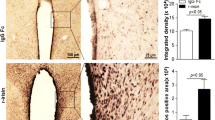
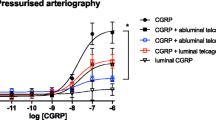
Abstract
Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) is a potent vasodilator located in the peripheral nerves including the perivascular nerves. Previous studies in our laboratory determined that the vasodilatory action of insulin is mediated in part by CGRP-containing neurons. Since insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) and insulin share molecular and receptor structural similarity as well as functional similarity, we investigated the role of the CGRP-containing neurons in IGF-1-mediated vasodilation. Wistar rats were made CGRP deficient by treatment with capsaicin (50 mg/kg) 1–3 d after birth. Vehicle-treated controls and CGRP-deficient rats were maintained for 12 to 13 wk. At this time rats were fasted overnight, anesthetized with urethane and chloralose, and prepared for cardiovascular recordings. The basal mean arterial pressure (MAP) was higher in CGRP-deficient rats when compared with controls. The infusion of IGF-1 resulted in an equivalent decrease in MAP in both the CGRP-deficient and control rats. IGF-1 infusion did not change the heart rate in control rats but decreased it in CGRP-deficient rats. IGF-1 also increased flow as determined by conductance in the iliac, renal, and superior mesenteric vascular beds in both vehicle controls and CGRP-deficient rats. We concluded that unlike insulin the IGF-1-mediated vasodilatory response is not mediated by the CGRP-dependent perivascular neurons.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zapf, J., Schmid, C., and Froesch, E. R. (1984). Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 13, 3–30.
Adams, T. E., Epa, V. C., Garrett, T. P., and Ward, C. W. (2000). Cell Mol. Life Sci. 57, 1050–1093.
Pete, G., Hu, Y., Walsh, M., Sowers, J., and Dunbar, J. C. (1996). Proc. Exp. Biol. Med. 213, 187–192.
Pete, G. and Dunbar, J. C. (1998). Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 20, 67–83.
Walsh, M. F., Barazi, M., Pete, G., Muniyappa, R., Dunbar, J. C., and Sowers, J. R. (1996). Endocrinology 137, 1798–1803.
Gillespie, C. M., Merkel, A. L., and Martin, A. A. (1997). J. Endocrinol. 155, 351–358.
Muniyappa, R., Walsh, M. F., and Rangi, J. S., et al. (1997). Life Sci. 61, 925–931.
Duanmu, Z., Lapanowski, K., and Dunbar, J. C. (1997). Proc. Exp. Biol. Med. 216, 93–97.
Sowers, J. R. (1997). Hypertension 29, 691–699.
Hauck, C. M. and Dunbar, J. C. (1999). Acta Diabetol. 36, 53–60.
Dunbar, J. C., O’Leary, D. S., Wang, G., and Wright-Richey, J. (1996). Acta Diabetol. 33, 263–268.
Salem, N. and Dunbar, J. C. (2002). Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 18, 238–244.
Kawasaki, H. (2002). Jpn. J. Pharmacol. 88, 37–43.
Edvinsson, L., Juul, R., and Jansen, I. (1994). Acta Neurol. Scand. 90, 324–330.
Preibisz, J. J. (1993). Am. J. Hypertens. 6, 434–450.
White, C. B., Roberts, A. M., and Joshua, I. G. (1993). Am. J. Physiol. 265, H1411-H1415.
Gennari, C. and Fischer, J. A. (1985). Calcif. Tissue Int. 37, 581–584.
Nakamura, T., Naruse, S., Ozaki, T., and Kumada, K. (1996). Regul. Pept. 65, 211–217.
Shen, Y. T., Pittman, T. J., Buic, P. S., et al. (2001). J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 298, 551–558.
Gangula, P. R., Zhao, H., Supowit, S. C., et al. (2000). Hypertension 35, 470–475.
Fisher, L. A., Kikkawa, D. O., Rivier, J. E., et al. (1983). Nature 305, 534–536.
Siren, A. L. and Feuerstein, G. (1988). J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 247, 69–78.
Takenaga, M. and Kawasaki, H. (1999). Eur. J. Pharmacol. 367, 239–245.
Mantelli, L., Amerini, S., Filippi, S., and Ledda, F. (1992). Neuropeptides 23, 193–198.
Gray, D. W. and Marshall, I. (1992). Br. J. Pharmacol. 107, 691–696.
Sternini, C., Reeve, J. R. Jr., and Brencha, N. (1987). Gastroenterology 93, 852–862.
Wimalawansa, S. J. (1993). Peptides 14, 247–252.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McRae, C.R., Rao, S.P. & Dunbar, J.C. Cardiovascular action of insulin-like growth factor-1 is not mediated by calcitonin gene-related peptide neurons. Endocr 19, 163–167 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1385/ENDO:19:2:163
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/ENDO:19:2:163