Abstract
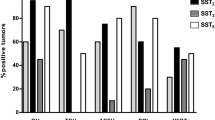
Somatostatin receptor (SSTR) subtypes 1, 2, and 5 are expressed in the normal human pituitary. SSTR2 and SSTR5 are expressed in almost all growth hormone (GH) cell adenomas, and prolactin (PRL)-secreting tumors express SSTR5 more than SSTR2. SSTR4 is not detected in all pituitary adenoma subtypes, and SSTR1 and SSTR3 are expressed in about 50% of tumors. Human GH is regulated through ligand binding to both SSTR2 and SSTR5, but octreotide and lanreotide, the two clinically available somatostatin analogs, bind to human SSTR2 much better than to SSTR5. Novel SSTR2- and SSTR5-selective analogs with improved binding affinity for these receptor subtypes are highly potent in suppressing GH release from cultures of human fetal pituitaries or GH-cell adenomas. Only SSTR5-selective analogs suppress in vitro PRL secretion from cultured prolactinomas. A new SSTR2+5 bispecific analog with high affinity and selectivity for both SSTR2 and SSTR5, and a somatostatin analog with a unique broad receptor (SSTR1, 2, 3, and 5) binding profile, are both able to inhibit in vitro GH release in GH cell adenomas partially sensitive to octreotide. Recently, a somatostatindopamine hybrid molecule was introduced with potentially functional synergy on GH and PRL release. Using the expanding knowledge on SSTRs and their ligand activation, the development of novel pharmacologic concepts may open new opportunities for effective manipulation of this complex intracellular signaling system. These concepts may achieve better control of pituitary hormone hypersecretion, pituitary size, as well as antitumor effects in patients with SSTR-expressing tumors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brazeau, P., Vale, W., Burgus, R., Ling, M., Rivier, J., and Guillemin, R. (1972). Science 129, 77–79.
Lamberts, S. W. J. (1988). Endocr. Rev. 9, 417–436.
Mandarino, L., Stenner, D., Blanchard, W., et al. (1981). Nature 291, 76, 77.
Reisine, T. and Bell, G. I. (1995). Endocr. Rev. 16, 427–442.
Patel, Y. C. and Srikant, C. B. (1997). Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 8, 398–405.
Breder, C. D., Yamada, Y., Yasuda, K., Seino, S., Saper, C. B., and Bell. G. I. (1992). J. Neurosci. 12, 3920–3934.
Kaupmann, K., Bruns, C., Hoyer, D., Seuwen, K., and Lubbert, H. (1993). FEBS Lett. 331, 53–59.
Day, R., Dong, W., Panetta, R., Kraicer, J., Greenwood, M. T., and Patel, Y. C. (1995). Endocrinology 136, 5232–5235.
Shimon, I., Taylor, J. E., Dong, J. Z., et al. (1997). J. Clin. Invest. 99, 789–798.
Miller, G. M., Alexander, J. M., Bikkal, H. A., Katznelson, L., Zervas, N. T., and Klibanski, A. (1995). J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 80, 1286–1392.
Panetta, R. and Patel, Y. C. (1995). Life Sci. 56, 333–342.
Greenman, Y. and Melmed, S. (1994). J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 78, 398–403.
Greenman, Y. and Melmed, S. (1994). J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 79, 724–729.
Jaquet, P., Ouafik, L., Saveanu, A., et al. (1999). J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 84, 3268–3276.
Jaquet, P., Saveanu, A., Gunz, G., et al. (2000). J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 85, 781–792.
Newman, C. B., Melmed, S., Snyder, P. J., et al. (1995). J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 80, 2768–2775.
Caron, P., Morange-Ramos, I., Conge, M., and Jaquet, P. (1997). J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 82, 18–22.
O’Carroll, A. M., Raynor, K., Lolait, S. J., and Reisine, T. (1994). Mol. Pharmacol. 48, 291–298.
Moreau, J.-P., Kim, S., Dong, J. Z., et al. (1996). Metabolism 45(Suppl. 1), 24–28.
Coy, D. H. and Taylor, J. E. (1996). Metabolism 45(Suppl. 1), 21–23.
Shimon, I., Yan, X., Taylor, J. E., Weiss, M. H., Culler, M. D., and Melmed, S. (1997). J. Clin. Invest. 100, 2386–2392.
Yang, L., Berk, S. C., Rohrer, S. P., et al. (1998). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 10,836–10,841.
Rohrer, S. P., Birzin, E. T., Mosley, R. T., et al. (1998). Science 282, 737–740.
Sharma, K., Patel, Y. C., and Srikant, C. B. (1996). Mol. Endocrinol. 10, 1688–1696.
Lamberts, S. W. J., van der Lely, A. J., and Hofland, L. J. (2002). Eur. J. Endocrinol. 146, 701–705.
Saveanu, A., Gunz, G., Dufour, H., et al. (2001). J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 86, 140–145.
Zambre, Y., Ling, Z., Chen, M. C., et al. (1999). Biochem. Pharmacol. 57, 1159–1164.
Tulipano, G., Soldi, D., Bagnasco, M., et al. (2002). Endocrinology 143, 1218–1224.
Bruns, C., Lewis, I., Briner, U., Meno-Tetang, G., and Weckbecker, G. (2002). Eur. J. Endocrinol. 146, 707–716.
Murray, R. D., Kim, K., Ren, S. G., Weckbecher, G., Bruns, C., and Melmed, S. (2002). In: Abstracts of the Endocrine Society’s 84th Annual Meeting, San Francisco (abstract OR58-6).
Hofland, L. J., Bruns, C., Weckbecker, G., et al. (2002). In: Abstracts of the Endocrine Society’s 84th Annual Meeting, San Francisco (abstract P2–108).
Afargan, M., Janson, E. T., Gelerman, G., et al. (2001). Endocrinology 142, 477–486.
Rocheville, M., Lange, D. C., Kumar, U., Sasi, R., Patel, R. C., and Patel, Y. C. (2000). J. Biol. Chem. 275, 7862–7869.
Rocheville, M., Lange, D. C., Kumar, U., Patel, S. C., Patel, R. C., and Patel, Y. C. (2000). Science 288, 154–157.
Saveanu, A., Lavaque, E. D., Gunz, G., et al. (2002). J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 87, 5545–5552.
Gulec, S. A., Drouant, G. J., Fuselier, J., et al. (2001). J. Surg. Res. 97, 131–137.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shimon, I. Somatostatin receptors in pituitary and development of somatostatin receptor subtype-selective analogs. Endocr 20, 265–269 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1385/ENDO:20:3:265
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/ENDO:20:3:265