Abstract
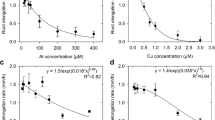
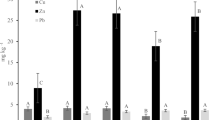
Interaction of elements in the course of element uptake by carrot (Daucas carota cv. U.S. harumakigosun) exerted by the addition of elements, such as Rb, Zn, and Al, was investigated. For the purpose of precise evaluation of uptake behavior, the simultaneous determination of absorption of Na, Be, Sr, Mn, Co, Zn, Ce, Pm, and Gd was conducted by the multitracer technique. For root uptakes, Al exhibited its influence on the uptake of essential elements and on the uptake of toxic or unbeneficial ones, presumably as a result of the large electric valency that caused cell membrane disintegrity. On the other hand, Zn as a divalent cation only affected the uptake of essential and beneficial elements. Rubidium, which is a monovalent cation, did not exhibit any effect on the uptake of other ions. Concerning shoot uptakes, inhibition by Zn and Al, but not by Rb, was observed for the uptake of Sr, Mn, Co, and Zn. From the preent investigation, it is suggested that there exists an interaction between added ions and the elements taken into plants and that the degree of interaction increases in the increasing order of ionic valency: M+ (Rb), M2+ (Zn), and M3+ (Al).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. W. Huang, J. E. Shaff, D. L. Grunes, and L. V. Kochian, Aluminum effects on calcium fluxes at the root apex of aluminum-tolerant and aluminum-sensitive wheat cultivars, Plant Physiol. 98, 230–237 (1992).
Z. Rengel and D. L. Robinson, Competitive Al3+ inhibition of net Mg2+ uptake by intact Lolium multiflorum roots, I. Kinetics, Plant Physiol. 91, 1407–1413 (1989).
H. Stienen and J. Bauch, Element content in tissue of spruce seedlings from hydroponic cultures simulating acidification and deacidification, Plant Soil 106, 231–238 (1988).
C. L. Fernando and S. H. Fernando, Effects of copper toxicity on growth and the uptake and translocation of metals in rice plants, J. Plant Nutr. 16, 1449–1464 (1993).
S. Ambe, T. Shinonaga, T. Ozaki, S. Enomoto, H. Yasuda, and S. Uchida, Ion competition effects on the selective absorption of radionuclides by komatsuna (Brassica rapa var. Perviridis), Environ. Exp. Bot. 41, 185–194 (1999).
A. A. Meharg and M. R. Macnair, Suppression of the high affinity phosphate uptake system: a mechanism of arsenate tolerance in Holcus lanatus L., J. Exp. Bot. 43, 519–524 (1992).
S. Ambe, S. Y. Chen, Y. Ohkubo, Y. Kobayashi, M. Iwamoto, M. Yanokura, et al., Preparation of radioactive multitracer solution from gold foil irradiated by 135 MeV/nucleon 14N ions, Chem. Lett. 149–152 (1991).
S. Ambe, S. Y. Chen, Y. Ohkubo, Y. Kobayashi, M. Iwamoto, M. Yanokura, et al., Preparation of radioactive multitracer solutions from Au, Ag, and Cu foils irradiated with high-energy heavy ions, Anal. Sci. 7(Suppl.), 317–320 (1991).
S. Ambe, Y. Ohkubu, Y. Kobayashi, M. Iwamoto, H. Maeda, and M. Yanokura, Multitracer study on transport and distribution of metal ions in plants, J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 195, 305–313 (1995).
T. Ban-nai, Y. Muramatsu, S. Yoshida, S. Uchida, S. Shibata, S. Ambe, et al., Multitracer study on the accumulation of radionuclides in mushrooms, J. Radiat. Res. 38, 213–218 (1997).
T. Shinonaga and S. Ambe, Multitracer study on absorption of radionuclides in atmosphere-plant model system, Water Air Soil Pollut. 101, 93–103 (1998).
S. Gouthu, R. G. Weginwar, T. Arie, S. Ambe, T. Ozaki, S. Enomoto, et al., Subcellular distribution and translocation of radionuclides in plants, Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 18, 2023–2027 (1999).
S. Ambe, T. Ozaki, S. Enomoto, and T. Shinonaga, Multitracer study on the soil-to-plant transfer of radionuclides in komatsuna at different growth stages, Environ. Technol. 20, 111–116 (1999).
T. Shinonaga, S. Ambe, and I. Yamaguchi, Uptake and distribution of trace elements in maturing soybean, Biol. Trace Element Res. 68, 235–248 (1999).
T. Ozaki, S. Enomoto, Y. Minai, S. Ambe, F. Ambe, and M. Yoshihiro, Beneficial effect of rare earth element on the growth of Dryopteris erythrosora, J. Plant Physiol. 156, 330–334 (2000).
T. Ozaki, S. Enomoto, Y. Minai, S. Ambe, F. Ambe, and Y. Makide, Influence of aluminum on the uptake of various cations from a solution into carrots, J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 235, 285–289 (1998).
T. Ozaki, S. Enomoto, Y. Minai, S. Ambe, F. Ambe, and Y. Makide, Effect of zinc on the uptake of various elements into carrot, J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 242, 703–707 (1999).
D. L. Godbold, E. Frits, and A. Hüttermann, Aluminium toxicity and forest decline, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85, 3888–3892 (1988).
H. Marschner, Mechanism of adaptation of plants to acid soils, Plant Soil 134, 1–20 (1991).
H. Matsumoto, Repression of proton extrusion from intact cucumber roots and the proton transport rate of microsomal membrane vesicles of the roots due to Ca2+ starvation, Plant Cell Physiol. 29, 79–84 (1988).
H. Matsumoto, Cell biology of alumium toxicity and tolerance in higher plants, Int. Rev. Cytol. 200, 1–46 (2000).
H. Marschner, Beneficial mineral elements, in Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants, Academic, London, pp. 405–435 (1995).
C. R. Caldwell and A. Haug, Temperature dependence of the barley root plasma membrane-bound Ca2+ and Mg2+-dependent ATPase, Physiol. Plant. 53, 117–124 (1981).
R. L. Legge, E. Thompson, J. E. Baker, and M. Lieberman, The effect of calcium on the fluidity and phase properties of microsomal membranes isolated from postclimacteric Golden Delicious apples, Plant Cell Physiol. 23, 161–169 (1982).
J. Lynch, G. R. Cramer, and A. Läuchli, Salinity reduces membrane-associated calcium in corn root protoplasts, Plant Physiol. 83, 390–394 (1987).
Z. Rengel and D. C. Elliott, Mechanism of aluminum inhibition of net 45Ca2+ uptake by Amaranthus protoplasts, Plant Physiol. 98, 632–638 (1992).
Z. Rengel, Role of calcium in aluminium toxicity, New Phytol. 121, 499–514 (1992).
Z. Rengel, Effects of Al, rare earth elements and other metals on net 45Ca2+ uptake by Amaranthus protoplasts, J. Plant Physiol. 143, 47–51 (1995).
Z. Rengel, The role of calcium in salt toxicity, Plant Cell Environ. 15, 625–632 (1992).
H. W. Woolhouse, in Encyclopedia of Plant Physiology, New Series, Volume 12C, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, (1983).
J. P. Gaur and N. Noraho, Adsorption and uptake of cadmium by Azolla pinnata: kinetics of inhibition by cations, Biomed. Environ. Sci. 8, 149–157 (1995).
C. H. Evans, Interesting and useful biochemical properties of lanthanides, Trends Biochem. Sci. 8, 445–449 (1983).
F. Rubio, W. Gassmann, and J. I. Schroeder, Sodium-driven potassium uptake by the plant potassium transporter HKT1 and mutations conferring salt tolerance, Science 270, 1660–1663 (1995).
S. Gassman, F. Rubio, and J. I. Schroeder, Alkali cation selectivity of the wheat root high-affinity potassium transporter HKT1, Plant J. 105, 852–869 (1996).
C. Schimansky, Der Einfluss einiger Versuchsparameter auf das Fluxverhalten von 28Mg bei Sinapis alba, Arch. Acker-Pflanzenvau Bodenkd. 15, 671–682 (1981).
H. J. M. Bowen, Environmental Chemistry of the Elements, Academic, London (1979).
M. Koyama, M. Shirakawa, J. Takada, Y. Katayama, and T. Matsubara, Trace elements in land plants: concentration ranges and accumulators of rare earths, Ba, Ra, Mn, Co and heavy halogens, J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 112, 489–506 (1987).
T. Ozaki, S. Enomoto, Y. Minai, S. Ambe, and Y. Makide, A survey of trace elements in pteridophytes, Biol. Trace Element Res. 74, 259–273 (2000).
S. Ambe, S. Y. Chen, Y. Ohkubo, Y. Kobayashi, H. Maeda, M. Iwamoto, et al., “Multi-tracer” a new tracer technique — its principle features, and application, J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 195, 297–303 (1995).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ozaki, T., Ambe, S., Minal, Y. et al. Effects of ionic valency of interacting metal elements in ion uptake by carrot (Daucas carota cv. U.S. harumakigosun). Biol Trace Elem Res 84, 197–211 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1385/BTER:84:1-3:197
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/BTER:84:1-3:197