Abstract
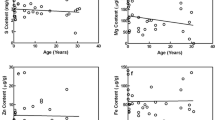
To elucidate compositional changes of peripheral nerves with aging, the authors investigated age-related changes of elements and their relationships in the optic, trigeminal, vagus, median, radial, ulnar, femoral, sciatic, tibial, and common peroneal nerves by inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectrometry. The subjects consisted of 10 men and 12 women, ranging in age from 65 to 91 yr. It was found that although accumulations of Ca and P occurred only in the trigeminal nerve at old age, it hardly occurred in the optic, vagus, median, radial, ulnar, femoral, sciatic, tibial, and common peroneal nerves at old age. The average contents of Ca and P were three and two times higher in the trigeminal nerve than in the other nine kinds of nerve, respectively. Likewise, the average content of Mg was a little higher in the trigeminal nerve compared with the other nerves.
With regard to the relationships among elements, significant direct correlations were found among the contents of Ca, P, S, and Mg in most, but not all, 10 kinds of nerve. In the trigeminal nerve, a significant inverse correlation was found between the contents of S and the other elements, such as Ca, P, and Mg. Regarding the relationships between the contents of S and other elements, the nerves, except for the trigeminal nerve, differed from those found in the arteries previously reported.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Tohno, S. Tohno, T. Minami, et al., Age-related changes of mineral contents in human thoracic aorta and in the cerebral artery, Biol. Trace Element Res. 54, 23–31 (1996).
T. Araki and Y. Tohno, Age dependency of nanosecond fluorescence characteristics in human artery, Front. Med. Biol. Eng. 7, 265–273 (1996).
S. Tohno and Y. Tohno, Age-related differences in calcium accumulation in human arteries, Cell. Mol. Biol. 44, 1253–1263 (1998).
S. Tohno, M. Masuda, Y. Tohno, et al., High accumulation of calcium and phosphorus in human iliac arteries, Biol. Trace Element Res. 70, 41–49 (1999).
S. Tohno, Y. Tohno, T. Minami, et al., A high accumulation of minerals in human internal jugular vein, Biol. Trace Element Res. 62, 17–23 (1998).
S. Tohno, Y. Moriwake, Y. Tohno, et al., Age-related changes of element contents in human mitral and tricuspid valves, Biol. Trace Element Res. 70, 137–147 (1999).
Y. Tohno, S. Tohno, M. Utsumi, et al., Age-indepedent constancy of mineral contents in human vertebrae and auditory ossicles, Biol. Trace Element Res. 59, 167–175 (1997).
Y. Tohno, M. Utsumi, S. Tohno, et al., Age-dependent changes of mineral contents in man’s and woman’s calcanei, Biol. Trace Element Res. 60, 81–90 (1997).
Y. Tohno, M. Utsumi, S. Tohno, et al., A constancy of mineral contents in human auditory ossicles, Acta Anat. Nippon. 72, 531–534 (1997).
M. Utsumi, S. Tohno, T. Minami, et al., Age-independent constancy of mineral contents in human ribs, Biol. Trace Element Res. 67, 165–171 (1999).
S. Tohno, Y. Tohno, T. Minami, et al., Difference of mineral contents in human intervertebral disks and its age-related change, Biol. Trace Element Res. 52, 117–124 (1996).
S. Tohno, Y. Tohno, T. Minami, et al., High accumulations of calcium and phosphorus in women’s pubic symphysis, Biol. Trace Element Res. 59, 177–185 (1997).
Y. Moriwake, Y. Tohno, S. Tohno, et al., Age-related changes of element contents in the human meniscus, Biol. Trace Element Res. 64, 229–235 (1998).
Y. Takano, Y. Moriwake, Y. Tohno, et al., Age-related changes of elements in the human articular disk of temporomandibular joint, Biol. Trace Element Res. 67, 269–276 (1999).
Y. Tohno, Y. Moriwake, Y. Takano, et al., Age-related changes of elements in human anterior cruciate ligaments and ligamenta capitum femorum, Biol. Trace Element Res. 68, 181–192 (1999).
Y. Tohno, Y. Takano, S. Tohno, et al., Age-dependent decreases of phosphorus and magnesium in human Achilles’s tendons, Biol. Trace Element Res. 74, 1–9 (2000).
N. Arnold and D. G. F. Harriman, The incidence of abnormality in control human peripheral nerves studied by single axon dissection, J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 33, 55–61 (1970).
A. H. Horris, N. W. Shock, and I. H. Wagman, Age changes in maximum conduction velocity of motor fibers of human ulnar nerves, J. Appl. Physiol. 5, 589–593 (1953).
I. H. Wagman and H. Lesse, Maximum conduction velocities of motor fibers of ulnar nerve in human subjects of various ages and sizes, J. Neurophysiol. 15, 235–244 (1952).
M. J. Wayner and R. Emmer, Spinal synaptic delay in young and aged rats, Am. J. Physiol. 194, 403–405 (1958).
A. Sato, Y. Sato, and H. Suzuki, Aging effects on conduction velocities of myelinated and unmyelinated fibers of peripheral nerves, Neurosci. Lett. 53, 15–20 (1985).
B. N. Berg, A. Wolf, and H. S. Simmus, Degenerative lesions of spinal roots and peripheral nerves in aging rats, Gerontologia 6, 72–80 (1962).
I. R. Griffiths and I. D. Duncan, Age changes in the dorsal and ventral lumbar nerve roots of dogs, Acta Neuropathol. 32, 75–85 (1975).
N. Grover-Johnson and P. S. Spencer, Peripheral nerve abnormalities in aging rats, J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 38, 316 (1979).
R. M. LoPachin, J. Lowery, J. Eichberg, et al., Distribution of elements in rat peripheral axons and nerve cell bodies determined by X-ray microprobe analysis, J. Neurochem. 51, 764–775 (1988).
R. M. LoPachin, V. R. LoPachin, and A. J. Saubermann, Effects of axotomy on distribution and concentration of elements in rat sciatic nerve, J. Neurochem. 54, 320–332 (1990).
Y. Tohno, S. Tohno, H. Matsumoto, et al., A trial of introducing soft X-ray apparatus into dissection practice for students, J. Nara Med. Assoc. 36, 365–370 (1985) (in Japanese).
Y. Tohno, S. Tohno, Y. Moriwake, et al., Accumulation of calcium and phosphorus accompanied by increase of magnesium and decrease of sulfur in human arteries, Biol. Trace Element Res. 82, 9–19 (2001).
Y. Tohno, S. Tohno, Y. Moriwake, et al., Simultaneous accumulation of calcium, phosphorus, and magnesium in various human arteries, Biol. Trace Element Res. 82, 21–28 (2001).
S. Tohno, Y. Tohno, Y. Moriwake, et al., Quantitative changes of calcium, phosphorus, and magnesium in common iliac arteries with aging, Biol. Trace Element Res. 84, 57–66 (2001).
S. Tohno, Y. Tohno, T. Minami, et al., Elements of calcified sites in human thoracic aorta, Biol. Trace Element Res. 86, 23–30 (2002).
Y. Tohno, S. Tohno, P. Mahakkanukrauh, et al., Mass ratios of magnesium to calcium and phosphorus in the arteries of Japanese and Thai, Biol. Trace Element Res. 91, 217–230 (2003).
S. Tohno, Y. Tohno, T. Minami, et al., Relationships among element contents in the internal jugular vein similar to the arteries, Biol. Trace Element Res. 88, 223–233 (2002).
S. Tohno, Y. Tohno, Y. Moriwake, et al., Compositional changes of the aortic valve similar to the artery with aging, Biol. Trace Element Res. 87, 83–93 (2002).
Y. Tohno, S. Tohno, H. Satoh, et al., Compositional changes of human mitral valves with aging, Biol. Trace Element Res. 88, 203–213 (2002).
Y. Tohno, S. Tohno, C. Azuma, et al., Age-related changes of elements in human thoracic ducts and azygos veins and relationships among elements, Biol. Trace Element Res., in press.
K. Furuta, Y. Tohno, S. Tohno, et al., Compositional changes of the xiphoid process and costal cartilage with aging, Biol. Trace Element Res. 95, 123–138 (2003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Utsumi, M., Tohno, S., Tohno, Y. et al. Age-related changes of elements with their relationships in human cranial and spinal nerves. Biol Trace Elem Res 98, 229–252 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1385/BTER:98:3:229
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/BTER:98:3:229