Abstract
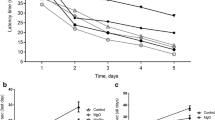
The purpose of these experiments was to determine whether dietary zinc depletion affected protein expression in the hippocampus. Eleven weanling Sprague-Dawley male rats (21 d) were fed the AIN-93G diet containing 1.5 ppm zinc and supplemented with 30 ppm of zinc in the drinking water. After 1 wk, the rats were randomly divided into three groups: control (n=3), pair fed (n=3), and zinc restricted (n=5). All groups consumed the same diet. The zinc-restricted group consumed water containing no zinc. The rats were sacrificed 3 wk later. Chelatable zinc levels in the hippocampus, as measured by N-(6-methoxy-8-quinolyl)-para-toluenesulfonamide (TSQ) staining, were significantly reduced in the zinc-restricted group. Analysis of hippocampal protein expression by two-dimensional electrophoresis (2DE) revealed increased expression of the P2X6 purinergic receptor in the zinc-restricted rats, as determined by MALDI mass spectrometry (MS) and database analysis. The data provided evidence for the dual effects of dietary zinc deficiency on the hippocampus, reducing ionic zinc levels and stimulating protein expression. The role the P2X6 receptor plays in the physiological response of the hippocampus to zinc depletion remains to be determined.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. C. Wallwork, Zinc and the central nervous system, Prog. Food Nutr. Sci. 11, 203–247 (1987).
J. C. Wallwork, D. B. Milne, R. L. Sims, and H. H. Sandstead, Severe zinc deficiency: effects on the distribution of nine elements (potassium, phosphorus, sodium, magnesium, calcium, iron, zinc, copper and manganese) in regions of the rat brain, J. Nutr. 113, 1895–1905 (1983).
J. E. Coleman, Zinc proteins: enzymes, storage proteins, transcription factors, and replication proteins, Annu. Rev. Biochem. 61, 897–946 (1992).
I. E. Dreosti, S. J. Manuel, R. A. Buckley, F. J. Fraser, and I. R. Record, The effect of late prenatal and/or early postnatal zinc deficiency on the development and some biochemical aspects of the cerebellum and hippocampus in rats, Life Sci. 28, 2133–2141 (1981).
B. L. Vallee, J. E. Coleman, and D. S. Auld, Zinc fingers, zinc clusters, and zinc twists in DNA-binding protein domains, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88, 999–1003 (1991).
B. L. Vallee and K. H. Falchuk, The biochemical basis of zinc physiology, Physiol. Rev. 73, 79 (1993).
M. Bureau, J. Laschet, F. Minier, and P. Chauvel, Intervention of GABAergic neurotransmission in partial epilepsies, Rev. Neurol. 153, S46-S54 (1997).
A. Draguhn, T. A. Verdorn, M. Ewert, P. H. Seeburg, and B. Sakman, Functional and molecular distinction between recombinant rat GABAA receptor subtypes by Zn2+, Neuron 5, 781–788 (1990).
T. G. Smart, S. J. Moss, X. Xie, and R. L. Huganir, GABAA receptors are differentially sensitive to zinc: dependence on subunit composition, Br. J. Pharmacol. 103, 1837–1839 (1991).
G. L. Westbrook and M. L. Mayer, Micromolar concentrations of Zn++ antagonize NMDA and GABA responses of hippocampal neurons, Nature 328, 640–643 (1987).
E. P. Huang, Metal ions and synaptic transmission: think zinc, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94, 13,386–13,387 (1997).
C. Acuna-Castillo, B. Morales, and J. P. Huidobro-Toro, Zinc and copper modulate differentially the P2Xsub4 receptor, J. Neurochem. 74, 1529–1537 (2000).
J. E. Lisman, J. M. Fellous, and X. J. Wang, A role for NMDA-receptor channels in working memory, Nat. Neurosci. 1, 273–275 (1998).
K. Nakazawa and Y. Ohno, Effects of neuroamines and divalent cations on cloned and mutated ATP-gated channels, Eur. J. Pharmacol. 325, 101–108 (1997).
P. Séguéla, A. Haghighi, J. J. Soghomonian, and E. Cooper, A novel neuronal P2X ATP receptor ion channel with widespread distribution in the brain, J. Neurosci. 16, 448–455 (1996).
K. Xiong, R. W. Peoples, J. P. Montgomery, Y. Chiang, R. R. Stewart, F. F. Weight, et al., Differential modulation by copper and zinc of P2X2 and P2X4 receptor function, J. Neurophysiol. 81, 2088–2094 (1999).
E. Palma, L. Maggi, R. Miledi, and F. Eusebi, Effects of Zn2+ on wild and mutant neuronal alpha7 nicotinic receptors, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 10,246–10,250 (1998).
R. Cloues, S. Jones, and D. A. Brown, Zn2+ potentiates ATP-activated currents in rat sympathetic neurons, Pflugers Arch. 424, 152–158 (1993).
C. Li, R. W. Peoples, Z. Li, and F. F. Weight, Zn2+ potentiates excitatory action of ATP on mammalian neurons, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90, 8264–8267 (1993).
M. A. Connor and C. Chavkin, Ionic zinc may function as an endogenous ligand for the haloperidol-sensitive sigma 2 receptor in rat brain, Mol. Pharmacol. 42, 471–479 (1992).
C. J. Fredrickson, S. W. Suh, D. Silva, C. J. Fredrickson, and R. B. Thompson, Importance of zinc in the central nervous system: the zinc-containing neuron, J. Nutr. 130, 1471S-1483S (2000).
C. J. Frederickson, Neurobiology of zinc and zinc-containing neurons, Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 31, 145–238 (1989).
J. Perez-Clausell and G. Danscher, Release of zinc sulphide accumulation into synaptic clefts after in vivo injection of sodium sulphide, Brain Res. 362, 358–361 (1986).
R. G. M. Morris, J. Garrud, N. P. Rawlins, and J. O’Keefe, Place-navigation impaired in rats with hippocampal lesions, Nature 297, 681–683 (1982).
R. J. Steele and R. G. M. Morris, Delay-dependent impairment of a matching-to-place task with chronic and intrahippocampal infusion of the NMDA-antagonist D-AP5, Hippocampus 9, 118–136 (1999).
G. W. Hesse, Chronic zinc deficiency alters neuronal function of hippocampal mossy fibers, Science 205, 1005–1007 (1979).
L. Slomianka, Neurons of origin of zinc-containing pathways and the distribution of zinc-containing boutons in the hippocampal region of the rat, Neuroscience 48, 325–352 (1992).
X. Xie and T. G. Smart, A physiological role for endogenous zinc in rat hippocampal synaptic neurotransmission, Nature 349, 521–524 (1991).
I. B. Introini-Collison, C. Castellano, and J. L. McGaugh, Interaction of GABAergic and beta-noradrenergic drugs in the regulation of memory storage, Behav. Neural Biol. 61, 150–155 (1994).
P. M. Moran, J. M. Kane, and P. C. Moser, Enhancement of working memory performance in the rat by MDL 26,479, a novel compound with activity at the GABAA receptor complex, Brain Res. 8, 156–158 (1992).
O. Paulsen and E. I. Moser, A model of hippocampal memory encoding and retrieval: GABAergic control of synaptic plasticity, Trends Neurosci. 21, 273–278 (1998).
X. Xie and T. G. Smart, Properties of GABA-mediated synaptic potentials induced by zinc in adult rat hippocampal pyramidal neurons, J. Physiol. 460, 503–523 (1993).
K. A. Keller, A. Grider, and J. A. Coffield, Age-dependent influence of dietary zinc restriction on short-term memory in male rats, Physiol. Behav. 72, 339–348 (2001).
C. J. Frederickson, E. J. Kasarskis, D. Ringo, and R. E. Frederickson, A quinoline fluoresence method for visualizing and assaying the histochemically reactive zinc (bouton zinc) in the brain, J. Neurosci. Methods 20, 91–103 (1987).
A. Grider and M. F. Mouat, The acrodermatitis enteropathica mutation affects protein expression in human fibroblasts: analysis by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis, J. Nutr. 128, 1311–1314 (1998).
M. M. Bradford, A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quanities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding, Anal. Biochem. 72, 248–254 (1976).
T. Rabilloud, A comparison between low background silver diammine and silvernitrate protein stains, Electrophoresis 13, 429–439 (1992).
K. A. Keller, Y. Chu, A. Grider, and J. A. Coffield, Supplementation with L-histidine during dietary zinc repletion improves short-term memory in zinc-restricted young adult male rats, J. Nutr. 130, 1633–1640 (2000).
R. E. Frederickson, C. J. Frederickson, and G. Danscher, In situ binding of bouton zinc reversibly disrupts performance on a spatial memory task, Behav. Brain Res. 38, 25–33 (1990).
A. Takeda, S. Takefuta, S. Okada, and N. Oku, Relationship between brain zinc and transient learning impairment of adult rats fed zinc-deficient diet, Brain Res. 859, 352–357 (2000).
J. Wensink, W. J. M. Lenglet, R. D. Vis, and C. J. A. van den Hamer, The effect of dietary zinc deficiency on the mossy fiber zinc content of the rat hippocampus, Histochemistry 87, 65–69 (1987).
A. Takeda, T. Akiyama, J. Sawashita, and S. Okada, Brain uptake of trace metals, zinc and manganese, in rats, Brain Res. 640, 341–344 (1994).
G. Collo, R. A. North, E. Kawashima, E. Merlo-Pich, S. Neidhart, A. Surprenant, et al., Cloning of P2X5 and P2X6 receptors and the distribution and properties of an extended family of ATP-gated ion channels, J. Neurosci. 16, 2495–2507 (1996).
M. Soto, M. Garcia-Guzman, C. Karschin, and W. Stuhmer, Cloning and tissue distribution of a novel P2X receptor from rat brain, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 223, 456–460 (1996).
B. F. King, A. Townsend-Nicholson, S. S. Wildman, T. Thomas, K. M. Spyer, and G. Burnstock, Coexpression of rat P2X2 and P2X6 subunits in Xenopus oocytes, J. Neurosci. 20, 4871–4877 (2000).
K. T. Le, K. Babinski, and P. Seguela, Central P2X4 and P2X6 channel subunits coassemble into a novel heteromeric ATP receptor, J. Neurosci. 18, 7152–7159 (1998).
P. Illes, K. Wirkner, W. Norenberg, S. A. Masino, and T. V. Dinwiddie, Interaction between the transmitters ATP and glutamate in the central nervous system, Drug Dev. Res. 52, 76–82 (2001).
E. Masaki, K. Yamazaki, Y. Ohno, H. Nishi, Y. Matsumoto, and M. Kawamura, The anesthetic interaction between adenosine triphosphate and N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor antagonists in the rat, Anesth. Analg. 92, 134–139 (2001).
E. Boue-Grabot, V. Archambault and P. Seguela, A protein kinase C site highly conserved in P2X subunits controls the desensitization kinetics of P2X(2) ATP-gated channels, J. Biol. Chem. 275, 10,190–10,195 (2000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chu, Y., Mouat, M.F., Coffield, J.A. et al. Expression of P2X6, a purinergic receptor subunit, is affected by dietary zinc deficiency in rat hippocampus. Biol Trace Elem Res 91, 77–87 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1385/BTER:91:1:77
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/BTER:91:1:77