Abstract
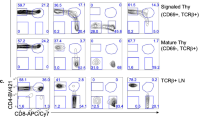
My colleagues and I are studying the regulation of T cell differentiation and lineage commitment in the thymus. Most recently, we have focused on the role of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway in these processes and, in particular, the temperal pattern of activation of this pathway and its effect on downstream gene targets. Our data suggest that thymocyte differentiation to either the CD4 or CD8 lineages requires sustained low-level signaling via MAPK, although the latter requires a weaker signal. We have proposed that both the amplitude and kinetics of MAPK signaling may be one aspect of the link between T cell receptor affinity and cell fate. In addition, we have shown that the Egr family of transcription factorsis induced as a consequence of MAPK activation during positive selection in the thymus, and we are taking several approaches to identify other genes that are involved in regulating this developmental process.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goldrath AW, Bevan MJ: Selecting and maintaining a diverse T-cell repertoire. Nature 1999;402: 255–262.
Jameson SC, Bevan MJ: T-cell selection. Curr Opin Immunol 1998;214–219.
Guidos CJ, Weissman, IL, Adkins B: In trathymic maturation of murine T lymphocytes from CD8+ precursors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1989;86:7542–7546.
Lundberg K, Shortman K: Small cortical thymocytes are subject to positive selection. J Exp Med 1994;179:1475–1483.
Downward J, Graves JD, Wame PH, Rayter S, Cantrell DA: Stimulation of p21 ras upon T-cell activation. Nature 1990;346:719–723.
Izquierdo M, Reif K, Cantrell DA: The regulation and function of p21 ras during T-cell activation and growth. Immunol Today 1995;16: 159–164.
Alberolla-Ila J, Hogquist KA, Swan KA, Bevan MJ, Perlmutter RM: Positive and negative selection involke distinct signaling pathways. J Exp Med 1996;184:9–18.
Cantrell D: T cell antigen receptor signal transduction pathways. Annu Rev Immunol 1996;14: 259–274.
Schaefer BC, Ware MF, Marrack P, Fanger GR, Kappler IW, Johnson GL, Monks CRF: Live cell fluorescence imaging of T cell MEKK2: redistribution and activation in response to antigen stimulation of the T cell receptor. Immunity 1999;11:411–421.
Oldham SM, Clark GJ, Gangarosa LM, Coffey RJ, Jr, Der CJ: Activation of the Raf-1/MAP kinase cascade is not sufficient for ras transformation of RIE-1 epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1996;93:6924–6928.
Swan KA, Alberola-Illa J, Gross JA, Appleby MW, Forbush KA, Thomas JF, Perlmutter RM: Involvement of p21 ras distinguishes positive and negative selection in thymocytes. EMBO J 1995;14:276–285.
O'Shea CC, Crompton T, Rosewell IR, Hayday AC, Owen MJ: Raf regulates positive selection. Eur J Immunol 1996;26:2350–2355.
Alberola-Ila J, Forbush KA, Seger R, Krebs EG, Perlmutter RM: Selective requirement for MAP kinase activation in thymocyte differentiation. Nature 1995;373: 620–623.
Pages G, Guerin S, Grall D, Bonino F, Smith A, Anjuere F, Auberger P, Pouyssegur J: Defective thymocyte maturation in p44 MAP kinase (Erk 1) knockout mice. Science 1999;286:1374–1377.
Kaye J, Hsu M-L, Sauron M-E, Jameson SC, Gascoigne NRJ, Hedrick SM: Selective development of CD4+ T cells in transgenic mice expressing a class II MHC-restricted antigen receptor. Nature 1989;341:746–749.
Kaye J, Ellenberger DE: Differentiation of an immature T cell line: a model of thymic positive selection. Cell 1992;71:423–435.
Poirier G, Lo D, Reilly C, Kaye J: Discrimination between thymic epithelial cells and peripheral antigen presenting cells in the induction of immature T cell differentiation. Immunity 1994;1: 385–391.
Anderson G, Owen JJ, Moore NC, Jenkinson EJ: Thymic epithelial cells provide unique signals for provide unique signals for positive selection of CD4+CD8+ thymocytes in vitro. J Exp Med 1994;179:2027–2031.
Shao H, Kopo D, Chen L-Y, Rubin E, Kaye J: Induction of the early growth response (Egr) family of transcription factorsduring thymics selection. J Exp Med 1997;185: 731–744.
Sugawara T, Moriguchi T, Nishida E, Takahama Y: Differential roles of ERK and p38MAP kinase pathways in positive and negative selection of T lymphocytes. Immunity 1998;9:565–574.
Ohoka Y, Kuwata T, Tozawa Y, Zhao Y, Mukai M, Motegi Y, Suzuki R, Yokoyama M, Iwata M: In vitro differentiation and commitment of CD4+ CD8+ thymocytes to the CD4 lineage, without TCR engagement. Int Immunol 1996;8:297–306.
Takahama Y, Nakauchi H: Phorbol ester and calcium ionophore can replace TCR signals that induce positive selection of CD4 T cells. J Immunol 1996;157: 1508–1513.
Lucas B, Germain RN: Unexpectedly complex regulation of CD4/CD8 coreceptor expression supports a revised model for CD4+CD8+ thymocytedifferentiation. Immunity 1996;5:461–477.
Surth CD, Sprent J: T-cell apoptosis detected in situ during positive and negative selection in the thymus. Nature 1994;372: 100–103.
Shao H, Wilkinson B, Lee B, Han PC, Kaye J: Slow accumulation of active mitogen-activated protein kinase during thymocyte differentiation regulates the temporal pattern of transcription factor gene expression. J Immunol 1999;163: 603–610.
Bonni A, Brunel A, West AE, Datta SR, Takasu MA, Greenberg ME: Cell survival promoted by the Ras-MAPK signaling pathway by transcription-dependentand-independent mechanisms. Science 1999;286:1358–1362.
Alam SM, Travers PJ, Wung JL, Nasholds W, Redpath S, Jameson SC, Gascoigne NR: T-cell-receptor affinity and thymocyte positive selection. Nature 1996;381: 616–620.
Ferrell JE, Jr, Machleder EM: The biochemical basis of anall-or-none cell fate switch in Xenopus oocytes. Science 1998;280:895–898.
Sharp LL, Schwarz DA, Bott CM, Marshall CJ, Hedrick SM: The influence of the MAPK pathway on T cell lineage commitment. Immunity 1997;7:609–618.
Bommhardt U, Basson MA, Krummrei U, Zamoyska R: Activation of the extracellular signal-related kinase/mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway discriminates CD4 versus CD8 lineage commitment in the thymus. J Immunol 1999;163:715–722.
Cao X, Koski RA, Gashler A, McKierran M, Morris CF, Gaffney R, Hay RV, Sukhatme VP: Identification and characterization of the Egr-1 gene product, a DNA-binding zinc fingerprotein induced by differentiation and growth signals. Mol Cell Biol 1990;10:1931–1939.
Joseph LJ, LeBeau MM, Jamieson GA, Jr, Acharya S, Shows TB, Rowley JD, Sukhatme VP: Molecular cloning, sequencing, and mapping of EGR2, a human early growth response gene encoding a protein with “zinc-bindign finger” structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1988;85:7164–7168.
Patwardhan S, Gashler A, Siegel MG, Chang LC, Joseph LJ, Shows TB, LeBeau MM, Sukhatme VP: EGR 3, a novelmember of the Egr family of genes encoding immediate early transcription factors. Oncogene 1991;6:917–928.
Gashler A, Sukhalme VP: Earth growth resporse protein 1 (Egr-1): Prototypeofa zinc-finger family of transcription factors. Prog Nucleic Acid Res 1995;50:191–224.
McMahon SB, Monroe JG: A ternary complex factor-dependent mechanism mediates induction of egr-1 through selective serum response elements following antigen receptor cross-linking in B lymphocytes. Mol Cell Biol 1995; 15:1086–1093.
Perez-Castillo A, Pipaon C, Garcia I, Alemany S: NGFl-A gene expression is necessary for T lymphocyte proliferation. J Biol Chem 1993;268:19,445–19,450
Miyazaki T, Lemonnier FA: Modulation of thymic selection by expression of an immediate-early gene, early growth response 1 (Egr-1). J Exp Med 1998;188:715–723.
Quilliam LA, Kato K, Rabun KM, Hisaka M, Huff SY, Camphell-Burk S, Der CJ: Identification of residues critical for rats (17N) growth-inhibitory phenotype and for ras interaction with guanine nucleotide exchange factors. Mol Cell Biol 1994;14:1113–1121.
Der CJ, Finkel T, Cooper GM: tBio
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaye, J. Regulation of T cell development in the thymus. Immunol Res 21, 71–81 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1385/IR:21:2-3:71
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/IR:21:2-3:71