Abstract
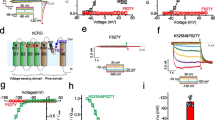
HERG (Human ether-à-go-go-related gene) potassium channels are crucial for cardiac action potential repolarization. HERG channels are also found in neuronal and tumor cells. The effect of pH0 on HERG is of clinical significance because of changes in pH during myocardial ischemia, inflammation, and respiratory alkalosis. We present evidence for the presence of multiple proton binding sites in HERG. Extracellular protons bind rapidly and reversibly to affect both activation and deactivation. However, these effects occur in two distinct pH0 ranges. The deactivation rate has a pKa of 6.76±0.02 compared to pKa of 5.50±0.02 for changes in current suppression, which suggests the presence of at least two proton binding sites on HERG with functionally distinct properties.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sanguinetti, M. C., Jiang, C., Curran, M. E., and Keating, M. T. (1995) A mechanistic link between an inherited and an acquired cardiac arrhythmia: HERG encodes the IKr potassium channel. Cell 81, 299–307.
Trudeau, M. C., Warmke, J. W., Ganetzky, B., and Robertson, G. A. (1995) HERG, a human inward rectifier in the voltage-gated potassium channel family. Science 269, 92–95.
Warmke, J. W. and Ganetzky, B. (1994) A family of potassium channel genes related to eag in Drosophila and mammals. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 91, 3438–3442.
Janse, M. J. and Wit, A. L. (1989) Electrophysiological mechanisms of ventricular arrhythmias resulting from myocardial ischemia and infarction. Physiol. Rev. 69, 1049–1169.
Yan, G. X. and Kleber, A. G. (1992) Changes in extracellular and intracellular pH in ischemic rabbit papillary muscle. Circulation Research Circ. Res. 71, 460–470.
Carmeliet, E. (1999) Cardiac ionic currents and acute ischemia: from channels to arrhythmias. Physiol. Rev. 79, 917–1017.
Berube, J., Chahine, M., and Daleau, P. (1999) Modulation of HERG potassium channel properties by external pH. Pflug. Arch.—Eur. J. Physiol. 438, 419–422.
Anumonwo, J. M., Horta, J., Delmar, M., Taffet, S. M., and Jalife, J. (1999) Proton and zinc effects on HERG currents. Biophys. J. 77, 282–298.
Terai, T., Furukawa, T., Katayama, Y., and Hiraoka, M. (2000) Effects of external acidosis on HERG current expressed in Xenopus oocytes. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 32, 11–21.
Jiang, M., Dun, W., and Tseng, G. N. (1999) Mechanism for the effects of extracellular acidification on HERG-channel function. Am. J. Physiol. 277, H1283-H1292.
Jo, S. H., Youm, J. B., Kim, I., Lee, C. O., Earm, Y. E., and Ho, W. K. (1999) Blockade of HERG channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes by external H+. Pflug. Arch.—Eur. J. Physiol. 438, 23–29.
Smith, P. L., Baukrowitz, T., and Yellen, G. (1996) The inward rectification mechanism of the HERG cardiac potassium channel. Nature 379, 833–836.
Wang, S., Morales, M. J., Liu, S., Strauss, H. C., and Rasmusson, R. L. (1996) Time, voltage and ionic concentration dependence of rectification of h-erg expressed in Xenopus oocytes. FEBS Letters 389, 167–173.
Spector, P. S., Curran, M. E., Zou, A., Keating, M. T., and Sanguinetti, M. C. (1996) Fast inactivation causes rectification of the IKr channel. J. Gen. Physiol. 107, 611–619.
Liu, S., Rasmusson, R. L., Campbell, D. L., Wang, S., and Strauss, H. C. (1996) Activation and inactivation kinetics of an E-4031-sensitive current from single ferret atrial myocytes. Biophys. J. 70, 2704–2715.
Shibasaki, T. (1987) Conductance and kinetics of delayed rectifier potassium channels in nodal cells of the rabbit heart. J. Physiol. 387, 227–250.
Gintant, G. A. (1996) Two components of delayed rectifier current in canine atrium and ventricle. Does IKs play a role in the reverse rate dependence of class III agents? Circ. Res. 78, 26–37.
Wang, S., Liu, S., Morales, M. J., Strauss, H. C., and Rasmusson, R. L. (1997) A quantitative analysis of the activation and inactivation kinetics of HERG expressed in Xenopus oocytes. J. Physiol. 502, 45–60.
Kiehn, J., Lacerda, A. E., Wible, B., and Brown, A. M. (1996) Molecular physiology and pharmacology of HERG. Single-channel currents and block by dofetilide. Circulation 94, 2572–2579.
Johnson, J. P. Jr, Balser, J. R., and Bennett, P. B. (1999) Enhancement of HERG K+ Currents by Cd2+ Destabilization of the Inactivated State Biophys. J. 77, 2534–2541.
Woodhull, A. M. (1973) Ionic blockage of sodium channels in nerve. J. Gen. Physiol. 61, 687–708.
Kiehn, J. (2000) Regulation of the cardiac repolarizing HERG potassium channel by protein kinase A. Trends in Cardiovascular Medicine 10, 205–209.
Muraki, K., Imaizumi, Y., Watanabe, M., Habuchi, Y., and Giles, W. R. (1995) Delayed rectifier K+ current in rabbit atrial myocytes. J. Physiol. 269, H524-H532.
Sanguinetti, M. C., Curran, M. E., Spector, P. S., and Keating, M. T. (1996) Spectrum of HERG K+-channel dysfunction in an inherited cardiac arrhythmia. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 93, 2208–2212.
Vereecke, J. and Carmeliet, E. (2000) The effect of external pH on the delayed rectifying K+ current in cardiac ventricular myocytes. Plug. Arch.—Eur. J. Physiol. 439, 739–751.
Jiang, Y., Ruta, V., Chen, J., Lee, A., and MacKinnon, R. (2003) The principle of gating charge movement in a voltage-dependent K+ channel. Nature 423, 42–48.
Kuo, A., Gulbis, J. M., Antcliff, J. F., Rahman, T., Lowe, E. D., Zimmer, J., et al. (2003) Crystal structure of the potassium channel KirBacl.1 in the closed state. Science 439, 739–751.
Li, X. Y., Bett, G. C. L., Jiang, X. J., Bondarenko, V. E., Morales, M. J., and Rasmusson, R. L. (2003) Regulation of N- and C-type inactivation by pH0 and potassium in normal and mutant Kv1.4 channels: Evidence for transmembrane communication. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 284, H71-H80.
Cuello, L. G., Romero, J. G., Cortes, D. M., and Perozo, E. (1998) pH-dependent gating in the Streptomyces lividans K+ channel. Biochemistry 37, 3229–3236.
Yellen, G. (1998) The moving parts of voltagegated ion channels. Quarterly Rev. Biophys. 31, 239–295.
Doyle, D. A., Morais, C. J., Pfuetzner, R. A., Kuo, A., Gulbis, J. M., Cohen, S. L., et al. (1998) The structure of the potassium channel: molecular basis of K+ conduction and selectivity. Science 280, 69–77.
Jiang, Y., Lee, A., Chen, J., Cadene, M., Chait, B. T., and MacKinnon, R. (2002) The open pore conformation of potassium channels. Nature 417, 523–526.
Bett, G. C. L. and Rasmusson, R. L. Models of cardiac ion channels, in: Quantitative Cardiac Electrophysiology. (Cabo, C. and Rosenbaum, D. S. eds.) Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York, NY, 2002.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bett, G.C.L., Rasmusson, R.L. Functionally-distinct proton-binding in HERG suggests the presence of two binding sites. Cell Biochem Biophys 39, 183–193 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1385/CBB:39:3:183
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/CBB:39:3:183