Abstract
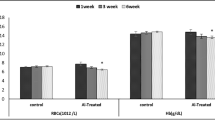
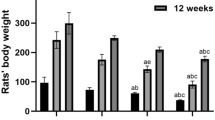
We have developed a rat model to investigate the relationship between aluminum exposure and aluminum accumulation, and with oxidative damage in brain tissues. Intraperitoneal injections of aluminum lactate for 7 wk (the total aluminum dosage per rat was approx 100 mg) significantly increased aluminum levels in the brain. The concentration of lipid peroxidation products (thiobarbituric acid-reactive substances [TBARS]) also increased in the brain following aluminum lactate injections. No significant correlations between the concentrations of aluminum and of TBARS were found in the whole brain. Subcellular analysis revealed that aluminum lactate injections led to a significant increase in the concentration of aluminum in the mitochondrial fraction but had no significant effect on the concentration of peroxides in any subcellular fraction.
These results suggest that aluminum accumulation induced by the aluminum lactate administration associates with the acceleration of lipid peroxidation in rat brain. Furthermore, these data indicate that the pro-oxidant effect of aluminum may be indirect and concentration independent. The experimental conditions used here provide an animal model of aluminum accumulation in the brain that should prove useful for further investigations of the mechanisms of aluminum neurotoxicity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. N. Martyn, D. J. P. Baker, C. Osmond, E. C. Harris, J. A. Edwardson, and R. F. Lace, Geographical relation between Alzheimer’s disease and aluminum in drinking water, Lancet 8629, 59–62 (1989).
A. B. Graves, E. White, T. D. Koepsell, B. V. Reifler, G. V. Belle, and E. B. Larson, The association between aluminum containing products and Alzheimer’s disease, J. Clin. Epidemiol. 43, 35–44 (1990).
D. R. Crapper-McLachlan and U. De Boni, Aluminum in human brain disease—an overview, Neurotoxicology 1, 3–16 (1980).
A. C. Alfrey, G. R. Legendre, and W. D. Kaehney, The dialysis encephalopathy syndrome, N. Engl. J. Med. 294, 184–188 (1976).
M. R. Wills and J. Savory, Water content of aluminum, dialysis, dementia, and osteomalacia, Environ. Health Perspect. 63, 141–147 (1985).
R. A. Yokel, The toxicology of aluminum in the brain: a review, Neurotoxicology 21, 813–828 (2000).
M. Ohtawa, M. Seko, and F. Takayama, Effect of aluminum ingestion on lipid peroxidation, Chem. Pharm. Bull. 31, 1415–1418 (1983).
R. Katyal, B. Desigan, C. P. Sodhi, and S. Ojha, Oral aluminum administration and oxidative injury, Biol. Trace Element Res. 57, 125–130 (1997).
C. G. Fraga, P. I. Oteiza, M. S. Golub, and M. E. Gershwin, Effect of aluminum on brain lipid peroxidation, Toxicol. Lett. 51, 213–219 (1990).
C. D. Smith, J. M. Carney, P. E. Starke-Reed, et al., Excess brain proten oxidation and enzyme dysfunction in normal aging and in Alzheimer disease, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88, 10,540–10,543 (1991).
D. T. Dexter, C. J. Carter, and F. R. Wells, Basal lipid peroxidation in substantia nigra is increased in Parkinson’s disease, J. Neurochem. 52, 381–389 (1989).
D. R. Rosen, T. Siddique, D. Patterson, et al., Mutations in Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase gene are associated with familial amytropric lateral sclerosis, Nature 362, 59–62 (1993).
S. V. Verstraeten, M. S. Golub, C. L. Keen, and P. I. Oteiza, Myelin is a preferential target of aluminum-mediated oxidative damage, Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 344, 289–294 (1994).
T. Ohyashiki, T. Karino, S. Suzuki, and K. Matsui, Effect of aluminum ion on Fe2+-induced lipid peroxidation in phospholipid liposomes under acidic conditions, J. Biochem. 120, 895–900 (1996).
M. S. Golub, C. L. Keen, and E. R. Gershwin, Effects of aluminum excess and manganese deficiency on neurobehavioral endpoints in adult mice, Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 112, 154–160 (1992).
P. I. Oteiza, C. L. Keen, B. Han, and M. S. Golub, Aluminum accumulation and neurotoxicity in Swiss-Webster mice after long-term dietary exposure to aluminum and citrate, Metabolism 42, 1296–1300 (1993).
A. E. Shohda, Z. G. Mohamed, T. F. Atef, and A. H. Mohamed, Effect of cadmium and aluminium intake on the antioxidant status and lipid peroxidation in rat tissues, J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 15, 207–214 (2001).
M. S. Golub, S. L. Germann, B. Han, and C. L. Keen, Lifelong feeding of high aluminum diet to mice, Toxicology 150, 107–117 (2000).
G. B. Chainy, A. Sahoo, and C. Swain, Effect of aluminum on lipid peroxidation of cerebral hemisphere of chick, Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 50, 85–91 (1993).
R. P. Bertholf, J. R. P. Nicholson, M. R. Wills, and J. Savory, Measurement of lipid peroxidation products in rabbit brain and organs (response to aluminum exposure). Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 17, 418–423 (1987).
M. F. Van Ginkel, G. B. Van der Voet, M. E. De Broe, and F. A. De Wolff, Effect of citric acid and maltol on the accumulation of aluminum in rat brain and bone, J. Lab. Clin. Med. 121, 453–460 (1993).
G. H. Hogeboom, in Methods in Enzymology, S. P. Colowick and N. O. Kaplan, eds., Academic, New York, Vol. 1, pp. 16–19 (1955).
T. Yonetani, in Methods in Enzymology, R. W. Estabrook and M. E. Pullman, eds., Academic, New York, Vol. 10, pp. 332–335 (1966).
H. W. Strobel and J. D. Dignam, in Methods in Enzymology, S. Fleischer and L. Packer, eds., Academic, New York, Vol. 52, pp. 89–96 (1979).
A. Kornberg and B. L. Horecker, in Methods in Enzymology, S. P. Colowick and N. O. Kaplan, eds., Academic, New York, Vol 1, pp. 323–324 (1955).
J. M. Kissane and E. Robins, The fluorometric measurement of deoxyribonucleic acid in animal tissues with special reference to the central nervous system, J. Biol. Chem. 233, 184–188 (1958).
J. A. Beuge and S. D. Aust, Microsomal lipid peroxidation, in Methods in Enzymology, S. Fleischer and L. Packer, eds., Academic, New York, Vol. 52, pp. 302–310 (1979).
C. P. Lebel and S. C. Bondy, Sensitive and rapid quantitation of oxygen reactive species formation in rat synaptosomes, Neurochem. Int. 17, 435–440 (1999).
R. Cathcart, E. Schwiers, and B. N. Ames, Detection of picomole levels of hydroperoxides using a fluorescent dichlorofluorescein assay, Anal. Biochem. 134, 111–116 (1983).
E. Kaneko, H. Hoshino, T. Yotsuyanagi, et al., Determination of aluminum in the human serum of a dialysis patient by ion-pair reverse-phase partition high-performance liquid chromatography, Anal. Chem. 63, 2219–2222 (1991).
M. F. Van Ginkel, G. B. Van der Voet, and F. A. De Wolff, Improved method of analysis for aluminum in brain tissue, Clin. Chem. 36, 658–661 (1990).
K. V. Subbarao, J. S. Richardson, and L. C. Ang, Autopsy samples of Alzheimer’s cortex show increased peroxidation in vitro, J. Neurochem. 55, 342–345 (1990).
D. R. Crapper, S. S. Krishnan, and A. J. Dalton, Brain aluminum distribution in Alzheimer’s disease and experimental neurofibrillary degeneration, Science 180, 511–513 (1973).
D. P. Perl and A. R. Brody, Alzheimer’s disease: X-ray spectrophotometric evidence of aluminum accumulation in neurofibrillary tangle-bearing neuron, Science 208, 297–299 (1980).
X. Xie, and R. A. Yokel, Aluminum facilitation of iron-mediated lipid peroxidation is dependent on substrate, pH, and aluminum and iron concentrations, Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 327, 222–226 (1996).
D. R. Crapper, S. S. Krishnan, and S. Qittkat, Aluminum, neurofibrillary degeneration and Alzheimer’s disease, Brain 99, 67–80 (1976).
P. F. Good, C. W. Olanow, and D. P. Perl, Neuromelanin-containing neurons of the substantia nigra accumulate iron and aluminum in Parkinson’s disease: a LAMMA study, Brain Res. 593, 343–346 (1992).
Y. Ogasawara, T. Sakamoto, K. Ishii, H. Takahashi, and S. Tanabe, Effect of administration routes and chemical forms of aluminum on the aluminum accumulation in the brain, Biol. Trace Element Res. 85, 269–278 (2002).
J. P. Blass, G. E. Gibson, K. Sheu, and R. S. Black, Mitochondria, aging and neurological disease, in Non Neuronal Cells in Alzheimer’s Disease, P. Zatta and M. Nicoli, eds., World Scientific, Singapore, pp. 95–107 (1995).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ogasawara, Y., Ohata, E., Sakamoto, T. et al. A model of aluminum exposure associated with lipid peroxidation in rat brain. Biol Trace Elem Res 96, 191–201 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1385/BTER:96:1-3:191
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/BTER:96:1-3:191