Abstract
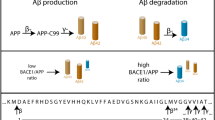
An integral membrane aspartyl protease, BACE, is responsible for β-secretase processing of the β-amyloid precursor protein (APP) to the large secreted sAPPβ and membrane-bound CTFβ of 99 residues. CTFβ is subsequently cleaved within the membrane by γ-secretase to the amyloid β protein (Aβ) that is deposited in the Alzheimer’s disease (AD) brain. In this manuscript, we argue that BACE is not limiting for Aβ production and report the existence of a high molecular weight complex of BACE that is more active than the monomer. We also present evidence that the BACE complex is enriched in lipid raft fractions prepared from brain membranes. These findings support the hypothesis that cleavage by BACE is limited by trafficking of APP (<10%) to a lipid raft-derived compartment containing the BACE complex. In addition, the localization of the BACE complex to lipid rafts can explain previous findings that cholesterol and glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored proteins are necessary for β-secretase processing of APP. We propose that the BACE complex is a better drug target than the monomer for specific inhibition of Aβ biogenesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson J. P., Jacobson-Croak K. L., and Sinha S. (2001) Assays for detecting beta-secretase inhibition. USA patent 6,329,163.
Benjannet S., Elagoz A., Wickham L., Mamarbachi M., Munzer J. S., Basak A., et al. (2001) Post-translational processing of beta-secretase (beta-amyloid-converting enzyme) and its ectodomain shedding. The pro- and transmembrane/cytosolic domains affect its cellular activity and amyloid-beta production. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 10,879–10,887.
Brown D. A. and London E. (1998) Functions of lipid rafts in biological membranes. Annu. Rev. Cell. Dev. Biol. 14, 111–136.
De Strooper B. and Annaert W. (2000) Proteolytic processing and cell biological functions of the amyloid precursor protein. J. Cell. Sci. 113, 1857–1870.
Gao Y. and Pimplikar S. W. (2001) The gamma-secretase-cleaved C-terminal fragment of amyloid precursor protein mediates signaling to the nucleus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 98, 14,979–14,984.
Gotz J., Chen F., van Dorpe J., and Nitsch R. M. (2001) Formation of neurofibrillary tangles in P301l tau transgenic mice induced by Aβ 42 fibrils. Science 293, 1491–1495.
Hardy J. (1992) Framing beta-amyloid. Nat. Genet. 1, 233–234.
Hong L., Koelsch G., Lin X., Wu X., Terzyan S., Ghosh A. K., et al. (2000) Structure of the protease domain of memapsin 2 (beta-secretase) complexed with inhibitor. Science 290, 150–153.
Lee S. J., Liyanage U., Bickel P. E., Xia W., Lansbury P. T., Jr., and Kosik K. S. (1998) A detergent-insoluble membrane compartment contains A β in vivo. Nat. Med. 4, 730–734.
Leissring M. A., Murphy M. P., Mead T. R., Akbari Y., Sugarman M. C., Jannatipour M., Anliker B., et al. (2002) A physiologic signaling role for the gamma-secretase-derived intracellular fragment of APP. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99, 4697–4702.
Lewis J., Dickson D. W., Lin W. L., Chisholm L., Corral A., Jones G., et al. (2001) Enhanced neurofibrillary degeneration in transgenic mice expressing mutant tau and APP. Science 293, 1487–1491.
Lu D. C., Rabizadeh S., Chandra S., Shayya R. F., Ellerby L. M., Ye X., et al. (2000) A second cytotoxic proteolytic peptide derived from amyloid beta-protein precursor. Nat. Med. 6, 397–404.
Mallender W. D., Yager D., Onstead L., Nichols M. R., Eckman C., Sambamurti K., et al. (2001) Characterization of recombinant, soluble beta-secretase from an insect cell expression system. Mol. Pharmacol. 59, 619–626.
Morishima-Kawashima M. and Ihara Y. (1998) The presence of amyloid beta-protein in the detergent-insoluble membrane compartment of human neuroblastoma cells. Biochemistry 37, 15,247–15,253.
Passer B., Pellegrini L., Russo C., Siegel R. M., Lenardo M. J., Schettini G., et al. (2000) Generation of an apoptotic intracellular peptide by gamma-secretase cleavage of Alzheimer’s β-amyloid precursor protein. J. Alz. Dis. 2, 289–301.
Pinnix I., Musunuru U., Tun H., Sridharan A., Golde T., Eckman C., et al. (2001) A novel gamma-secretase assay based on detection of the putative C-terminal fragment-gamma of amyloid beta protein precursor. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 481–487.
Pinnix I., Council J. E., Roseberry B., Onstead L., Mallender W., Sucic J., and Sambamurti K. (2001b) Convertases other than furin cleave beta-secretase to its mature form. FASEB J. 15, 1810–1812.
Refolo L. M., Pappolla M. A., LaFrancois J., Malester B., Schmidt S. D., Thomas-Bryant T., et al. (2001) A cholesterol-lowering drug reduces beta-amyloid pathology in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 8, 890–899.
Refolo L. M., Pappolla M. A., Malester B., LaFrancois J., Bryant-Thomas T., Wang R., et al. (2000) Hypercholesterolemia accelerates the Alzheimer’s amyloid pathology in a transgenic mouse model. Neurobiol. Dis. 7, 321–331.
Riddell D. R., Christie G., Hussain I., and Dingwall C. (2001) Compartmentalization of beta-secretase (Asp2) into low-buoyant density, noncaveolar lipid rafts. Curr. Biol. 11, 1288–1293.
Sambamurti K., Greig N. H., and Lahiri D. K. (2002) Advances in the cellular and molecular biology of the beta-amyloid protein in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuromol. Med. 1, 1–31.
Sambamurti K., Hardy J., Refolo L. M., and Lahiri D. K. (2002b) Targeting APP metabolism for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Drug Dev. Res. 56, 211–227.
Sambamurti K., Sevlever D., Koothan T., Refolo L. M., Pinnix I., Gandhi S., et al. (1999) Glycosylphos-phatidylinositol-anchored proteins play an important role in the biogenesis of the Alzheimer’s amyloid beta-protein. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 26,810–26,814.
Scheuner D., Eckman C., Jensen M., Song X., Citron M., Suzuki N., et al. (1996) Secreted amyloid beta-protein similar to that in the senile plaques of Alzheimer’s disease is increased in vivo by the presenilin 1 and 2 and APP mutations linked to familial Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Med. 2, 864–870.
Sherrington R., Rogaev E. I., Liang Y., Rogaeva E. A., Levesque G., Ikeda M., et al. (1995) Cloning of a gene bearing missense mutations in early-onset familial Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 375, 754–760.
Simons M., Keller P., De Strooper B., Beyreuther K., Dotti C. G., and Simons K. (1998) Cholesterol depletion inhibits the generation of beta-amyloid in hippocampal neurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 6460–6464.
Sparks D. L., Scheff S. W., Hunsaker J. C. III, Liu H., Landers T., and Gross D. R. (1994) Induction of Alzheimer-like beta-amyloid immunoreactivity in the brains of rabbits with dietary cholesterol. Exp. Neurol. 126, 88–94.
Tun H., Marlow L., Pinnix I., Kinsey R., and Sambamurti K. (2002) Lipid rafts play an important role in Aβ biogenesis by regulating the β-secretase pathway. J. Mol. Neurosci. 19, 31–35.
Yan S. D., Fu J., Soto C., Chen X., Zhu H., Al-Mohanna F., et al. (1997) An intracellular protein that binds amyloid-beta peptide and mediates neurotoxicity in Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 389, 689–695.
Yankner B. A., Dawes L. R., Fisher S., Villa-Komaroff L., Oster-Granite M. L., and Neve R. L. (1989) Neurotoxicity of a fragment of the amyloid precursor associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Science 245, 417–420.
Yankner B. A., Duffy L. K., and Kirschner D. A. (1990) Neurotrophic and neurotoxic effects of amyloid beta protein: reversal by tachykinin neuropeptides. Science 250, 279–282.
Yu C., Kim S. H., Ikeuchi T., Xu H., Gasparini L., Wang R., and Sisodia S. S. (2001) Characterization of a presenilin-mediated amyloid precursor protein carboxyl-terminal fragment gamma. Evidence for distinct mechanisms involved in gamma-secretase processing of the APP and Notch1 transmembrane domains. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 43,756–43,760.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marlow, L., Cain, M., Pappolla, M.A. et al. β-secretase processing of the Alzheimer’s amyloid protein precursor (APP). J Mol Neurosci 20, 233–239 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1385/JMN:20:3:233
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/JMN:20:3:233