Abstract
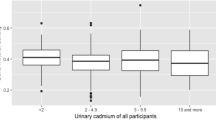
Bone damage caused by exposure to cadmium (Cd) is often seen in Cd-polluted areas, and increased excretion of calcium (Ca) in urine is thought to be an important factor affecting bone damage. In order to clarify the significance of urinary Ca excretion in bone damage, we investigated the urinary excretion levels of Ca and phosphorus (P) of inhabitants of a Cd-polluted area and compared them to those of nonexposed subjects, and explored the possible association between urinary Ca or P and β 2-microglobulin (β 2-MG). The target subjects were 3164 inhabitants of the Cd-polluted Kakehashi River basin. Ca and Ca/P measurements were significantly higher in the Cd-polluted area than in the controls.
In multiple-regression analysis, where either Ca or P was used as the criterion variable, and age, Cd, and β 2-MG were used as explanatory variables, there were positive associations between Ca and Cd and β 2-MG in both sexes. Therefore, the increased excretion level of Ca was the result of renal dysfunction. Bone damage is not thought to be caused by increased excretion of Ca alone because urinary excretion levels of Ca do not differ greatly between people with and without bone damage.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Nogawa, Itai-itai disease and follow-up studies, in Cadmium in the Environment. Part 2: Health Effects, J. O. Nriagu, ed., Wiley-Interscience, New York, pp. 1–37 (1981).
K. Nogawa and T. Kido, Itai-itai disease and health effects of cadmium, in Toxicology of Metals, L. W. Chang, ed., CRC, New York, pp. 353–369 (1996).
K. Nogawa, E. Kobayashi, R. Honda, and A. Ishizaki, Clinico-chemical studies on chronic cadmium poisoning (Part 1). Results of urinary examinations, Jpn. J. Hyg. 34, 407–414 (1979) (in Japanese).
K. Aoshima, K. Iwata, and M. Kasuya, Environmental exposure to cadmium and effects on human health. Part 2. Bone and mineral metabolism in inhabitants of the cadmium-polluted Jinzu River basin in Toyama Prefecture. Jpn. J. Hyg. 43, 864–871 (1988) (in Japanese).
M. Fukushima, A. Ishizaki, K. Nogawa, M. Sakamoto, and E. Kobayashi, Epidemiological studies on renal failure of inhabitants in “Itai-itai” disease endemic district (Part 1). Some urinary findings of inhabitants living in and around the endemic district of the Jinzu River basin, Jpn. J. Public Health 21, 65–73 (1974) (in Japanese).
E. Kobayashi, An epidemiological study on the health effects of environmental cadmium. (Part 1). Some urinary findings by sex and age, Jpn. J. Public Health 29, 123–133 (1981) (in Japanese).
K. Nogawa, A. Ishizaki, M. Fukushima, I. Shibata, and N. Hagino, Studies on the women with acquired Fanconi syndrome observed in the Ichi River basin polluted by cadmium. Is this Itai-itai disease? Environ. Res. 10, 280–307 (1975).
T. Kido, K. Nogawa, Y. Yamada, R. Honda, I. Tsuritani, M. Ishizaki, et al., Osteopenia in inhabitants with renal dysfunction induced by exposure to environmental cadmium, Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 61, 271–276 (1989).
T. Kido, K. Nogawa, Y. Hochi, M. Hayano, R. Honda, I. Tsuritani, et al., The renal handling of calcium and phosphorus in environmental cadmium-exposed subjects with renal dysfunction, J. Appl. Toxicol. 13, 43–47 (1993).
T. Kido, I. Tsuritani, R. Honda, M. Ishizaki, Y. Yamada, and K. Nogawa, A direct determination of urinary cadmium by graphite-furnace atomic absorption spectrometry using the Zeeman effect. J. Kanazawa Med. Univ. 9, 70–75 (1984) (in Japanese).
R. W. Bonsnes and H. H. Taussky, On the calorimetric determination of creatinine by the Jaffe reaction, J. Biol. Chem. 158, 581–591 (1945).
R. J. L. Allen, The estimation of phosphorus, Biol. J. 34, 858–865 (1940).
T. Kjellstrom, Mechanism and epidemiology of bone effects of cadmium, IARC Sci. Publ. 118, 301–310 (1992).
K. Nogawa, I. Tsuritani, T. Kido, R. Honda, Y. Yamada, and M. Ishizaki, Mechanism for bone disease found in inhabitants environmentally exposed to cadmium: decreased serum 1α, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D level. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 59, 21–30 (1987).
I. Tsuritani, R. Honda, M. Ishizaki, Y. Yamada, T. Kido, and K. Nogawa, Impairment of vitamin D metabolism due to environmental cadmium exposure, and possible relevance to sex-related differences in vulnerability to the bone damage. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health 37, 519–533 (1992).
K. Tsuchiya and S. Iwao, Results and evaluation on cadmium intake of Cd-exposed inhabitants in Akita, Ishikawa and Nagasaki Prefectures, Kankyo Hoken Rep. 44, 86–115 (1978) (in Japanese).
K. Nogawa, R. Honda, T. Kido, I. Tsuritani, Y. Yamada, M. Ishizaki, et al., A dose-response analysis of cadmium in the general environment with special reference to total cadmium intake limit, Environ. Res. 48, 7–16 (1989).
T. Kido, Z. A. Shaihk, H. Kito, R. Honda, and K. Nogawa, Dose-response relationship between dietary cadmium intake and metallothioneinuria in a population from a cadmium-polluted area of Japan, Toxicology 66, 271–278 (1991).
T. Kido and K. Nogawa, Dose-response relationship between total cadmium intake and β 2-microglobulinuria using logistic regression analysis, Toxicol. Lett. 69, 113–120 (1993).
T. Kido, Z. A. Shaihk, H. Kito, R. Honda, and K. Nogawa, Dose-response relationship between total cadmium intake and metallothioneinuria using logistic regression analysis, Toxicology 80, 207–215 (1993).
Y. Hochi, T. Kido, K. Nogawa, H. Kito, and Z. A. Shaihk, Dose-response relationship between total cadmium intake and prevalence of renal dysfunction using general linear models, J. Appl. Toxicol. 15, 109–116 (1995).
J. P. Buchet, R. Lauwerys, H. Roels, A. Bernard, P. Bruaux, F. Claeys, et al., Renal effects of cadmium body burden of the general population, Lancet 336, 699–702 (1990).
J. Staessen, A. Amery, A. Bernard, P. Bruaux, J. P. Buchet, F. Claeys, et al., Effects of exposure to cadmium on calcium metabolism: a population study. Br. J. Ind. Med. 48, 710–714 (1991).
J. Staessen, A. Bernard, J. P. Buchet, F. Claeys, G. Ducoffre, R. Fagard, et al., Effects of cadmium exposure on the cardiovascular system and on calcium metabolism: results of a cross-sectional population study. IARC Sci. Publ. 118, 263–269 (1992).
A. Cardenas, I. Ramis, G. Hotter, J. Rosello, E. Gelpi, H. Roels, et al., Human and experimental studies on renal eicosanoid response to long-term cadmium exposure, Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 116, 155–160 (1992).
J. Staessen and R. Lauwerys, Health effects of environmental exposure to cadmium in a population study, J. Hum. Hypotheses 7, 195–199 (1993).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hayashi, Y., Kobayashi, E., Okubo, Y. et al. Excretion levels of urinary calcium and phosphorus among the inhabitants of Cd-polluted Kakehashi River basin of Japan. Biol Trace Elem Res 91, 45–55 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1385/BTER:91:1:45
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/BTER:91:1:45