Abstract
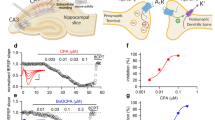
Arachidonic acid (AA), released in response to muscarinic acetylcholine receptor (mAChR) stimulation, previously has been reported to function as a reversible feedback inhibitor of the mAChR. To determine if the effects of AA on binding to the mAChR are subtype specific and whether AA inhibits ligand binding to other G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), the effects of AA on ligand binding to the mAChR subtypes (M1, M2, M3, M4, and M5) and to the μ-opioid receptor, β2-adrenergic receptor (β2-AR), 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor (5-HTR), and nicotinic receptors were examined. AA was found to inhibit ligand binding to all mAChR subtypes, to the β2-AR, the 5-HTR, and to the μ-opioid receptor. However, AA does not inhibit ligand binding to the nicotinic receptor, even at high concentrations of AA. Thus, AA inhibits several types of GPCRs, with 50% inhibition occurring at 3–25 µM, whereas the nicotinic receptor, a non-GPCR, remains unaffected. Further research is needed to determine the mechanism by which AA inhibits GPCR function.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berzaghi M. P., Cooper J., Castren E., Zafra F., Sofroniew M., et al. (1993) Cholinergic regulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and nerve growth factor (NGF) but not neurotrophin-3 (NT-3) mRNA levels in the developing rat hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 13, 3818–3826.
Cakir Y., Plummer H. K. III, Tithof P. K., and Schuller H. M. (2002) Beta-adrenergic and arachidonic acid-mediated growth regulation of human breast cancer cell lines. Int. J. Oncol. 21, 153–157.
Chalimoniuk M., King-Pospisil K., Pedersen W. A., Malecki A., Wylegala E., Mattson M. P., et al. (2004) Arachidonic acid increases choline acetyltransferase activity in spinal cord neurons through a protein kinase C-mediated mechanism. J. Neurochem. 90, 629–636.
Christopoulos A. and Kenakin T. (2002) G protein-coupled receptor allosterism and complexing. Pharmacol. Rev. 54, 323–374.
Conklin B. R., Brann M. R., Buckley N. J., Ma A. L., Bonner T. I., and Axelrod J. (1988) Stimulation of arachidonic acid release and inhibition of mitogenesis by cloned genes for muscarinic receptor subtypes stably expressed in A9 L cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 85, 8698–8702.
Cunha R. A., Constantino M. D., Fonseca E., and Ribeiro J. A. (2001) Age-dependent decrease in adenosine A1 receptor binding sites in the rat brain. Eur. J. Biochem. 268, 2939–2947.
Cunha R. A., Ribeiro J. A., and Malva J. O. (2004) Presynaptic kainate receptors modulating glutamatergic transmission in the rat hippocampus are inhibited by arachidonic acid. Neurochem. Int. 44, 371–379.
Davies P. and Maloney A. J. F. (1976) Selective loss of central cholinergic neurons in Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet. 2, 1403.
Devane W. A. and Axelrod J. (1994) Enzymatic synthesis of anandamide, an endogenous ligand for the cannabinoid receptor, by brain membranes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 91, 6698–6701.
Farias G. G., Godoy J. A., Hernandez F., Avila J., Fisher A., and Inestrosa N. C. (2004) M1 muscarinic receptor activation protects neurons from β-amyloid toxicity. A role for Wnt signaling pathway. Neurobiol. Dis. 17, 337–348.
Fawcett J. R., Bordayo E. Z., Jackson K., Liu H., Peterson J., Svitak A., and Frey W. H. II (2002) Inactivation of the human brain muscarinic acetylcholine receptor by oxidative damage catalyzed by a low molecular weight endogenous inhibitor from Alzheimer’s brain is prevented by pyrophosphate analogs, bioflavonoids and other antioxidants. Brain Res. 950, 10–20.
Felder C. C., Kanterman R. Y., Ma A. L., and Axelrod J. (1990) Serotonin stimulates phospholipase A2 and the release of arachidonic acid in hippocampal neurons by a type 2-serotonin receptor that is independent of inositolphospholipid hydrolysis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 87, 2187–2191.
Fukuda K., Kato S., Morikawa H., Shoda T., and Mori K. (1996) Functional coupling of the δ-, μ-, and κ, opioid receptors to mitogen-activated protein kinase and arachidonate release in Chinese hamster ovary cells. J. Neurochem. 67, 1309–1316.
Glick J., Santoyo G., and Casey P. J. (1996) Arachidonate and related unsaturated fatty acids selectively inactivate the guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory protein, Gz. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 2949–2954.
Jensen A. A. and Spalding T. A. (2004) Allosteric modulation of G-protein coupled receptors. Eur. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 21, 407–420.
Kim J., Isokawa M., Ledent C., and Alger B. E. (2002) Activation of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors enhances the release of endogenous cannabinoids in the hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 22, 10182–10191.
Kimura T., Ohta T., Watanabe K., Yoshimura H., and Yamamoto I. (1998) Anandamide, an endogenous cannabinoid receptor ligand, also interacts with 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) receptor. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 21, 224–226.
King M. E., Gamblin T. C., Kuret J., and Binder L. I. (2000) Differential assembly of human tau isoforms in the presence of arachidonic acid. J. Neurochem. 74, 1749–1757.
Kirstein S. L. and Insel P. A. (2004) Autonomic nervous system pharmacogenomics: a progress report. Pharmcol. Rev. 56, 31–52.
Kjome J. R., Swenson K. A., Johnson M. N., Bordayo E. Z., Anderson L. E., Klevan A. I., et al. (1998) Inhibition of antagonist and agonist binding to the human brain muscarinic receptor by arachidonic acid. J. Mol. Neurosci. 10, 209–217.
Lagalwar S., Bordayo E. Z., Hoffmann K. L., Fawcett J. R., and Frey W. H. II (1999) Anandamides inhibit binding to the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor. J. Mol. Neurosci. 13, 55–62.
Leggett J. D., Aspley S., Beckett S. R. G., D’ Antona A. M., and Kendall D. A. (2004) Oleamide is a selective endogenous agonist of rat and human CB1 cannabinoid receptors. Br. J. Pharmacol. 141, 253–262.
Levey A. I. (1996) Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor expression in memory circuits: implication of treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 93, 13541–13546.
Liu L., Roberts M. L. and Rittenhouse A. R. (2004) Phospholipid metabolism is required for M1 muscarinic inhibition of N-type calcium current in sympathetic neurons. Eur. Biophys. J. 33, 255–264.
Lorenzini A., Hrelia S., Bordoni A., Biagi P., Frisoni L., Marinucci T., Cristofalo V. J. (2001) Is increased arachidonic acid release a cause or a consequence of replicative senescence? Exp. Gerontol. 36, 65–78.
Marks M. J. and Collins A. C. (1982) Characterization of nicotine binding in mouse brain and comparison with the binding of alpha-bungarotoxin and quinuclidinyl benzilate. Mol. Pharmacol. 22, 554–564.
Menzaghi F., Behan D. P., and Chalmers D. T. (2002) Constitutively activated G- protein coupled receptors: a novel approach to CNS drug discovery. CNS Neurol. Dis. 1, 105–121.
Oktem H. A. and Apaydin S. (1998) Arachidonic acid modulation of 3H-naloxone specific binding to rat brain opioid receptors. Neurobiology 6, 323–332.
Rodriguez-Puertas R., Pascual R. J., Vilaro T., and Pazos A. (1997) Autoradiographic distribution of M1, M2, M3, and M4 muscarinic receptor subtypes in Alzheimer’s disease. Synapse 26, 341–350.
Rosenblum K., Futter M., Jones M., Hulme E. C., and Bliss T. V. P. (2000) ERKI/II regulation by the muscarinic acetylcholine receptors in neurons. J. Neurosci. 20, 977–985.
Saitoh H., Namatame Y., Hirano A., and Sugawara M. (2004) An excised patch membrane sensor for arachidonic acid released in mouse hippocampal slices under stimulation of L-glutamate. Anal. Biochem. 329, 163–172.
Sato T., Hashizume T., Nakao K., Akiba S., and Fujii T. (1989) Platelet desensitization by arachidonic acid is associated with the suppression of end operoxide/thromboxane A2 binding to the membrane receptor. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 992, 168–173.
Scarpero H. M. and Dmochowski R. R. (2003) Muscarinic receptors: what we know. Curr. Urol. Rep. 4, 421–428.
Smith P. K., Krohn R. I., Hermanson G. T., Mallia A. K., Gartner F. H., Provenzane M. D., et al. (1985) Measurement of protein using bicinchonic acid. Ann. Biochem. 150, 76–85.
Thomas E. A., Carson M. J., Neal M. J., and Sutcliffe G. (1997) Unique allosteric regulation of 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor-mediated signal transduction by oleamide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 94, 14115–14119.
van Koppen C. J. and Bjorn K. (2003) Regulation of muscarinic acetylcholine receptor signaling. Pharmacol. Ther. 98, 197–220.
Whitehouse P.J., Price D. L., Struble R. G., Clark A. W., Coyle J. T., and DeLong M. R. (1982) Alzheimer’s disease and senile dementia: loss of neurons in the basal forebrain. Science 215, 1237–1239.
Xu H., Lichtstein D., Kassis S., Lutz R. A., Rodbard D., and Chernick S. S. (1988) Multiple interactions of unsaturated fatty acids with opiate and ouabain binding sites and β-adrenergic sensitive adenylate cyclase system. J. Recept. Res. 8, 205–223.
Yasuda H., Kishiro K., Izumi N., and Nakanishi M. (1985) Biphasic liberation of arachidonic and stearic acids during cerebral ischemia. 45, 168–172.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bordayo, E.Z., Fawcett, J.R., Lagalwar, S. et al. Inhibition of ligand binding to g protein-coupled receptors by arachidonic acid. J Mol Neurosci 27, 185–194 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1385/JMN:27:2:185
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/JMN:27:2:185