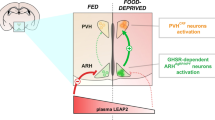
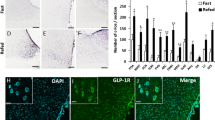
Abstract
Neonatal monosodium l-glutamate (MSG) treatment destroys hypothalamic arcuate nucleus neuronal bodies, thus inducing several metabolic abnormalities. As a result, rats develop a phenotype characterized by hyperleptinemia and by impaired NPY but normal prepro-orexin hypothalamic mRNAs expression. Thus, our study was designed to explore whether hypothalamic effects of orexin A on food intake and glucocorticoid production develop in the absence of full hypothalamic NPY-ergic activity. For this purpose we evaluated, in control and MSG-treated rats, the consequences of intracere-broventricular (icv) orexin A administration on food intake and changes in circulating levels of ACTH and glucocorticoid. Our results indicate that orexin A icv treatment stimulated hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis activity in both MSG-damaged and normal animals, with this response even more pronounced in neurotoxin-damaged rats. Conversely, food intake was only enhanced by icv orexin A injection in normal rats. Our study further supports that acute hypothalamic effects of orexin A on food intake and glucocorticoid production are due to independent neuronal systems. While intact arcuate nucleus activity is needed for the orexinergic effect induced by icv orexin A administration, conversely, orexin A-stimulated HPA axis function takes place even in the absence of full NPY-ergic activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kalra, S. P., Dube, M. G., Pu, S., Xu, B., Horvath, T. L., and Kalra, P. S. (1999). Endocr. Rev. 20, 68–100.
Leibowitz, S. F. (1989). Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 575, 221–233.
Kalra, S. P., Dube, M. G., Sahu, A., Phelps, C. P., and Kalra, P. S. (1991). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88, 10931–10935.
Sakurai, T., Amemiya, A., Ishii, M., et al. (1998). Cell 92, 573–585.
Horvath, T. L., Diano, S., and van den Pol, A. N. (1999). J. Neurosci. 19, 1072–1087.
Backberg, M., Hervieu, G., Wilson, S., and Meister, B. (2002). Eur. J. Neurosci. 15, 315–328.
Suzuki, R., Shimojima, H., Funahashi, H., et al. (2002). Neurosci. Lett. 324, 5–8.
Toshinai, K., Date, Y., Murakami, N., et al. (2003). Endocrinology 144, 1506–1512.
Ida, T., Nakahara, K., Kuroiwa, T., et al. (2000). Neurosci. Lett. 293, 119–122.
Jaszberenyi, M., Bujdoso, E., Pataki, I., and Telegdy, G. (2001). J. Neuroendocrinol. 12, 1174–1178.
Russell, S. H., Small, C. J., Dakin, C. L., et al. (2001). J. Neuroendocrinol. 13, 561–566.
Samson, W. K., Taylor, M. M., Follwell, M., and Ferguson, A. V. (2002). Regul. Pept. 104, 97–103.
Brunton, P. J. and Russell, J. A. (2003). J. Neuroendocrinol. 15, 633–637.
Munck, A., Guyre, P. M., and Holbrook, N. J. (1984). Endocr. Rev. 5, 25–44.
Perelló, M., Moreno, G., Camihort, G., et al. (2004). Endocrine 24, 167–176.
Morris, M. J., Tortelli, C. F., Filippis, A., and Proietto, J. (1998). Regul. Pept. 75–76, 441–447.
Dolnikoff, M. S., Kater, C. E., Egami, M., de Andrade, I. S., and Marmo, M. R. (1988). Neuroendocrinology 48, 645–649.
Macho, L., Fickova, M., Jezova, D., and Zorad, S. (2000). Physiol. Res. 49, S79-S85.
Burde, R. M., Schainker, B., and Kayes, J. (1971). Nature 233, 58–60.
Redding, T. W., Schally, A. V., Arimura, A., and Wakabayashi, I. (1971). Neuroendocrinology 8, 245–255.
Edwards, C. M., Abusnana, S., Sunter, D., Murphy, K. G., Ghatei, M. A., and Bloom, S. R. (1999). J. Endocrinol. 160, R7-R12.
Smart, D., Jerman, J. C., Brough, S. J., Neville, W. A., Jewitt, F., and Porter, R. A. (2000). Br. J. Pharmacol. 129, 1289–1291.
Date, Y., Ueta, Y., Yamashita, H., et al. (1999). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96, 748–753.
Peyron, C., Tighe, D. K., van den Pol, A. N., et al. (1998). J. Neurosci. 18, 9996–10015.
Nambu, T., Sakurai, T., Mizukami, K., Hosoya, Y., Yanagisawa, M., and Goto, K. (1999). Brain. Res. 827, 243–260.
de Lecea, L., Kilduff, T. S., Peyron, C., et al. (1998). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 322–327.
Trivedi, P., Yu, H., MacNeil, D. J., Van der Ploeg, L. H., and Guan, X. M. (1998). FEBS Lett. 438, 71–75.
Larsen, P. J., Fledelius, C., Knudsen, L. B., and Tang-Christensen, M. (2001). Diabetes 50, 2530–2539.
Diano, S., Horvath, B., Urbanski, H. F., Sotonyi, P., and Horvath, T. L. (2003). Endocrinology 144, 3774–3778.
Bjorbaek, C., Elmquist, J. K., Michl, P., et al. (1998). Endocrinology 139, 3485–3491.
Zhu, Y., Yamanaka, A., Kunii, K., Tsujino, N., Goto, K., and Sakurai, T. (2002). Physiol. Behav. 77, 251–257.
Lu, X. Y., Bagnol, D., Burke, S., Akil, H., and Watson, S. J. (2000). Horm. Behav. 37, 335–344.
Jain, M. R., Horvath, T. L., Kalra, P. S., and Kalra, S. P. (2000). Regul. Pept. 87, 19–24.
Lopez, M., Seoane, L. M., Garcia, M. C., Dieguez, C., and Senaris, R. (2002). Neuroendocrinology 75, 34–44.
Broberger, C. (1999). Brain Res. 848, 101–113.
Tamura, H., Kamegai, J., Shimizu, T., Ishii, S., Sugihara, H., and Oikawa, S. (2002). Endocrinology 143, 3268–3275.
Dube, M. G., Kalra, S. P., and Kalra, P. S. (1999). Brain Res. 842, 473–477.
Kiss, A., Skultetyova, I., and Jezova, D. (1999). Neurol. Res. 21, 775–780.
Wahlestedt, C., Skagerberg, G., Ekman, R., Heilig, M., Sundler, F., and Hakanson, R. (1987). Brain Res. 417, 33–38.
Blanco, M., Lopez, M., García-Caballero, T., et al. (2001). J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 86, 1616–1619.
Malendowicz, L. K., Tortorella, C., and Nussdorfer, G. G. (1999). J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 70, 185–188.
Karteris, E., Machado, R. J., Chen, J., Zervous, S., Hillhouse, E. W., and Randeva, H. S. (2005). Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. In press.
Spinedi, E., Johnston, C. A., and Negro-Vilar, A. (1984). Endocrinology 115, 267–272.
Larsen, P. J., Mikkelsen, J. D., Jessop, D., Lightman, S. L., and Chowdrey, H. S. (1994). J. Endocrinol. 141, 497–503.
Magarinos, A. M., Estivariz, F., Morado, M. I., and De Nicola, A. F. (1988). Neuroendocrinology 48, 105–111.
Perello, M., Gaillard, R. C., Chisari, A., and Spinedi, E. (2003). Neuroendocrinology 78, 176–184.
Skultetyova, I., Kiss, A., and Jezova, D. (1998). Neuroendocrinology 67, 412–420.
Heiman, M. L., Ahima, R. S., Craft, L. S., Schoner, B., Stephens, T. W., and Flier, J. S. (1997). Endocrinology 138, 3859–3863.
Spinedi, E., Giacomini, M., Jacquier, M. C., and Gaillard, R. C. (1991). Neuroendocrinology 53, 160–170.
Chomczynski, P. and Sacchi, N. (1987). Anal. Biochem. 162, 156–159.
Kanenishi, K., Ueno, M., Momose, S., et al. (2004). Neurosc. Lett. 368, 73–77.
Giovambattista, A., Chisari, A. N., Gaillard, R. C., and Spinedi, E. (2000). Neuroendocrinology 72, 341–349.
McElroy, W. D. and Swanson, C. P. (eds.). (1974). Biostatistical analysis. Prentice-Hall-Englewood Cliffs: New Jersey.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moreno, G., Perelló, M., Gaillard, R.C. et al. Orexin a stimulates hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis function, but not food intake, in the absence of full hypothalamic NPY-ergic activity. Endocr 26, 99–106 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1385/ENDO:26:2:099
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/ENDO:26:2:099