Abstract
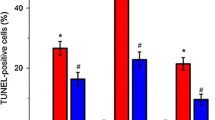
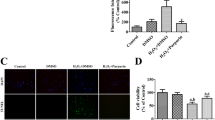
The activation of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) in the reperfused brain after ischemia has been assumed but never has been directly presented. Our studies indicate a different dynamic of PARP activity alteration in hippocampus during reperfusion after 3 and 10 min of transient forebrain ischemia in gerbils. The phasic stimulation of PARP activity was observed during reperfusion 15 min, 120 min, and 4 d after 3 min of ischemia with subsequent lowering of its activity close to control value on the seventh day of reperfusion. After 10 min of ischemic insult, PARP activity significantly increased from the third to the seventh day of reperfusion. The protein level of PARP was not significantly changed during reperfusion after 3 and 10 min of ischemia, with one exception: On the third day after 10 min of ischemia, PARP protein level was 28% lower compared to control; however, no enhancement of 85-kDa protein immunoreactivity was observed. These data indicate the lack of PARP cleavage in hippocampus of gerbils subjected to ischemia-reperfusion injury. The inhibitor of PARP, 3-aminobenzamide (3-AB) in a dose of 30 mg/kg b.w. (body weight) injected intravenously directly after 3 min of ischemia protects >60% of neuronal cells against death in the CA1 layer of hippocampus but has no effect after 10 min of ischemic episode. 3-AB decreased forebrain edema significantly after 3 and 10 min of ischemia. Our data indicate that PARP inhibitor(s) might offer a potent therapeutic strategy for short global ischemia. The combination of PARP inhibitor with potent antioxidant might enhance its ameliorating effect.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beckman J. S. and Crow J. P. (1993) Pathological implications of nitric oxide, superoxide and peroxynitrite formation. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 21, 330–334.
Chalimoniuk M. and Strosznajder J. (1998) NMDA receptor-dependent nitric oxide and cGMP synthesis in brain hemispheres and cerebellum during reperfusion after transient forebrain ischemia in gerbils: effect of 7-nitroindazole J. Neurosci. Res. 54, 681–690.
Colbourne F., Sutherland G. R., and Auer R. N. (1999) Electron microscopic evidence against apoptosis as the mechanism of neuronal death in global ischemia. J. Neurosci. 19, 4200–4210.
Dawson V. L., Dawson T. M., London E. D., Bredt D. S., and Synder S. H. (1991) Nitric oxide mediates glutamate neurotoxicity in primary cortical cultures. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88, 6368–6371.
Eliasson M. J. L., Sampei K., Mandir A. S., Hurn P. D., Traystman R. J., Bao J., et al. (1997) Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase gene disruption renders mice resistant to cerebral ischemia. Nat. Med. 3(10), 1089–1095.
Endres M., Scott G., Namura S., Salzman A. L., Huang P. L., Moskowitz M. A., and Szabo C. (1998) Role of peroxynitrite and neuronal nitric oxide synthase in the activation of poly (ADP-ribose) synthetase in a murine model of cerebral ischemia-reperfusion. Neurosci. Lett. 248, 41–44.
Endres M., Wang Z., Namura S., Waeber C., and Moskowitz M. A. (1997) Ischemic brain injury is mediated by the activation of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 17, 1143–1151.
Fukuda T., Wang H., Nakanishi H., Yamamoto K., and Kosaka T. (1999) Novel nonapoptotic morphological changes in neurons of the mouse hippocampus following transient hypoxic-ischemia. Neurosci. Res. 33(1), 49–55.
Gaal J. C., Smith K. R., and Pearson C. K. (1987) Cellular euthanasia mediated by a nuclear enzyme: a central role for nuclear ADP-ribosylation in cellular methabolism. Trends Biol. Sci. 12, 129–130.
Hatfield R. H., Gill R., and Brazell C. (1992) The dose-response relationship and therapeutic window for dizocipline (MK-801) in a rat focal ischaemia model. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 216, 1–7.
Herzeg Z. and Wang Z. Q. (2001) Functions of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) in DNA repair, genomic integrity and cell death. Mutat. Res. 477, 97–110.
Johnson G. S. (1981) Benzamide and its derivatives inhibit nicotinamide methylation as well as ADP-ribosylation. Biochem. Int. 2, 611–617.
Lipton P. (1999) Ischemic cell death in brain neurons. Physiol. Res. 79, 1431–1568.
Liu J., Ying W., Massa S., Duriez P. J., Swanson R. A., Poirier G. G., and Sharp F. R. (2000) Effects of transient global ischemia and kainate on poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) gene expression and proteolytic cleavage in gerbil and rat brains. Mol. Brain Res. 80, 7–16.
Lo E. H., Bosque-Hamilton P., and Meng W. (1998) inhibition of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase—Reduction of ischemic injury and attenuation of N-methyl-d-aspartate-induced neurotransmitter dysregulation. Stroke 29, 830–836.
Martin L. J., Al-Abdulla N. A., Brambrink A. M., Kirsch J. R., Sieber F. E., and Portera-Cailliau C. (1998) Neurodegeneration in excitotoxicity, global cerebral ischemia, and target deprivation: a perspective on the contributions of apoptosis and necrosis. Brain Res. Bull. 46, 281–309.
Milam K. M. and Cleaver J. E. (1984) Inhibitors of poly(adenosine diphosphate-ribose)synthesis: effect on other metabolic processes. Science 223, 589–591.
Moroni F., Meli E., Peruginelli F., Chiarugi A., Cozzi A., Picca R., et al. (2001) Poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase inhibitors atenuate necrotic but not apoptotic neuronal death in experimental models of cerebral ischemia. Cell Death Difer. 8, 921–932.
Nagayama T., Simon R. P., Chen D., Henshall D. C., Pei W., Stetler R. A., and Chen J. (2000) Activation of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase in the rat hippocampus may contribute to cellular recovery following sublethal transient global ischemia. J. Neurochem. 74, 1636–1645.
Nicholson D. W., Ali A., Thornberry N. A., Villancourt J. P., Ding C. K., Gallant M., et al. (1995) Identification and inhibition of the ICE/CED-3 protease necessary for mammalian apoptosis. Nature 376, 37–43.
Nicotera P., Leist M., and Manzo L. (1999) Neuronal cell death: a demise with different shapes. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 20, 46–51.
Paschen W., Olah L., and Mies G. (2000) Effect of transient focal ischemia of mouse brain on energy state and NAD levels: no evidence that NAD depletion plays a major role in secondary disturbances of energy metabolism. J. Neurochem. 75, 1675–1680.
Plaschke K., Kopitz J., Weigand M. A., Martin E., and Bardenheuer H. J. (2000) The neuroprotective effect of cerebral poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase inhibition in a rat model of global ischemia. Neurosci. Lett. 284, 109–112.
Prasad S. C., Soladatenkor V, Notario V. Smulson M., and Drotchilo A. (1999) Detection of heterogeneity of poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase in MDA-MD468 brest cancer cells: two dimensional gel analyzing. Electrophoresis 20, 618–625.
Satoh M. S. and Lindahl T. (1992) Role of poly(ADP-ribose) formation in DNA repair. Nature 356, 356–358.
Small D. L. and Buchan A. M. (1996) Mechanisms of cerebral ischemia: intracellular cascades and therapeutic interventions. J. Cardiothor. Vasc. An. 10, 139–146.
Smith S. (2001) The world according to PARP. Trends Biochem. Sci. 26, 174–179.
Szabo C. and Dawson V. L. (1998) Role of poly(ADP-ribose) synthase in inflammation and ischemia-reperfusion. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 19, 287–298.
Takahashi K., Greenberg J. H., and Greenberg H. (2000) The effect of reperfusion on neuroprotection using an inhibitor of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. Neuroreport 10, 2017–2022.
Takahashi K., Greenberg J. H., Jackson P., Maclin K., and Zhang J. (1997) Neuroprotective effects of inhibiting poly(ADP-ribose) synthetase on focal cerebral ischemia in rats. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 17, 1137–1142.
Thiemermann C., Bowes J., Myint F. P., and Vane J. R. (1997) Inhibition of the activity of poly(ADP-ribose) synthase reduces ischemia-reperfusion injury in the heart and skeletal muscle. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94, 679–683.
Tokime T., Nozaki K., Sugino T., Kikuchi H., Hashimoto N., and Ueda K. (1998) Enhanced poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation after focal ischemia in rat brain. J. Cereb. Blood. Flow Metab. 18, 991–997.
Zhang J., Dawson V. L., Dawson T. M., and Snyder S. H. (1994) Nitric oxide activation of poly(ADP-ribose) synthetase in neurotoxicity. Science 263, 687–689.
Ziegler M. and Oei S. L. (2001) A cellular survival switch: poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation stimulates DNA repair and silences transcription. Bioessays 23, 543–548.
Zingarelli B., Cuzzocrea S., Zsengeller Z., Salzman A. L., and Szabo C. (1997) Protection against myocardial ischemia and reperfusion injury by 3-aminobenzamide, an inhibitor of poly(ADP-ribose) synthetase. Cardiovasc. Res. 36, 205–202.
Zingarelli B., Salzman A. L., and Szabo C. (1998) Genetic disruption of poly(ADP-ribose) synthetase inhibits the expression of P-selectin and intracellular adhesion molecule-1 in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Circ. Res. 83, 85–94.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Strosznajder, R.P., Gadamski, R., Czapski, G.A. et al. Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase during reperfusion after transient forebrain ischemia. J Mol Neurosci 20, 61–71 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1385/JMN:20:1:61
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/JMN:20:1:61