Abstract
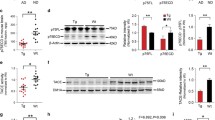
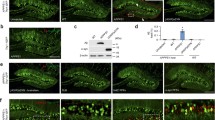
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease associated with increased expression of amyloid precursor protein (APP) and the deposition of its proteolytic cleavage products, the amyloid-β peptides, Aβ1–40 and Aβ1–42. Peptide nucleic acids (PNAs) have been shown to block the expression of proteins at transcriptional and translational levels. In this study we used a sense and an antisense PNA specifically targeted to APP to inhibit the transcription and translation of APP by complementary binding to DNA or mRNA, respectively. Using Western blotting, APP showed a drastic decrease (50% and 90% reduction, in two separate experiments, as compared with saline control) with the injection of sense APP mRNA levels were higher at the same time point after injection of APP sense PNA, most probably because of a compensatory mechanism in response to the drop of APP that might have occurred at an earlier time point (0–1 h) and was reflected in a drop at the protein level at 1 h. The injection of antisense PNA showed about 70% decrease in APP as measured by Western blotting. Unmodified PNA can be used in vivo to reduce the levels of APP, which plays a critical role in the development of AD.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adlerz L., Soomets U., et al. (2003) Down-regulation of amyloid precursor protein by peptide nucleic acid oligomer in cultured rat primary neurons and astrocytes. Neurosci. Lett. 336(1), 55–59.
Corey D. R. (1997) Peptide nucleic acids: expanding the scope of nucleic acid recognition. Trends Biotechnol. 15(6), 224–229.
Demidov V. V., Potaman V. N., et al. (1994) Stability of peptide nucleic acids in human serum and cellular extracts. Biochem. Pharmacol. 48(6), 1310–1313.
Fraser G. L., Holmgren J., et al. (2000) Antisense inhibition of delta-opioid receptor gene function in vivo by peptide nucleic acids. Mol. Pharmacol. 57(4), 725–731.
Hanvey J. C., Peffer N. J., et al. (1992) Antisense and antigene properties of peptide nucleic acids. Science 258(5087), 1481–1485.
Hardy J. (1997) Amyloid, the presenilins and Alzheimer’s disease. Trends Neurosci. 20(4), 154–159.
McMahon B. M., Stewart J. A., et al. (2002) Peptide nucleic acids specifically cause antigene effects in vivo by systemic injection. Life Sci. 71(3), 325–337.
McMahon B. M., Stewart J. A., et al. (2001) Intraperitoneal injection of antisense peptide nucleic acids targeted to the mu receptor decreases response to morphine and receptor protein levels in rat brain. Brain Res. 904(2), 345–349.
Nielsen P. E., Egholm M., et al. (1993) Peptide nucleic acids (PNAs): potential antisense and anti-gene agents. Anticancer Drug Des. 8(1), 53–63.
Panegyres P. K. (2001) The functions of the amyloid precursor protein gene. Rev. Neurosci. 12(1), 1–39.
Pinnix I., Musunuru U., et al. (2001) A novel gamma secretase assay based on detection of the putative C-terminal fragment-gamma of amyloid beta protein precursor. J. Biol. Chem. 276(1), 481–487.
Pooga M., Soomets U., et al. (1998) Cell penetrating PNA constructs regulate galanin receptor levels and modify pain transmission in vivo. Nat. Biotechnol. 16(9), 857–861.
Rezaei K., Xu I. S., et al. (2001) Intrathecal administration of PNA targeting galanin receptor reduces galanin-mediated inhibitory effect in the rat spinal cord. Neuroreport 12(2), 317–320.
Roberts G. W., Gentleman S. M., et al. (1991) Beta A4 amyloid protein deposition in brain after head trauma. Lancet 338(8780), 1422,1423.
Sambamurti K., Greig N. H., et al. (2002) Advances in the cellular and molecular biology of the beta-amyloid protein in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuromol. Med. 1(1), 1–31.
Savage M. J., Trusko, S. P., et al. (1998) Turnover of amyloid beta-protein in mouse brain and acute reduction of its level by phorbol ester. J. Neurosci. 18(5), 1743–1752.
Selkoe D. J. (1994) Cell biology of the amyloid beta-protein precursor and the mechanism of Alzheimer’s disease. Annu. Rev. Cell Biol. 10, 373–403.
Siman R., Card J. P., et al. (1989) Expression of beta-amyloid precursor protein in reactive astrocytes following neuronal damage. Neuron 3(3), 275–285.
Tyler B. M., Jansen K., et al. (1999) Peptide nucleic acids targeted to the neurotensin receptor and administered i.p. cross the blood-brain barrier and specifically reduce gene expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 96(12), 7053–7058.
Tyler B. M., McCormick D. J., et al. (1998) Specific gene blockade shows that peptide nucleic acids readily enter neuronal cells in vivo. FEBS Lett. 421(3), 280–284.
Tyler-McMahon B., Stewart J., et al. (2001) Altering behavioral responses and dopamine transporter protein with antisense peptide nucleic acids. Biochem. Pharmacol. 62, 929–932.
Wittung P., Kajanus J., et al. (1995) Phospholipid membrane permeability of peptide nucleic acid. FEBS Lett. 375(3), 27–29.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boules, M., Williams, K., Gollatz, E. et al. Down-regulation of amyloid precursor protein by peptide nucleic acid in vivo. J Mol Neurosci 24, 123–128 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1385/JMN:24:1:123
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/JMN:24:1:123