Abstract
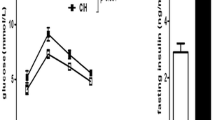
Hypoxia leads to a decrease in food intake and attenuated weight gain in rats. The purpose of this study was to measure plasma leptin and insulin in young rats exposed to hypoxia for 7 d as compared to a normoxic control group of the same age. One group was exposed from birth to 7 d of age; the other was exposed from 28 to 35 d of age (weaned at 21 d of age). As expected, body weight was significantly lower in rats of either age exposed to hypoxia for 7 d. Plasma leptin was significantly lower in hypoxic (2.0±0.2 ng/mL; n=41) compared with normoxic (2.6±0.3 ng/mL; n=30) 7-d-old rats. Plasma leptin was also significantly lower in hypoxic (1.1±0.1 ng/mL; n=20) as compared to normoxic (1.5±0.1 ng/mL; n=20) 35-d-old rats. Seven-day-old rats exposed to hypoxia demonstrated significant increases in plasma glucose and insulin whereas 35-d-old rats exhibited a decrease inboth variables. We conclude that exposure to hypoxia for 7 d leads to a decrease in body weight and plasma leptin in infant and juvenile rats. The decrease in leptin may be an attempt to reverse hypoxia-induced anorexia.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cerretelli, P. and Hoppeler H. (1996) In: Handbook of Physiology. Section 4. Environmental Physiology. volume II. Fregly, M. J. and Blatteis, C. M. (eds.) Oxford University: New York.
Butterfield, G. E., Gates, J., Fleming, G., Brooks, G. A., Sutton, J. R., and Reeves, J. T. (1992) J. Appl. Physiol. 72, 1741–1748.
Singh, S. B., Sharma, A., Sharma, K. N., and Selvamurthy, W. J. (1996). J. Appl. Physiol. 80, 1133–1137.
Moromisato, D. Y., Moromisato, M. Y., Zanconato, S., Roberts, C. T., Brosel, J. A., and Cooper, D. M. (1996), Crit. Care Med. 24, 919–924.
Gloster, J., Hasleton, P. S., Harris, P., and Heath, D. (1974). Environ. Physiol. Biochem. 4, 251–258.
Fushiki, T., Kano, T., Ito, K., Hirofuji, D., Inoue, K., Moritani, T., and Sugimoto, E. (1992). Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 70, 1522–1524.
Elia, A., Elgoyhen, A. B., Bugallo, G., Rio, M. E., and Bozzini, C. E. (1985). Acta Physiol. Pharmacol. Latinoam. 35, 311–318.
Buchanan, C., Mahesh, V., Zamorano, P., and Brann, D. (1998). Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 9, 146–150.
Fruhbeck, G., Jebb, S. A., and Prentice, A. M. (1998). Clin. Physiol. 18, 399–419.
Kiess, W., Siebler, T., Englaro, P., Kratzsch, J., Deutscher, J., Meyer, K., Gallaher, B., and Blum, W. F. (1998) J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 11, 483–496.
Raff, H., Jankowski, B. M., Bruder, E. D., Engeland, W. C., and Oaks, M. K. (1999). Endocrinology 140, 3147–3153.
Thomas, T., and Marshall, J. M. (1995). J. Physiol. 487, 513–525.
Harris, R. J. (1974). J. Pediatr. 84, 578–584.
Trottier, G., Koski, K. G., Brun, T., Toufexia, D. J., Richard, D., and Walker, C.-D. (1998). Endocrinology 139, 3704–3711.
Raff, H. (1996), In: Handbook of Physiology Section 4: Environmental Physiology, Fregly, M. J., and Blatteis, C. M. (eds.). Oxford University Press: New York.
Sawhney, R. C., Malhotra, A. S., Singh, T., Rai, R. M., and Sinha, K. C. (1986). Int. J. Biometeor. 30, 231–238.
Raff, H., Sandri, R. B., and Segerson, T. P. (1986). Am. J. Physiol. 250, R240-R244.
Ramos, S., Goya, L., Alvarez, C., and Pascual-Leone, A. M. (1998). Endocrinology 139, 4782–4792.
Raff, H. and Chadwick, C. J. (1986). Clin. Exper. Pharmacol. Physiol. 13, 827–830.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raff, H., Bruder, E.D. & Jankowski, B.M. The effect of hypoxia on plasma leptin and insulin in newborn and juvenile rats. Endocr 11, 37–39 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1385/ENDO:11:1:37
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/ENDO:11:1:37