liebaers I. L., and Herschkowitz N. (1980) Prenatal mucopolysaccharidosis II (Hunter): a pathogenetic study. Pediatr. Res. 14, 749–756.
Yu R. K. and Saito M. (1989) Structure and localization of gangliosides, in Neurobiology of Glycoconjugates, Margolis, R. U., and Margolis, R. K., eds., Plenum Press, New York, pp. 1–42.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jones, M.Z., Alroy, J., Downs-Kelly, E. et al. Caprine mucopolysaccharidosis IIID. J Mol Neurosci 24, 277–291 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1385/JMN:24:2:277
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/JMN:24:2:277