Abstract
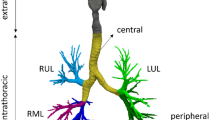
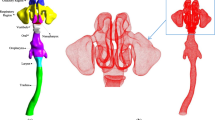
Information regarding the deposition patterns of inhaled particles has important implications to the fields of medicine and risk assesment. The former concerns the targeted delivery of inhaled pharmacological drugs (aerosol therapy); the latter concerns the risk assessment of inhaled air pollutants (inhalation toxicology). It is well documented in the literature that the behavior and fate of inhaled particles may be formulated using three families of variables: respiratory system morphologies, aerosol characteristics, and ventilatory parameters. It is straightforward to propose that the seminal role is played by morphology per se because the structures of individual airways and their spatial orientations within lungs affect the motion of air and the trajectories of transported particles. In previous efforts, we have developed original algorithms to describe airway networks within lungs and employed them as templates to interpret the results of single photon emission computed tomography (SPECTs) studies. In this work, we have advanced the process of mathematical modeling and computer simulations to produce three-dimensional (3D) images. We have tested the new in silico model by studying two different branching concepts: an inclusive (all airways present) system and a single “typical” pathway system. When viewed with the glasses supplied with this volume, the 3D nature of airway branching networks within lungs as displayed via our original computer graphics software is clear. We submit that the new technology will have numerous and seminal functions in future medical and toxicological regimens, the most fundamental being the creation of a platform to view natural 3D structures in vivo with related biological processes (e.g., disposition of inhaled pharmaceuticals).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Martonen, T. B. (1993) Mathematical model for the selective deposition of inhaled pharmaceuticals. J. Pharm. Sci. 82, 1191–1199.
Martonen, T. B. and Katz, I. (1993) Deposition patterns of polydisperse aerosols within human lungs. J. Aerosol Med. 6, 251–274.
Martonen, T. B. and Katz, I. (1993) Deposition patterns of aerosolized drugs within human lungs: effects of ventilatory parameters. Pharm. Res. 10, 871–878.
Martonen, T. B. and Katz, I. M. (1994) Interrelated effects of morphology and ventilation on drug deposition patterns. S.T.P. Pharm. Sci. 4, 11–18.
Martonen, T. B. and Schroeter, J. D. (2003) Risk assessment dosimetry model for inhaled particulate matter: I. Human subjects. Toxicol. Lett. 138, 119–132.
Martonen, T. B. and Schroeter, J. D. (2003) Risk assessment dosimetry model for inhaled particulate matter: II. Laboratory surrogates (rat). Toxicol. Lett. 138, 133–142.
Martonen, T. B., Fleming, J., Schroeter, J. D., Conway, J., and Hwang, D. (2003) In silico modeling of asthma. Adv. Drug Del. Rev. 55, 829–849.
Martonen, T. B., Bell, K. A., Phalen, R. F., Ho, A., and Wilson, A. F. (1982) Growth rate measurements and deposition modelling of hygroscopic aerosols in human tracheobronchial models. In: Inhaled Particles V. (Walton, W., ed.). Pergamon Press, Oxford; pp 93–108.
Finlay, W. H. (1998) Estimating the type of hygroscopic behavior exhibited by aqueous droplets. J. Aerosol Med. 11, 221–229.
Martonen, T. B., Yang, Y., Dolovich, M., and Guan, X. (1997) Computer simulations of lung morphologies within planar gamma images. Nucl. Med. Commun. 18, 861–869.
Martonen, T. B., Hwang, D., Guan, X., and Fleming, J. S. (1998) Supercomputer description of human lung morphology for imaging analysis. J. Nucl. Med. 39, 745–750.
Martonen, T. B., Musante, C. J., Segal, R. A., Schroeter, J. D., Hwang, D., Dolovich, M., et al. (2000) Lung models: strengths and limitations. Respir. Care 45, 712–736.
Martonen, T. B. (1982) Analytical model of hygroscopic particle behavior in human airways. Bull. Math. Biol. 44, 425–442.
Martonen, T. B. (1983) On the fate of inhaled particles in the human: a comparison of experimental data with theoretical computations based on a symmetric and asymmetric lung. Bull. Math. Biol. 45, 409–424.
Musante, C. J. and Martonen, T. B. (2000) Computer simulations of particle deposition in the developing lung. J. Air Waste Manage. Assoc. 50, 1426–1432.
Segal, R. A., Guan, X., Shearer, M., and Martonen, T. B., (2000) Mathematical model of airflow in the lungs of children. I. Effects of tumor sizes and locations. J. Theor. Med. 2, 199–213.
Guan, X., Segal, R. A., Shearer, M., and Martonen, T. B. (2000) Mathematical model of airflow in the lungs of children. II. Effects of ventilatory parameters. J. Theor. Med. 3, 51–62.
Martonen, T. B., Katz, I. M., and Cress, W. (1995) Aerosol drug deposition as a function of airway disease: cystic fibrosis. Pharm. Res. 12, 96–102.
Martonen, T. B., Hwang, D., Katz, I., and Yang, Y. (1997) Cystic fibrosis: treatment with a supercomputer drug delivery model. Adv. Engin. Software 28, 359.
Segal, R. A., Martonen, T. B., Kim, C. S., and Shearer, M. (2002) Computer simulations of particle deposition in the lungs of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients. Inhal. Toxicol. 14, 705–720.
Findeisen, W. (1935) Uber das absetzen kleiner in der luft suspendierter teilchen in der menschlichen lunge bei der atmung. Pfluegers Arch. Ges. Physiol. 236, 367–379.
Landahl, H. D. (1950) On the removal of airborne droplets by the human respiratory tract. I. The lung. Bull. Math. Biophys. 12, 43–56.
Beeckmans, J. M. (1965) The deposition of aerosols in the respiratory tract. I. Mathematical analysis and comparison with experimental data. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 43, 157–172.
Martonen, T. B., Yang, Y., and Xue, Z. (1994) Influences of cartilaginous rings on tracheobronchial fluid dynamics. Inhal. Toxicol. 6, 185–203.
Martonen, T. B., Yang, Y., and Xue, X. (1994) Effects of acarinal ridge shapes on lung airstreams. Aerosol Sci. Tech. 21, 119–136.
Martonen, T. B., Zhang, Z., and Yang, Y. (1995) Airway surface irregularities promote particle diffusion in the human lung. Rad. Prot. Dosim. 59, 5–14.
Martonen, T. B., Zhang, Z., and Yang, Y. (1997) Particle diffusion from developing flows in rough-walled tubes, Aerosol Sci. Technol. 26, 1–11.
Zhang, Z. and Martonen, T. (1995) Deposition of ultrafine aerosols in human tracheobronchial airways. Inhal. Toxicol. 9, 99–110.
Zhang, Z. and Martonen, T. (1996) Comparison of theoretical and experimental particle diffusion data within human airway casts. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 27, 97–108.
Martonen, T. B., Zhang, Z., Yang, Y., and Bottei, G. Gas transport in human airways. Inhal. Toxicol. 7, 303–318.
Martonen, T. B. and Guan, X. (2001) Effects of tumors on inhaled pharmacologic drugs: I. Flow patterns. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 35, 233–243.
Martonen, T. B. and Guan, X. (2001) Effects of tumors on inhaled pharmacologic drugs: II. Particle motion. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 35, 245–253.
Zhang, Z., Kleinstreuer, C., and Hickey, A. J. (2002) Aerosol transport and deposition in a triple bifurcation bronchial airway model with local tumors. Inhal. Tox. 14, 1111–1133.
Martonen, T. B. (2001) Commentary: effects of asymmetric branch flow rates on aerosol deposition in bifurcating airways. J. Med. Engr. Tech. 25, 124–126.
Musante, C. J. and Martonen, T. B. (2001) Computational fluid dynamics in human lungs: I. Effects of natural airway features. p. 131–145. In Medical Applications of Computer Modelling: The Respiratory System. (Martonen, T. B., ed.) WIT Press, Southampton, UK.
Musante, C. J. and Martonen, T. B. (2001) Computational fluid dynamics in human lungs: II. Effects of airway disease. p. 147–164. In Medical Applications of Computer Modelling: The Respiratory System. (Martonen, T. B., ed.) WIT Press, Southampton, UK.
Guan, X. and Martonen, T. B. (1997) Simulations of flow in curved tubes. Aerosol Sci. Tech. 26, 485.
Guan, X. and Martonen, T. B. (2000) Flow transition in bends and applications to airways. J. Aerosol Sci. 31, 833–847.
Martonen, T. B., Guan, X., and Schreck, R. M. (2001) Fluid dynamics in airway bifurcations: I. Primary flows. Inhal. Toxicol. 13, 261–279.
Martonen, T. B., Guan, X., and Schreck, R. M. (2001) Fluid dynamics in airway bifurcations: II. Secondary currents. Inhal. Toxicol. 13, 281–289.
Martonen, T. B., Guan, X., and Schreck, R. M. (2001) Fluid dynamics in airway bifurcations: III. Localized flow conditions. Inhal. Toxicol. 13, 291–305.
Comer, J. J., Kleinstreuer, C., and Zhang, Z. (2001) Flow structures and particle deposition patterns in double-bifurcation airway models. Part 1. Air flow fields. J. Fluid Mech. 435, 25–54.
Comer, J. J., Kleinstreuer, C., and Kim, C. S. (2001) Flow structures and particle deposition patterns in double-bifurcation airway models. Part 2. Aerosol transport and deposition. J. Fluid Mech. 435, 55–80.
Zhang, Z., Kleinstreuer, C., and Kim, C. S. (2001) Effects of curved inlet tubes on air flow and particle deposition in bifurcating lung models. J. Biomech. 34, 659–669.
Zhang, Z., Kleinstreuer, C., and Kim, C. S. (2002) Cyclic micron-sized particle inhalation and deposition in a triple bifurcation lung airway model. J. Aerosol. Sci. 33, 257–281.
Schlesinger, R. B. and Lippmann, M. (1976) Particle deposition in the trachea: in vivo and in hollow casts. Thorax 31, 678–684.
Chan, T. L., Schreck, R. M., and Lippmann, M. (1980) Effect of the laryngeal jet on particle deposition in the human trachea and upper bronchial airways. J. Aerosol Sci. 11, 447–459.
Martonen, T. B. (1983) Measurement of particle dose distribution in a model of a human larynx and tracheobronchial tree. J. Aerosol Sci. 14, 11–22.
Cohen, B. S., Sussman, R. G., and Lippmann, M. (1990) Ultrafine particle deposition in a human tracheobronchial cast. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 12, 1082–1091.
Cohen, B. S. and Asgharian, B. (1990) Deposition of ultrafine particles in the upper airways: an empirical analysis. J. Aerosol Sci. 27, 139–150.
Martonen, T. B. and Lowe, J. (1983) Assessment of aerosol deposition patterns in human respiratory tract casts. pp. 151–164. In: International Symposium on Aerosols in the Mining and Industrial Work Environment. (Liu, B. and V. Marple, eds.), Ahn Arbor Science, Ann Arbor, MI.
Katz, I. M. and Martonen, T. B. (1997) Flow patterns in three dimensional laryngeal models. J. Aerosol Med. 9, 501–511.
Katz, J. M. and Martonen, T. B. (1997) Three-dimensional fluid particle trajectories in the human larynx and trachea. J. Aerosol Med., 9, 513–519.
Katz, I. M., Martonen, T. B., and Flaa, W. (1997) Three-dimensional computational study of inspiratory aerosol flow through the larynx: the effect of glottal aperture modulation. J. Aerosol Sci. 28, 1073–1083.
Katz, I. M., Davis, B. M., and Martonen, T. B. (1999) A numerical study of particle motion within the human larynx trachea. J. Aerosol Sci. 30, 173–183.
Keyhani, K., Scherer, P. W., and Mozell, M. M. (1995) Numerical simulation of airflow in the human nasal cavity. J. Biomech. Eng. 117, 429–441.
Subramaniam, R. P., Richardson, R. B., Morgan, K. T., and Guilmette, R. A. (1998) Computational fluid dynamics simulations of inspiratory airflow in the human nose naropharynx. Inhal Tox., 10, 91–120.
Frederick, C. B., Bush, M. L., Lomax, L. G., Black, K. A., Finch, L., Kimbell, J. S., et al. (1998) Application of a hybrid computational fluid dynamics and physiologically based inhalation model for interspecies dosimetry extrapolation of acidic vapors in the upper airways. Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 152, 211–231.
Schroeter, J. D., Musante, C. J., Hwang, D., Burton, R., Guilmette, R., and Martonen, T. B. (2001) Hygroscopic growth and deposition of inhaled secondary cigarette smoke in human nasal pathways. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 34, 137–143.
Martonen, T. B., Zhang, Z., Yu, G., and Musante, C. J. (2001) Three-dimensional computer modeling of the human upper respiratory tract. Cell Biochem. Biophys 35, 255–261.
Martonen, T. B., Quan, L., Zhang, Z., and Musante, C. J. (2002) Flow simulation in the human upper respiratory tract. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 37, 27–36.
Martonen, T. B., Zhang, Z., Yue, G., and Musante, C. J. (2002) 3-D particle transport within the human upper respiratory tract. J. Aerosol Sci. 33, 1095–1110.
Martonen, T. B., Zhang, Z., Yue, G. and Musante, C. J. (2003) Fine particle deposition within human nasal airways. Inhal. Toxicol. 15, 283–303.
Weibel, E. R. (1963) Morphometry of the Human Lung, Academic Press, New York.
Weibel, E. R. (1991) Design of airways and blood vessels as branching trees. In The Lung-Scientific Foundations (Crystal, R. G., West, J. B., Barnes, P. J., Cherniack, N. S., and Weibel, E. R. eds. Raven Press, New York; pp. 711–720.
Sbirlea-Apjiu G., Lemaire, M., Katz, I., Conway, J., Fleming, J., and Martonen, T. (2004) Simulation of the regional manifestation of asthma. J. Pharm. Sci. 93, 1205–1216.
Martonen, T. B., Barnett, A. E., and Miller, F. J. (1985) Ambient sulfate deposition in man: modeling the influence of hygroscopicity. Environ. Health Persp. 63, 11–24.
Martonen, T. ., Ménache, M. G., Hofmann, W., and Eisner, A. D. (1989) The role of particle hygroscopicity in aerosol therapy and inhalation toxicology. In: Extrapolation Modeling of Inhaled Particles and Gases: Lung Dosimetry. (Crapo, J. D., Smolko, E. D., Miller, F. J. Graham, J. A., and Hayes, A. W., eds.). Academic Press, New York, pp. 303–316.
Finlay, W. H., Stapleton, K. W., and Zuberbuhler, P. (1997) Fine particle fraction as a measure of mass depositing in the lung during inhalation of nearly isotonic nebulized aerosols. J. Aerosol Sci. 28, 1301–1309.
Hickey, A. J. and Martonen, T. B. (1993) Behavior of hygroscopic pharmaceutical aerosols and the influence of hydrophobic additives. Pharm. Res. 10, 1–7.
Lippmann, M. and Albert, R. E. (1969) The effect of particle size on the regional deposition of inhaled aerosols in the human respiratory tract. Am. Ind. Hyg. Assoc. J. 30, 257–275.
Chan, T. L. and Lippmann, M. L. (1980) Experimental measurement and empirical modelling of the regional deposition of inhaled particles in humans. Am. Ind. Hyg. Assoc. J. 41, 399–409.
Stahlhofen, W., Gebhart, J., and Heyder, J. (1981) Biological variability of regional deposition of aerosol particles in the human respiratory tract. Am. Ind. Hyg. Assoc. J. 42, 348–352.
Heyder, J., Gebhart, J., Rudolf, G., Schiller, C. F., and Stahlhofen, W. (1986) Deposition of particles in the human respiratory system in the size range 0.005–15 mm. J. Aerosol Sci. 17, 811–825.
Horsfield, K. (1991) Pulmonary airways and blood vessels considered as confluent trees, In: The Lung: Scientific Foundations (Crystal, R. G., West, J. B., Barnes, P. J., Cherniack, N. S., and Weibel, E. R., eds.), Raven Press, New York; pp. 721–727.
Horsfield, K., Dart, G., Olson, D. E., Filley, G. F., and Cumming, G. (1971) Models of the human bronchial tree. J. Appl. Physiol. 31, 207–217.
Martonen, T. B., Yang, Y., Hwang, D., and Fleming, J. S. (1994) Mapping the human lung using Delaunay tessellation. Comput. Biomed. Res. 27, 245–262.
Martonen, T. B., Yang, Y., Hwang, D., and Fleming, J. S. (1995) Computer model of human lung morphology to complement SPECT analyses. Int. J. Biomed. Comput. 40, 5–16.
Martonen, T. B., Yang, Y., Hwang, D., and Fleming, J. S. (1995) Computer simulations of human lung structures for medical applications. Comput. Biol. Med. 25, 431–446.
Martonen, T. B., Schroeter, J. D., Hwang, D., Fleming, J. S., and Conway, J. H. (2000) Human lung morphology models for particle deposition studies. Inhal. Toxicol. 12, 109–121.
Kitaoka, H., Takaki, R., and Suki, B. (1999) A three-dimensional model of the human airway tree. J. Appl. Physiol. 87, 2207–2217.
Lee, Z., Berridge, M. S., Finlay, W. H., and Heald, D. L. (2000) Mapping PET-measured triamcinolone acetonide (TAA) aerosol distribution into deposition by airway generation. Int. J. Pharm. 199, 7–16.
Lee, Z., Berridge, M. S., and Heald, D. L. (2000) Evaluation of planar gamma camera scintigraphy vs. PET imaging used for pulmonary deposition of inhaled aerosols. Int. J. Nucl. Med. 1, 28–39.
Lee, Z., Ljungberg, M., Muzic, R. F., Jr., and Berridge, M. S. (2001) Usefulness and pitfalls of planar g-scintigraphy for measuring aerosol deposition in the lungs: a Monte Carlo investigation. J. Nucl. Med. 42, 1077–1083.
Schroeter, J. D., Fleming, J. S., Hwang, D., and Martonen, T. B. (2002) A computer model of lung morphology to analyze SPECT images. Comp. Med. Imag. Graph. 26, 237–246.
Spencer, R. M., Schroeter, J. D., and Martonen, T. B. (2001) Computer simulations of lung airway structures using data-driven surface modeling techniques. Comp. Biol. Med. 31, 499–511.
Bailey, M., and Clark, D. (1998) Using ChromaDepth to obtain inexpensive single-image stereovision for scientific visualization. J. Graph. Tools 3, 1–9.
Newcott, W. R. (1998) Return to Mars. Nat. Geographic 194, 2–29.
MacInnis, J. B. (1998) Titanic: tragedy in three dimensions. Nat. Geographic 194, 120–127.
Burton, R. T., Isaacs, K. K., Fleming, J. S., and Martonen, T. B. (2004) Computer reconstruction of a human lung boundary model from magnetic resonance images. Respir. Care 49, 180–185.
Fleming, J. S., Nassim, M., Hashish, A., Bailey, A., Conway, J., Holgate, S., et al. (1995) Description of pulmonary deposition of radiolabelled aerosol by airway generation using a conceptual three dimensional model of lung morphology. J. Aerosol Med. 8, 341–356.
Fleming, J. S., Nassim, M., Hashish, A., Bailey, A., Conway, J., Holgate, S., et al. Three dimensional description of pulmonary deposition of inhaled aerosol using data from multi-modality imaging. J. Nuclear Med. 37, 873–877 (1996).
Fleming, J. S., Hashish, A., Conway, J., Nassim, M., Holgate, S., Halson, P., et al. (1996) Assessment of deposition of inhaled aerosol in the respiratory tract of man using three dimensional multimodality imaging and mathematical modelling. J. Aerosol Med. 9, 317–327.
Fleming, J. S., Hashish, A. H., Conway, J. H., Hartley-Davies, R., Nassim, M. A., Guy, M. J., et al. (1997) A technique for simulating radionuclide images from the aerosol deposition pattern in the airway tree. J. Aerosol Med. 10, 199–212.
Feming, J. S., Conway, J. H., Holgate, S. T., Moore, E. A., Hashish, A. H., Bailey, A. G., et al. (1998) Evaluation of the accuracy and precision of lung aerosol deposition measurements from planar radionuclide imaging using simulation. Phys. Med. Biol. 43, 2423–2429.
Fleming, J. S., Sauret, V., Conway, J. H., Holgate, S. T., Bailey, A. G., and Martonen, T. B. (2000) Evaluation of the accuracy and precision of lung aerosol deposition measurements from single photon emission computed tomography using simulation, J. Aerosol Med. 13, 187–198.
Fleming, J. S., Conway, J. H., Holgate, S. T., Bailey, A. G., and Martonen, T. B. (2000) Comparison of methods for deriving aerosol deposition by airway generation from three-dimensional radionuclide imaging. J. Aerosol Sci. 31, 1251–1259.
Katz, I. M., Schroeter, J. D., and Martonen T. B. (2001) Factors affecting the deposition of aerosolized insulin. 3, 387–397.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martonen, T., Isaacs, K. & Hwang, D. Three-dimensional simulations of airways within human lungs. Cell Biochem Biophys 42, 223–249 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1385/CBB:42:3:223
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/CBB:42:3:223