Abstract
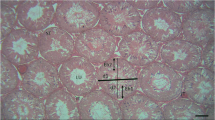
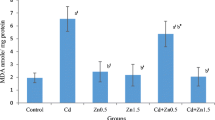
When male rats were given a single dose of cadmium (Cd) (3.58 mg CdCl2·H2O/kg, ip) 72 hr prior to sacrifice, the testicular 7-ethoxyresorufin O-deethylase (EROD) and glutathione S-transferase (GST) activities toward the substrates 1-chloro-2,4-dinitrobenzene (CDNB), 1,2-dichloro-4-nitrobenzene (DCNB), ethacrynic acid (EAA), 1,2-epoxy-3-(p-nitrophenoxy)-propane (EPNP), and cumene hydroperoxide (CHPx) decreased significantly as compared to controls. Cd also inhibited reduced glutathione (GSH) level while increasing the lipid peroxidation (LP) level significantly. When the animals were given a single dose of nickel (Ni) (59.5 mg NiCl2·6H2O/kg, ip) 16 hr prior to sacrifice, significant decreases were observed in EROD and GST activities toward CDNB, EAA, EPNP, and CHPx, and GSH level. No significant alterations were noted in DCNB GST activity and LP level by Ni. For the combined treatment, rats received the single dose of Ni 56 hr after the single dose of Cd and were killed 16 hr later. In these animals, lesser depressions were observed on EROD activity and LP level than those of Cd alone. The combination of metals significantly inhibited GST activities and GSH level but not to a greater degree than noted by Cd or Ni alone. Plasma testosterone levels of Cd-, Ni-, and combination-treated rats decreased significantly compared to controls. The strongest depression was achieved by Cd alone. Cd, both alone and in combination with Ni, increased the tissue Ni uptake significantly. Ni, however, did not produce such an effect on the tissue uptake of Cd in either case. Cd treatment caused interstitial edema and coagulation necrosis in seminiferous tubules and also caused fibrinoidal necrosis in vascular endothelium. Ni treatment did not produce any pathological testicular alterations compared to controls. Combined treatment produced fewer pathological alterations (i.e., only interstitial edema) than that of Cd treatment. These results reveal that the combination of Cd and Ni does not have a synergistic effect on testicular xenobiotic metabolizing enzymes, and in contrast, Ni has an ameliorating effect on pathological disturbances caused by Cd alone in the rat testis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. B. Hammond and R. P. Beliles, Metals, in Toxicology, J. Doull, C. D. Klaassen, and M. O. Amdur, eds., Macmillan, New York, pp. 409–467 (1980).
A. Léonard, G. B. Gerber, and P. Jacquet, Carcinogenicity, mutagenicity and teratogenicity of Ni, Mutat. Res. 87, 1–15 (1981).
K. S. Kasprzak, Nickel, in Advances in Modern Environmental Toxicology, L. Fishbein, A. Furst, and M. A. Mechlman, eds., Princeton University Press, Princeton, NJ, Vol. 2, pp. 145–183 (1987).
G. Kazantzis, The mutagenic and carcinogenic effects of cadmium: an update, Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 15, 83–100 (1987).
F. W. Sunderman, Jr., Mechanism of nickel carcinogenesis, Scand. J. Work Environ. Health 15, 1–12 (1989).
M. İşcan and T. Çoban, Nickel effect on hepatic cytochrome P450 dependent monooxygenases in mice, in Cytochrome P450: Biochemistry and Biophysics, I. Schuster, ed., Taylor & Francis, London, pp. 787–789 (1989).
M. İşcan and A. Karakaya, Cadmium sensitivity differences between liver microsomal drug metabolizing enzyme systems of guinea-pig and rat, Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 90C, 101–105 (1988).
M. İşcan, T. Çoban and B. C. Eke, Responses of hepatic xenobiotic metabolizing enzymes of mouse, rat and guinea pig to nickel, Pharmacol. Toxicol. 71, 434–442 (1992).
M. İşcan, T. Çoban and M. İşcan, Combined effect of cadmium and nickel on rat hepatic monooxygenases: possible stimulation of certain cytochrome P-450 isozymes, Toxicol. Lett. 62, 191–199 (1992).
M. İşcan, T. Çoban, B. C. Eke, and M. İşcan, The responses of hepatic monooxygenases of guinea pig to cadmium and nickel, Biol. Trace. Element Res. 38, 129–137 (1993).
R. C. Schnell, Cadmium-induced alteration of drug action, Fed. Proc. 37, 28–34 (1978).
M. İşcan, T. Çoban, B. C. Eke, and M. İşcan, Differential responses of hepatic monooxygenases and glutathione S-transferases of mice to a combination of cadmium and nickel, Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 111C, 61–68 (1995).
M. İşcan, T. Çoban, and B. C. Eke, Differential combined effects of cadmium and nickel on hepatic and renal glutathione S-transferases of the guinea pig, Environ. Health. Perspect. 102(Suppl. 9), 69–72 (1994).
F. Planas-Bohne and M. Elizade, Activity of glutathione S-transferase in rat liver and kidneys after administration of lead and cadmium, Arch. Toxicol. 66, 365–367 (1992).
C. P. Siegers, M. Schenke, and M. J. Younes, Influence of cadmium chloride, mercuric chloride, and sodium vanadate on the glutathione-conjugating enzyme system in liver, kidney, and brain of mice, Toxicol. Environ. Health 22, 141–148 (1987).
F. J. Gonzales, C. L. Crespi, and H. V. Gelboin, cDNA-expressed human cytochrome P450s: a new age of molecular toxicology and human risk assessment, Mutat. Res. 247, 113–127 (1991).
M. İşcan, B. C. Eke, and T. Çoban, Combined effects of cadmium and nickel on hepatic glutathione S-transferases in rats, Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 104C, 453–456 (1993).
B. C. Eke and M. İşcan, A study on the combined effects of cadmium and nickel on pulmonary and renal xenobiotic metabolizing enzymes in rats, Toxicol. Lett. 123(Suppl. 1), 51–52, (2001).
M. J. Hoey, The effects of metallic salts on the histology and functioning of the rat testis, J. Reprod. Fertit. 12, 461–471 (1966).
Ş. Saygı, G. Deniz, O. Kutsal, and N. Vural, Chronic effects of cadmium on kidney, liver, testis and fertility of male rats, Biol. Trace. Element Res. 31, 209–214 (1991).
A. S. Chung and M. D. Maines, Differential effect of cadmium on GSH-peroxidase activity in the Leydig and the Sertoli cells of rat testis. Suppression by selenium and the possible relationship to heme concentration, Biochem. Pharmacol. 36, 1367–1372 (1987).
M. İşcan, E. Arınç, N. Vural, and M. Y. İşcan, In vivo effects of 3-methylcolantrene, phenobarbital, pyrethrum and 2,4,5-T isooctylester on liver lung and kidney microsomal mixed function oxidase system of guinea-pig: a comparative study, Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 77C, 177–190 (1984).
N. Sugawara and C. Sugawara, Selenium protection against testicular lipid peroxidation from cadmium, J. Appl. Biochem. 6, 199–204 (1984).
A. O. Ada, Investigation of the combined effects of cadmium and nickel on rat testicular xenobiotic metabolizing enzymes, M.Sc. thesis, Ankara University, Ankara, Turkey (2000).
M. D. Burke and R. T. Mayer, Ethoxyresorufin; direct fluorometric assay of a microsomal O-dealkylation which is preferentially inducible by 3-methylcholantrene, Drug. Metab. Dispos. 2, 583–588 (1974).
J. Sedlak and R. H. Lindsay, Estimation of total protein-bound and non protein sulphydryl groups in tissue with Ellman’s reagent, Anal. Biochem. 25, 192–205 (1968).
W. H. Habig, M. J. Pabst, and W. B. Jakoby, Glutathione-S-transferase. The first enzymatic step in mercapturic acid formation, J. Biol. Chem. 249, 7130–7139 (1974).
R. Lawrence and R. Burke, Glutathione peroxidase activity in selenium-deficient rat liver, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 71, 952–958 (1976).
M. Mihara, M. Uchiyama, and K. Fukuzawa, Thiobarbituric acid value on fresh homogenate of rat as a parameter of lipid peroxidation in aging, CCl4 intoxication, and vitamin E deficiency, Biochem. Med. 23, 302–311 (1980).
O. H. Lowry, N. J. Roserbrough, A. L. Farr, and R. J. Randall, Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent, J. Biol. Chem. 193, 265–275 (1951).
J. Satsmadjis and F. V. Talladouri, Determination of trace metals at concentrations above the linear calibration range by electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry, Anal. Chimi. Acta 131, 83–90 (1981).
M. D. Maines and A. Kappas, A regulatio of cytochrome P-450-dependent microsomal drug-metabolizing enzymes by nickel, cobalt, and iron, Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 22, 780–790 (1977).
M. İşcan and M. D. Maines, Differential regulation of heme and drug metabolism in rat testis and prostate: response to cis-platinum and human chorionic gonadotropin, J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 253, 73–79 (1990).
N. Mukhtar, I. P. Lee, G. L. Foureman, and J. R. Bend, Epoxide metabolizing enzyme acivities in rat testes: postnatal development and relative activity in interstitial and spermatogenic cell compartments, Chem. Biol. Interact. 22, 153–165 (1978).
D. W. Nebert, The Ah locus: genetic differences in toxicity, cancer, mutation, and birth defects, Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 20, 153–174 (1989).
D. R. Nelson, L. Koymans, T. Kamataki, J. J. Stegeman, R. Feyereisen, D. J. Waxman, et al., P450 superfamily: update on new sequences, gene mapping, and recommended nomenclature, Pharmacogenetics 6, 1–42 (1996).
D. W. Nebert and F. J. Gonzalez, P450 genes: structure, evolution, and regulation, Annu. Rev. Biochem. 56 945–993 (1987).
T. M. Bray and C. G. Taylor, Tissue glutathione nutrition and oxidative stress, Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 71, 746–751 (1993).
G. Gstraunthaler, W. Pfaller, and P. Kotanko, Glutathione depletion and in vitro lipid peroxidation in mercury or maleate induced acute renal failure, Biochem. Pharmacol. 32, 2969–2972 (1983).
B. Ketterer and G. J. Mulder, Glutathione conjugation, in Conjugation Reactions in Drug Metabolism, G. J. Mulder, ed., Taylor & Francis, London, pp. 307–364 (1990).
B. Mannervik, Y. C. Awasthi, P. G. Board, J. D. Hayes, C. Di Ilio, B. Ketterer, et al., Nomenclature for human glutathione transferases, Biochem. J. 282, 305–308 (1992).
D. J. Meyer, B. Coles, S. E. Pemble, K. S. Gilmore, G. M. Fraser, and B. Ketterer, Theta, a new class of glutathione transferases purified from rat and man, Biochem. J. 274, 409–414 (1991).
E. Campbell, Y. Takahashi, M. Abramovitz, M. Peretz, and I. Listowsky, A distinct human testis and brain μ-class glutathione S-transferase: molecular cloning and characterization of a form present even in individuals lacking hepatic type μ isoenzymes, J. Biol. Chem. 265, 9188–9193 (1990).
J. Gandy, T. Primiano, R. F. Novak, W. R. Kelce, and J. L. York, Differential expression of glutathione S-transferase isoforms in compartments of the testis and segments of the epididymis of the rat, Drug. Metab. Dispos. 24, 725–733 (1996).
B. Mannervik and U. H. Danielson, Glutathione transferases-structure and catalytic activity, Crit. Rev. Biochem. 23, 283–337 (1988).
B. Ketterer and D. J. Meyer, Glutathione transferases: a possible role in the detoxication and repair of DNA and lipid hydroperoxides, Mutat. Res. 214, 33–40 (1989).
K. H. Tan, D. J. Meyer, J. Belin, and B. Ketterer, Inhibition of microsomal lipid peroxidation by glutathione and glutathione transferases B and AA. Role of endogenous phospholipase A2, Biochem. J. 220, 243–252 (1984).
A. Aoki and A. P. Hoffer, Reexamination of the lesions in rat testis caused by cadmium, Biol. Reprod. 18, 579–591 (1978).
M. D. Maines, Characterization of heme oxygenase activity in Leydig and Sertoli cells of the rat testes. Differential distribution of activity and response to cadmium, Biochem. Pharmacol. 33, 1493–1502 (1984).
M. D. Maines, A. S. Chung, and R. K. Kutty, The inhibition of testicular heme oxygenase activity by cadmium. A novel cellular response, J. Biol. Chem. 257, 14,116–14,121 (1982).
M. D. Maines, Regional distribution of the enzymes of haem biosynthesis and the inhibition of 5-aminolaevulinate synthase by manganese in the rat brain, Biochem. J. 190, 315–321 (1980).
M. D. Maines and A Kappas, Cobalt stimulation of heme degradation in the liver. Dissociation of microsomal oxidation of heme from cytochrome P-450, J. Biol. Chem. 250, 4171–4177 (1975).
M. D. Maines and J. C. Veltman, Phenylhydrazine-mediated induction of haem oxygenase activity in rat liver and kidney and development of hyperbilirubinaemia. Inhibition by zinc-protoporphyrin, Biochem. J. 217, 409–417 (1984).
S. K. Tandon, S. Kandelwal, A. K. Mathur, and M. Ashquin, Preventive effects of nickel on cadmium hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity, Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 14, 391–396 (1984).
E. L. B. Novelli, R. T. Hernandez, J. L. V. B. Novelli Filho, and L. L. Barbosa, Differential/combined effect of water contamination with cadmium and nickel on tissues of rats, Environ. Pollut. 103, 295–300 (1998).
R. W. Chen, P. A. Wagner, W. G. Hoekstra, and H. E. Ganther, Affinity labelling studies with 109 cadmium in cadmium-induced testicular injury in rats, J. Reprod. Fertil. 38, 293–306 (1974).
A. S. Chung and M. D. Maines, Effect of selenium on glutathione metabolism. Induction of gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase and glutathione reductase in the rat liver, Biochem. Pharmacol. 30, 3217–3223 (1981).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
İşcan, M., Ada, A.O., Çoban, T. et al. Combined effects of cadmium and nickel on testicular xenobiotic metabolizing enzymes in rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 89, 177–190 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1385/BTER:89:2:177
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/BTER:89:2:177