Abstract
To examine whether the calcium accumulation in aged arteries is related to the way of walking, the mineral contents were determined in the arteries of Japanese monkeys of quadrupedal walk by inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectrometry. Sixteen Japanese monkeys consisting of 7 males and 9 females ranging in age from 2 to 33 yr were studied.
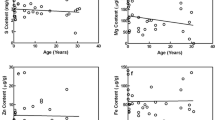
The accumulation of calcium, phosphorus, and magnesium occurred progressively in most, but not all, of the arteries with aging. It was found that independent of the upper and lower limbs, a higher accumulation of calcium, phosphorus, and magnesium occurred in the arteries of the proximal regions with aging, compared with the arteries of the distal regions.
In a comparison between the arteries of anatomically corresponding regions of the upper and lower limbs, the accumulation of calcium and magnesium was 20–60% higher in the external iliac and femoral arteries of the lower limb than in the axillary and brachial arteries of the upper limb. Regarding phosphorus, the accumulation was 20–120% higher in the external iliac and femoral arteries than in the axillary and brachial arteries. It was known that in humans, the accumulation of calcium, phosphorus, and magnesium was three to seven times higher in the arteries of the lower limb than in the arteries of the upper limb. It is clear that there is a very significant difference in the accumulation of calcium and magnesium in the arteries of the lower limbs between Japanese monkeys and humans. The present study suggests that the accumulation of calcium and magnesium in the arteries of the lower limb with aging is affected by the way of walking.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Tohno, S. Tohno, T. Minami, et al., Age-related changes of mineral contents in the human thoracic aorta and in the cerebral artery, Biol. Trace Element Res. 54, 23–31 (1996).
S. Tohno, Y. Tohno, T. Minami, et al., High accumulation of elements in the human femoral artery, Biol. Trace Element Res. 63, 177–183 (1998).
S. Tohno, Y. Tohno, T. Minami, et al., Differential accumulation of calcium and phosphorus in aged human arteries, Acta Anat. Nippon. 72, 451–454 (1997).
S. Tohno, Y. Tohno, T. Minami, et al., High accumulation of minerals in the human arteries of lower limb, Biol. Trace Element Res. 63, 177–183 (1998).
Y. Tohno, S. Tohno, T. Minami, et al., Age-related changes of mineral contents in the human aorta and internal thoracic artery, Biol. Trace Element Res. 61, 219–226 (1998).
S. Tohno and Y. Tohno, Age-related differences in calcium accumulation in human arteries, Cell. Mol. Biol. 44, 1253–1263 (1998).
S. Tohno, M. Masuda, Y. Tohno, et al., High accumulation of calcium and phosphorus in human iliac arteries, Biol. Trace Element Res. 70, 41–49 (1999).
M. Masuda, S. Tohno, Y. Tohno, et al., Element content of human umbilical artery and vein in umbilical cord, Biol. Trace Element Res. 69, 235–240 (1999).
S. Tohno, Y. Tohno, M. Hayashi, et al., Accumulation of calcium in the arteries in Japanese monkey, Biol. Trace Element Res. 82, 77–86 (2001).
S. Tohno, Y. Tohno, M. Hayashi, Y. Moriwake, and T. Minami, Accumulation of magnesium as well as calcium and phosphorus in Japanese monkey arteries with aging, Biol. Trace Element Res. 84, 81–92 (2001).
Y. Tohno, S. Tohno, Y. Tateyama, et al., Visual demonstration of calcium accumulation in human arteries of upper and lower limbs, Biol. Trace Element Res. 81, 115–125 (2001).
Y. Tohno, S. Tohno, Y. Moriwake, C. Azuma, Y. Ohnishi, and T. Minami, Accumulation of calcium and phosphorus accompanied by increase of magnesium and decrease of sulfur in human arteries, Biol. Trace Element Res. 82, 9–19 (2001).
Y. Tohno, S. Tohno, Y. Moriwake, C. Azuma, Y. Ohnishi, and T. Minami, Simultaneous accumulation of calcium, phosphorus, and magnesium in various human arteries, Biol. Trace Element Res. 82, 21–28 (2001).
S. Tohno, Y. Tohno, Y. Moriwake, C. Azuma, Y. Ohnishi, and T. Minami, Quantitative changes of calcium, phosphorus, and magnesium in common iliac arteries with aging, Biol. Trace Element Res. 84, 57–66 (2001).
Y. Tohno, S. Tohno, P. Mahakkanukrauh, et al., Simultaneous accumulation of magnesium with calcium and phosphorus in aorta and iliac arteries of Thai, Biol. Trace Element Res. 84, 19–35 (2001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tohno, S., Tohno, Y., Hayashi, M. et al. Comparison of mineral contents between the arteries in upper and lower limbs of japanese monkeys. Biol Trace Elem Res 95, 173–184 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1385/BTER:95:2:173
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/BTER:95:2:173