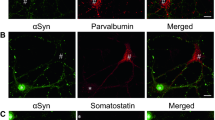
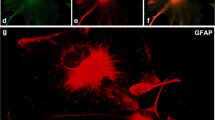
Abstract
α-Synuclein is a small presynaptic protein associated with both normal synaptic plasticity and neurodegenerative processes. Its normal cellular function, however, remains unknown. Even though it is highly enriched in the brain, its presence was reported in other human adult tissues. In the present study, we examined tissue expression of α-synuclein in human and rat prenatal development. Using Western blot analysis, various peripheral tissues from 15 to 23 gestational weeks, human and E19 rat fetuses, along with human and rat adult tissues, were assayed. α-Synuclein expression was observed in all fetal human organs examined. In adult human tissues the high expression of α-synuclein was maintained in the brain, whereas in other organs the expression was greatly reduced. In contrast, both in fetal and adult rat tissues, α-synuclein was only detected in the brain. In addition to a 19-kDa α-synuclein band, 36- and 52-kDa immunoreactive bands were observed in all fetal and adult human organs, with the exception of the brain, but their identity remains to be determined. These findings suggest that apart from its function in development of the nervous system, α-synuclein has an important function in peripheral tissues as well during normal human prenatal development.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alves da Costa C. (2003) Recent advances on alphasynuclein cell biology: functions and dysfunctions. Curr. Mol. Med. 3, 17–24.
Baba M., Nakajo S., Tu P. H., Tomita T., Nakaya K., Lee V. M., et al. (1998) Aggregation of alpha-synuclein in Lewy bodies of sporadic Parkinson’s disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. Am. J. Pathol. 152, 879–884.
Campbell B. C., McLean C. A., Culvenor J. G., Gai W. P., Blumbergs P. C., Jakala P., et al. (2001) The solubility of alpha-synuclein in multiple system atrophy differs from that of dementia with Lewy bodies and Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurochem. 76, 87–96.
Clayton D. F. and George J. M. (1998) The synucleins: the family of proteins involved in synaptic function, plasticity, neurodegeneration and disease. Trends Neurosci. 21, 249–254.
Feany M. B. and Bender W. W. (2000) A Drosophila model of Parkinson’s disease. Nature 404, 394–398.
Hashimoto M., Yoshimoto M., Sisk A., Hsu L.J., Sundsmo M., Kittel A., et al. (1997) NACP, a synaptic protein involved in Alzheimer’s disease, is differentially regulated during megakaryocyte differentiation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 237, 611–616.
Hsu L. J., Mallory M., Xia Y., Veinbergs I., Hashimoto M., Yoshimoto M., et al. (1998) Expression pattern of synucleins (non-Aβ component of Alzheimer’s disease amyloid precursor protein/α-synuclein) during murine brain development. J. Neurochem. 71, 338–344.
Hsu L. J., Sagara Y., Arroyo A., Rockenstein E., Sisk A., Mallory M., et al. (2000) α-Synuclein promotes mitochondrial deficit and oxidative stress. Am. J. Pathol. 157, 401–410.
Kahle P. J., Neumann M., Ozmen L., Muller V., Jacobsen H., Schindzielorz A., et al. (2000) Subcellular localization of wild-type and Parkinson’s disease-associated mutant alpha-synuclein in human and transgenic mouse brain. J. Neurosci. 20, 6365–6373.
Krüger R., Kuhn W., Mller T., Woitalla D., Graeber M., Köel S., et al. (1998) Ala30Pro mutation in the gene encoding α-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease. Nat. Genet. 18, 106–108.
Langston J. W., Sastry S., Chan P., Forno L. S., Bolin L. M., and Di Monte D. A. (1998) Novel synuclein-immunoreactive proteins in brain samples from the Contursi kindred, Parkinson’s, and Alzheimer’s disease. Exp. Neurol. 154, 684–690.
Lavedan C. (1998) The synuclein family. Genome Res. 9, 871–880.
Maroteaux L. and Scheller R. H. (1991) The rat brain synucleins; family of proteins transiently associated with neuronal membrane. Mol. Brain Res. 11, 335–343.
Masliah E., Rockenstein E., Veinbergs I., Mallory M., Hashimoto M., Takeda A., et al. (2000) Dopaminergic loss and inclusion body formation in α-synuclein mice: implications for neurodegenerative disorders. Science 287, 1265–1269.
Matsuoka Y., Vila M., Lincoln S., McCormack A., Picciano M., LaFrancois J., et al. (2001) Lack of nigral pathology in transgenic mice expressing human alphasynuclein driven by the tyrosine hydroxylase promoter. Neurobiol. Dis. 8, 535–539.
Petersen K., Olesen O. F., and Mikkelsen J. D. (1999) Developmental expression of α-synuclein in rat hippocampus and cerebral cortex. Neuroscience 91, 651–659.
Polymeropoulos M. H., Lavedan C., Leroy E., Ide S. E., Dehejia A., Dutra A., et al. (1997) Mutation in the alpha-synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson’s disease. Science 276, 2045–2047.
Shin E. C., Cho S. E., Lee D. K., Hur M. W., Paik S. R., Park J. H., and Kim J. (2000) Expression patterns of alpha-synuclein in human hematopoietic cells and in Drosophila at different developmental stages. Mol. Cells 10, 65–70.
Tanji K., Mori F., Imaizumi T., Yoshida H., Matsumiya T., Tamo W., et al. (2002) Upregulation of alpha-synuclein by lipopolysaccharide and interleukin-1 in human macrophages. Pathol. Int. 9, 572–577.
Ueda K., Fukushima H., Masliah E., Xia Y., Iwai A., Yoshimoto M., et al. (1993) Molecular cloning of cDNA encoding an unrecognised component of amyloid in Alzheimer disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 90, 11282–11286.
Ueda K., Saitoh T., and Mori H. (1994) Tissue-dependent alternative splicing of mRNA for NACP, the precursor of non-Aβ component of Alzheimer’s disease amyloid. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 205, 1366–1372.
Uversky V. N., Lee H., Li J., Fink A. L., and Lee S. (2001) Stabilization of partially folded conformation during α-synuclein oligomerization in both purified and cytosolic prepatations. J. Biol. Chem. 47, 43495–43498.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baltic, S., Perovic, M., Mladenovic, A. et al. α-Synuclein is expressed in different tissues during human fetal development. J Mol Neurosci 22, 199–203 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1385/JMN:22:3:199
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/JMN:22:3:199