Abstract
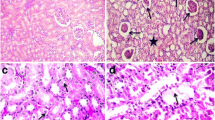
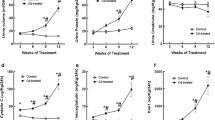
The aim of this study was to determine the cadmium-induced immunohistochemical and morphological changes in the renal cortex of adult male rats exposed to high doses of cadmium for 30 d. Animals used as controls received a standard diet and water ad libitum. The animals used for this study received 15 ppm CdCl2 in their drinking water for 1 mo. The mean arterial pressure (MAP), the mean blood Cd level, and the mean tissue Cd content were significantly higher when compared to controls (p < 0.01). Immunohistochemical studies demonstrated a weak labeling to type IV collagen and laminin, but a strong labeling to fibronectin in the renal cortex of the Cd-treated animals when compared to controls. The ultrastructural alterations found in Cd-treated rats were a diminution in the amount of filtration slits, increased fusion of foot processes in epithelial cells of the glomeruli, increase of lysosomal structures and pinocytic vesicles as well as large mitochondria in proximal tubule cells, and degenerated cells in distal tubules. Additionally, the glomerular basement membrane was slightly thickened. In conclusion, cadmium toxicity results in alterations in the renal extracellular matrix and tubular or glomerular cells, which could play an important role in renal dysfunction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. van Goor, W. Coers, M. L. van der Horst, et al., Distribution of cytocykelatal proteins, integrins, leucocyte adhesion molecules and extracellular matrix proteins in plastic-embedded human and rat kidneys, Anal. Quant. Cytol. Histol. 23, 345–354 (2001).
O. J. Lucis, M. E. Lynk, and R. Lucis, Turnover of cadmium 109 in rats, Arch. Environ. Health 18, 307–310 (1969).
K. Nomiyama, Y. Sugata, A. Yammoto, et al., Effect of dietary cadmium on rabbits. I. Early signs of cadmium intoxication, Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 31, 4–12 (1975).
M. Sato, M. Sasaki, and Y. Nagai, Increased urinary excretion of collagen metabolites in cadmium-metallothionein nephropathy, Arch. Toxicol. 61, 116–119 (1987).
J. Stejskal and V. D. Stejskal, The role of metals in autoimmunity and the link to neuroendocrinology, Neuroendocrinol. Lett. 20, 351–364 (1999).
J. M. Weinberg, P. G. Harding, and H. D. Humes, Mitochondrial bioenergetics during the initiation of mercuric chloride induced renal injury. II. Functional alterations of renal cortical mitochondria isolated after mercuric chloride treatment, J. Biol. Chem. 257, 68–74 (1982).
H. Saito, R. Shioji, Y. Hurukawa, et al., Cadmium-induced proximal tubular dysfunction in a cadmium-polluted area, Contrib. Nephrol. 6, 1–12 (1977).
K. Kawai, K. Fukuda, and M. Kimura, Morphological alterations in experimental cadmium exposure with special reference to the onset of renal lesion, in Effect and Dose-Response Relationship of Toxic Metals, G. F. Nordberg, ed., Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp. 343–370 (1976).
E. Gurr, Biological Staining Methods, Searle Diagnostic Gurr Products, Buckinghamshire, UK (1973).
S. Sanchez, R. Perez Aguilar, S. Genta, et al., Renal extracellular matrix alterations in lead-treated rats, J. Appl. Toxicol. 21, 417–423 (2001).
J. J. Bozzola and L. D. Russel, Electron Microscopy Principles and Techniques for Biologists, Jones and Barltlett, Boston (1992).
M. Asar, U. A. Kayisli, V. N. Izgut-Uysal, et al., Cadmium-induced changes in parietal cell structure and functions of rats, Biol. Trace Element Res. 74, 153–170 (2000).
C. Tohyama, Z. A. Shaikh, K. Nogawa, et al., Urinary metallothionein as a new index of renal dysfunction in “Itai-Itai” disease patients and other Japanase women environmentally exposed to cadmium, Arch. Toxicol. 50, 159–166 (1982).
N. Manabe, A. Kinoshita, M. Yamaguchi, et al., Changes in quantitative profile of extracellular matrix components in the kidneys of rats with adriamycin-induced nephropathy, J. Vet. Med. Sci. 63, 125–133 (2001).
H. W. Schnaper, J. B. Kopp, A. C. Poncelet, et al., Increased expression of extracellular matrix proteins and decreased expression of matrix protease after serial passage of glomerular mesangial cells, J. Cell. Sci. 109, 2521–2528 (1996).
S. Tomooka, W. A. Border, B. C. Marshall, et al., Glomerular matrix accumulation is linked to inhibition of the plasmin protease system, Kidney Int. 42, 1462–1469 (1992).
K. Uchio, N. Manabe, A. Kinoshita, et al., Abnormalities of extracellular matrices and transforming growth factor betal localization in the kidney of the hereditary nephrotic mice (ICGN Strain), J. Vet. Med. Sci. 61, 769–776 (1999).
K. Uchio, N. Manabe, K. Tamura, et al., Decreased matrix metalloproteinase activity in the kidneys of hereditary nephrotic mice (ICGN Strain), Nephron 86, 145–151 (2000).
K. E. Driscoll, J. K. Maurer, J. Poynter, et al., Stimulation of rat alveolar macrophage fibronectin release in a cadmium chloride model of lung injury and fibrosis, Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 116, 30–37 (1992).
G. A. Müller, J. Markovic-Lipkovski, and H. P. Rodemann, The progression of renal diseases: on the pathogenesis of renal interstitial fibrosis, Klin. Wochenschr. 69, 576–586 (1991).
R. C. Chambers, G. J. Laurent, and G. Westergren-Thorsson, Cadmium inhibits proteoglycan and procollagen production by cultured human lung fibroblasts, Am. J. Respir. Cell. Mol. Biol. 3, 498–506 (1998).
R. C. Chambers, R. J. McAnulty, A. Shock, et al., Cadmium selectively inhibits fibroblast procollagen production and proliferation, Am. J. Physiol. 267, L300-L308 (1994).
X. Yang, L. A. Borg, C. M. Siman, et al., Maternal antioxidant treatments prevent diabetes-induced alterations of mitochondrial morphology in rat embryos, Anat. Rec. 251, 303–315 (1998).
A. L. Lehninger, The Mitochondrion: Molecular Basis of Structure and Function, W. A. Benjamin Inc, New York (1964).
C. De Duve and R. Wattiaux, Functions of lysosomes, Annu. Rev. Physiol. 28, 435–492 (1966).
M. Nishizumi, Electron microscopic study of cadmium nephrotoxicity in the rat, Arch. Environ. Health. 24, 215–225 (1972).
J. H. R. Kagi and B. L. Vallee, Metallothionein: a cadmium and zinc-containing protein from equine renal cortex, J. Biol. Chem. 236, 2433–2442 (1961).
K. Kajikawa, I. Nakanishi, and K. Kuroda, Morphological changes of the kidney and bone of rats in chronic cadmium poisoning, Exp. Mol. Pathol. 34, 9–24 (1981).
P. Castano and E. C. Vigiliani, Cadmium nephropathy: ultrastructural observations (horseradish peroxidase), J. Occup. Med. 14, 125–128 (1972).
R. Ceruti, G. Ghisleni, E. Ferretti, et al., Wild rats as monitors of environmental lead contamination in the urban area of Milan, Italy, Environ. Pollut. 117, 255–259 (2002).
E. Puvion and M. Lange, Functional significance of perichromatin granule accumulation induced by cadmium chloride in isolated rat liver cells, Exp. Cell. Res. 128, 47–58 (1980).
K. Ree, H. E. Rugstad, and A. Bakka, Ultrastructural changes in the nucleus of a human epithelial cell line exposed to cytotoxic agents. The effect of PUVA and cadmium, Acta. Pathol. Microbiol. Immunol. Scand. A 90, 427–435 (1982).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Asar, M., Kayisli, Ü.A., Izgüt-Uysal, V.N. et al. Immunohistochemical and ultrastructural changes in the renal cortex of cadmium-treated rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 97, 249–263 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1385/BTER:97:3:249
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/BTER:97:3:249