Abstract
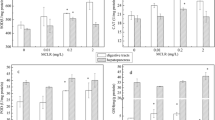
The biochemical toxicity of arsenic trioxide (AsIII) in a freshwater edible fish Channa punctatus has been studied on exposures ranging from 7 to 90 d. The arsenic concentration increased exponentially in liver, kidney, gills, and muscles of fish up to 60 d of exposure to arsenic. However, arsenic concentration in these tissues declined at 90 d of exposure. This relationship between period of exposure and concentration of arsenic in selected tissues suggests an adaptive response of fish to arsenic. Furthermore, exposure to arsenic-induced lipid peroxidation in these organs increased initially at 7 d of exposure; however, it decreased up to 60 d of exposure but increased again at 90 d of treatment. Values of reduced glutathione (GSH) reflected the observations of lipid peroxidation. The role of GSH in this adaptive response has been discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Lunde, Activation analysis of bromine, iodine and arsenic in oils from fishes, whale, phyto and zooplankton of marine and limnetic biotopes, Int. Rev. Gesselschaft Hydrobiol. 52, 265 (1967).
A. A. Schroeder and J. J. Balassa, Abnormal trace metals in man: arsenic, J. Chronic Dis. 19, 85–106 (1966).
H. Windom, R. Stickney, and D. Smith, Arsenic, cadmium, copper, mercury and zinc in some species of north Atlantic finfish, J. Fish Res. Board Can. 30, 275–279 (1973).
N. Kotsanis and J. Iliopoulou-Georgudaki, Arsenic induced liver hyperplasia and kidney fibrosis in rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss by microinjection technique: a sensitive animal bioassay for environmental metal-toxicity. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 52, 169–178 (1999).
E. T. Snow, Metal carcinogenesis: mechanistic implications, Pharmacol. Ther. 53, 31–65 (1992).
T. Ochi, F. Nakajima, T. Sakurai, et al., Dimethylarsinic acid causes apoptosis in HL-60 cells via interaction with glutathione, Arch. Toxicol. 70, 815–821 (1996).
R. A. Jordan and J. B. Shenkman, Relationship between malondialdehyde production and arachidonate consumption during NADPH-supported microsomal lipid peroxidation, Biochem. Pharmacol. 31, 1393–1400 (1982).
O. H. Lowry, N. J. Rosenbrough, A. L. Farr, et al., J. Biol. Chem. 193, 265 (1951).
G. L. Ellman, Tissue sulfhydryl groups, Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 82, 70–77 (1959).
S. Ohmori, M. Ikeda, E. Kasahara, et al., A colorimetric determination of total glutathione based on its c-terminal glycine residue and its application to blood, liver and yeast, Chem. Pharm. Bull. 29(5), 1355–1360 (1981).
R. A. Fischer, Statistical Methods for Research Workers, 11th ed., Oliver and Boyd, London (1950).
J. D. Peden, J. A. Crothers, C. E. Waterfall, et al., Heavy metals in Somerset marine organisms, Marine Pollut. Bull. 4, 7–9 (1973).
B. A. Fowler, R. C. Fay, R. L. Walter, et al., Levels of toxic metals in marine organisms collected from south California coastal waters, Environ. Health Perspect. 12, 71–76 (1975).
H. Yamauchi and Y. Yamamura, Metabolism and excretion of orally administrated arsenic trioxide in the hamster, Toxicology 34, 113–121 (1985).
F. Bertelero, E. Marafante, J. Edel Rade, et al., Biotransformation and intracellular binding of arsenic in tissues of rabbits after intraperitoneal administration of 74As labeled arsenite, Toxicology 20, 35–44 (1981).
J. T. Stevens, L. L. Hall, J. D. Farmer, et al., Disposition of 14C and/or 74As-cacodylic acid in rats after intravenous, intrathecal, or peroral administration, Environ. Health Perspect. 19, 151–153 (1977).
M. Vahter, Biotransformation of trivalent and pentavalent inorganic arsenic in mice and rats, Environ. Res. 25, 286–293 (1981).
D. R. Germolec, J. Spalding, H. S. Yu, et al., Arsenic enhancement of skin neoplasia by chronic stimulation of growth factors, Am. J. Pathol. 153, 1775–1785 (1998).
M. P. Waalkes, M. J. Harvey, and C. D. Klaassen, Relative in vitro affinity of hepatic metallothionein for metals, Toxicol. Lett. 20, 33–39 (1984).
F. Ayala-Feirro, D. S. Barber, L. T. Rael, et al., In vitro tissue specificity for arsenic and arsenite toxicity in the rat, Toxicol. Sci. 52, 122–125 (1999).
H. V. Aposhian, Enzymatic methylation of arsenic species and other new approaches to arsenic toxicity, Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 37, 397–419 (1997).
N. Scott, K. M. Hattelid, N. E. Mackenzie, et al., Reaction of arsenic(III) and arsenic(V) species with glutathione, Chem. Res. Toxicol. 6, 102–106 (1993).
S. Ahmad, W. A. Anderson, and K. T. Kitchin, Dimethylarsinic acid effects on six biochemical parameters in B6C3FI mice, Toxicol. Sci. 48(Suppl.) 353, (1999).
S. J. Flora, S. C. Pant, P. R. Malhotra, et al., Biochemical and histopathological changes in arsenic intoxicated rats coexposed to ethanol, Alcohol 14, 563–568 (1991).
A. Santra, A. Maiti, and D. N. G. Mazumder, The mechanism of liver damage due to chronic feeding of arsenic-contaminated water in mice, Arsenic Health Effects Symposium, Hunt Valley (1997), abstract 9.
W. C. Chang, S. H. Chen, H. L. Wu, et al., Cytoplasmic effect of reduced glutathione in arsenical-induced endothelial cell injury, Toxicology 69, 101–110 (1991).
W. Chen, J. L. Martindale, N. J. Holbrook, et al., Tumor promoter arsenite activates extracellular signal-regulated kinase through a signaling pathway mediated by epidermal growth factor receptor, Mol. Cell. Biol. 18, 5178–5188 (1998).
A. B. Fischer, J. P. Buchet, and R. R. Lauwerys, Arsenic uptake, cytotoxicity and detoxification studied in mammalian cells in culture, Arch. Toxicol. 57, 168–172 (1985).
M. Schuliga, S. Chouchane, and E. T. Snow, Upregulation of glutathione-related genes and enzyme activities in cultured human cells by sublethal concentrations of inorganic arsenic, Toxicol. Sci. 70, 183–192 (2002).
V. Bencko and K. Symon, Dynamics of arsenic cumulation in hairless mice after peroral administration, J. Hyg. Epidemiol. Microbiol. Immunol. 13, 248–253 (1969a).
V. Bencko, V. Cmarko, and S. Palan, The cumulation dynamics of arsenic in the tissue of rabbits exposed in the area of ENO plant, Cesk. Hyg. 13, 18–22 (1968).
K. Katsura, Medicolegal studies of arsenic poisoning II. Distribution of arsenic in visceral organs and arsenic concentrations of bone and hair in arsenic poisoning, Shikoku Igaku Zasshi. 12, 706–720 (1958).
L. S. Tisa and B. P. Rosen, Molecular characterization of an anion pump, J. Biol. Chem. 265, 190–194 (1990).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Allen, T., Singhal, R. & Rana, S.V.S. Resistance to oxidative stress in a freshwater fish Channa punctatus after exposure to inorganic arsenic. Biol Trace Elem Res 98, 63–72 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1385/BTER:98:1:63
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/BTER:98:1:63