Abstract
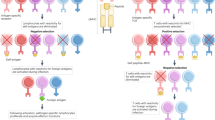
Self-tolerance induction is largely a reflection of negative selection (deletion) of autoreactive T cells in the thymus. Evidence is presented that negative selection occurs at a relatively late stage of thymocytes differentiation and affects a population of semimature HSAhi CD4+8− cells found in the medulla. Negative selection involves a number of cell-surface molecules on T cells, including Fas, CD28, CD5, and CD43. These molecules appear to act in consort, thereby ensuring that negative selection is highly efficient.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Robey E, Fowlkes BJ: Selective events in T cell development. Annu Rev Immunol 1994;12:675–705.
Nossal GJV: Negative selection of lymphocytes. Cell 1994;76:229–239.
Sprent J: Central tolerance of T cells. Int Rev Immunol 1995;13:95–105.
Fink PJ, Bevan MJ: Positive selection of thymocytes. Adv Immunol 1995;59:99–133.
Amsen D, Kruisbeek AM: Thymocyte selection: not by TCR alone. Immunol Rev 1998;165:209–229.
Viret C, Wong FS, Janeway CAJ Jr: Designing and maintaining the mature TCR repertoire: the continuum of self-peptide: self-MHC complex recognition. Immunity 1999;10:559–568.
Ernst B, Lee D-S, Chang J, et al. The peptide ligands mediating positive selection in the thymus control T cell survival and homeostatic proliferation in the periphery. Immunity 1999;11:173–181.
Goldrath AW, Bevan MJ: Low-affinity ligands for the TCR drive proliferation of mature CD8+ T cells in lymphopenic hosts. Immunity 1999;11:183–190.
Shi Y, Bissomete RP, Parfrey N, et al.: In vivo administration of antibodies to the CD3-T cell receptor complex induces cell death (apoptosis) in immature thymocytes. J Immunol 1991;146:3340–3346.
Murphy KM, Heimberger AB, Loh DH: Induction by antigen of intrathymic apoptosis of CD4+ CD8+ TCR1 thymocytes in vivo. Science 1990;250:1720–1723.
Jondal M, Okret S, McConkey D: Killing of immature CD4+ CD8+ thymocytes in vivo by anti-CD3 or 5′ (N-ethyl)-carboxamide-adenosine is blocked by glucocorticoid receptor antagonist RU-486. Eur J Immunol 1993;23:1246–1250.
Xue Y, Murdjeva M, Okret S, et al.: Inhibition of 1-Ad-, but not Db-restricted peptide-induced thymic apoptosis by glucocorticoid receptor antagonist RU486 in T cell receptor transgenic mice. Eur J Immunol 1996;26:428–434.
Martin S, Bevan MJ: Antigen-specific and nonspecific deletion of immature cortical thymocytes caused by antigen injection. Eur J Immunol 1997;27:2726–2736.
von Boehmer H: Developmental biology of T cells in T cell receptor transgenic mice. Annu Rev Immunol 1990;8:531–556.
Laufer TM, Climcher LH, Lo D: Using thymus anatomy to dissect T cell repertoire selection. Semin Immunol 1999;11:65–70.
Page DM, Kane LP, Allison JP, et al.: Two signals are required for negative selection of CD4+CD8+ thymocytes. J Immunol 1993;151:1868–1880.
Punt JA, Osbome BA, Takahama Y, et al.: Negative selection of CD4+CD8+ thymocytes by T cell receptor-induced apoptosis requires a costimulatory signal that can be provided by CD28. J Exp Med 1994;179:709–713.
Aiba Y, Mazda O, Davis MM, et al.: Requirement of a second signal from antigen presenting cells in the clonal deletion of immature T cells. Int J Immunol 1994;6:1475–1483.
Kishimoto H, Sprent J: Negative selection in the thymus includes semi-mature T cells. J Exp Med 1997;185:263–272.
Kishimoto H, Sprent J: Strong TCR ligation without costimulation causes rapid onset of Fas-dependent apoptosis of naive murine CD4+ T cells. J Immunol 1999;163:1817–1826.
Green DR, Scott DW: Activation-induced apoptosis in lymphocytes. Curr Opin Immunol 1994;6:476–487.
Nagata S, Golstein P: The Fas death factor. Science 1995;267:1449–1456.
Marrack P, Kappler JW: The staphylococcalentero toxins and their relatives. Science 1990;248:704–711.
Kishimoto H, Surh CD, Sprent J: A role for Fas in negative selection of thymocytes in vivo. J Exp Med 1998;187:1427–1438.
Theofilopoulos AN: The basis of autoimmunity: Part I. Mechanisms of aberrant self-recognition. Immunol Today 1995;16:90–98.
Shahinian A, Pfeffer K, Lee KP, et al.: Differential T cell costimulatory requirements in CD28-deficient mice. Science 1993;261:609–612.
Kishimoto H, Sprent J: Several different cell-surface molecules control negative selection of medullary thymocytes. J Exp Med 1999;190:65–73.
Punt JA, Havran W, Abe R, et al.: T cell receptor (TCR)-induced death of immature CD4+ CD8+ thymocytes by two distinct mechanisms differing in their requirement for CD28 costimulation: implications for negative selection in the thymus. J Exp Med 1997;186:1911–1922.
Page DM: Thymic selection and autoreactivity are regulated by multiple coreceptors involved in T cell activation. J Immunol 1999; 163:3577–3581.
van Oers NSC: T cell receptor-mediated signs and signals governing T cell development. Semin Immunol 1999;11:227–237.
Mariathason S, Jones RG, Ohashi PS: Signals involved in thymo-
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kishimoto, H., Sprent, J. The thymus and negative selection. Immunol Res 21, 315–323 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1385/IR:21:2-3:315
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/IR:21:2-3:315